.jpg)
In News
Recently, Stockholm International Peace Research Institute published the latest data on military expenditure.
Major Findings
- The total “global military expenditure rose to $1981 billion last year, an increase of 2.6 per cent in real terms from 2019.
- The five biggest spenders in 2020, which together accounted for 62 per cent of global military expenditure, were the United States, China, India, Russia and the United Kingdom.
- This was the biggest year-on-year rise in the military burden since the global financial and economic crisis in 2009.
Military spending in the context of
- USA: In 2020 US military expenditure reached an estimated $778 billion, representing an increase of 4.4 per cent over 2019.
- As the world’s largest military spender, the USA accounted for 39 per cent of total military expenditure in 2020.
- ‘The recent increases in US military spending can be primarily attributed to heavy investment in research and development, and several long-term projects such as modernizing the US nuclear arsenal and large-scale arms procurement.
- This reflects growing concerns over perceived threats from strategic competitors such as China and Russia.
- China: China’s military expenditure, the second-highest in the world, is estimated to have totalled $252 billion in 2020.
- China accounted for 13 per cent global share.
- This represents an increase of 1.9 per cent over 2019 and 76 per cent over the decade 2011–20.
- ‘China stands out as the only major spender in the world not to increase its military burden in 2020 despite increasing its military expenditure, because of its positive GDP growth last year.
- India: India’s military expenditure was $72.9 billion.
- India was the third-largest military spender in the world in 2020 While India’s spending since 2019 grew by 2.1 per cent.
- India accounted for 3.7 per cent of the globe’s share.
- Russia: Its military expenditure increased by 2.5 percent in 2020 to reach $61.7 billion.
- This was the second consecutive year of growth. Nevertheless, Russia’s actual military spending in 2020 was 6.6 per cent lower than its initial military budget, a larger shortfall than in previous years.
- UK: With a total of $59.2 billion, the UK became the fifth largest spender in 2020.
- The UK’s military spending was 2.9 percent higher than in 2019 but 4.2 percent lower than in 2011.
- NATO members: Economic downturn leads to more NATO members passing the spending target.
- Nearly all members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) saw their military burden rise in 2020.
- As a result, 12 NATO members spent 2 per cent or more of their GDP on their militaries.
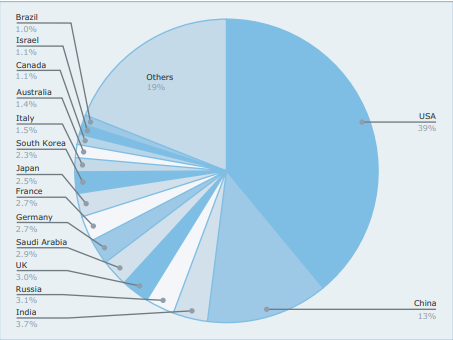
Image Courtesy: SIPRI
Other notable developments
- Largest military spenders in the Asia and Oceania region: In addition to China, India ($72.9 billion), Japan ($49.1 billion), South Korea ($45.7 billion) and Australia ($27.5 billion) were the largest military spenders in the Asia and Oceania region.
- Military expenditure in sub-Saharan Africa: It increased by 3.4 per cent in 2020 to reach $18.5 billion.
- The biggest increases in spending were made by Chad (+31 per cent), Mali (+22 per cent), Mauritania (+23 per cent) and Nigeria (+29 per cent), all in the Sahel region, as well as Uganda (+46 per cent).
- Military expenditure in South America: It fell by 2.1 per cent to $43.5 billion in 2020. The decrease was largely due to a 3.1 per cent drop in spending by Brazil, the sub region’s largest military spender.
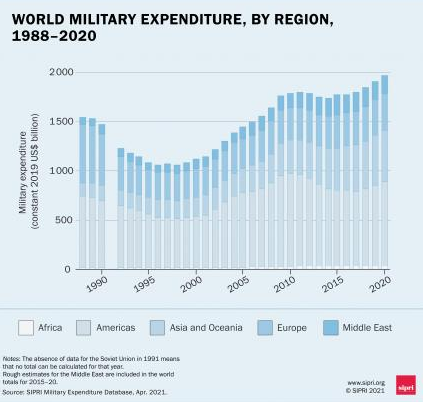
Image Courtesy: SIPRI
|
Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI)
About NATO:
|
Previous article
Facts in News
Next article
Project DANTAK