Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is set to launch the NISAR satellite from Sriharikota on July 30 onboard a GSLV Mk-II rocket.
NISAR Satellite
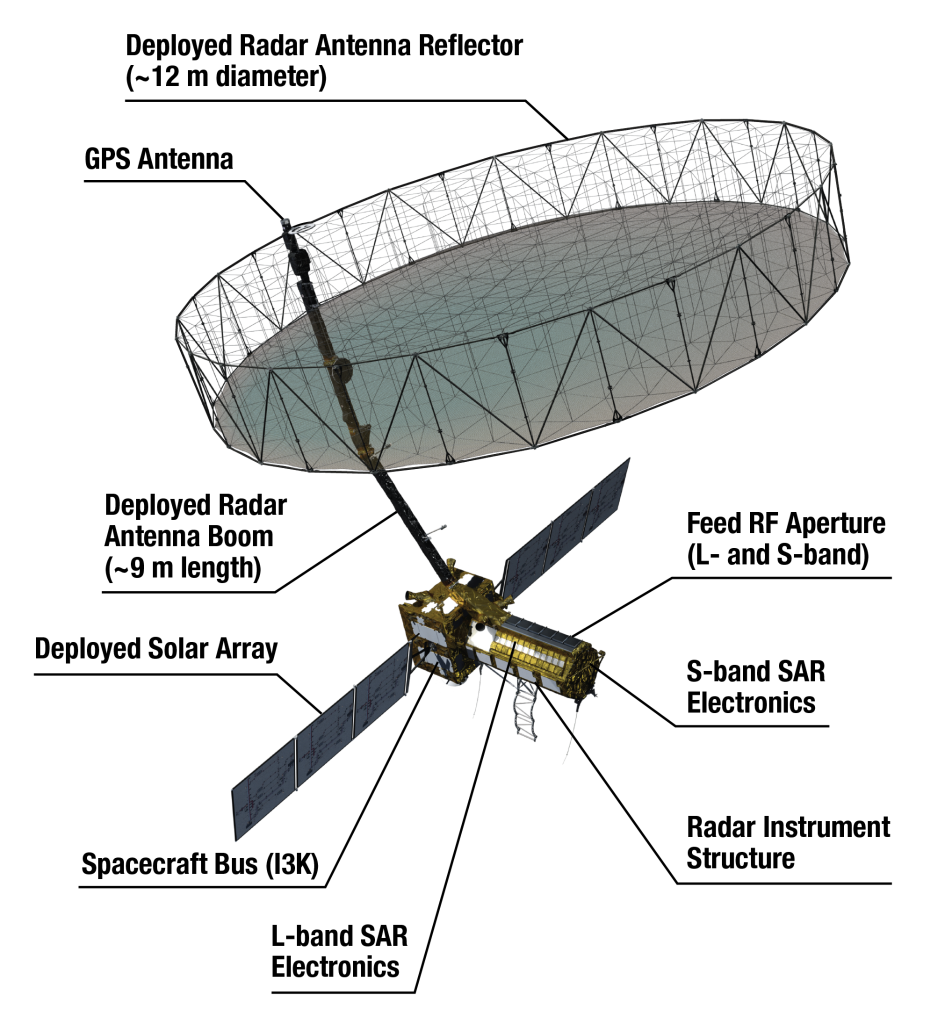
- NISAR is an Earth-observation satellite that stands for NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar.
- It is Jointly developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the Indian Space Research Organisation under a partnership agreement signed in 2014.
- It will be launched into a polar Sun-synchronous dawn-dusk orbit at 747 km altitude and an inclination of 98.4º.
- NISAR is the first satellite mission to collect radar data in two microwave bandwidth regions, called the L-band and the S-band.
- The S-band payload has been made by the ISRO and the L-band payload by the U.S.
Monitoring of Earth Surface
- The NISAR system comprises a dual frequency, fully polarimetric radar, with an imaging swath greater than 150 miles (240 km).
- This design permits complete global coverage every 12-days, allowing researchers to create time-series interferometric imagery and systematically map the changing surface of Earth.
- It can monitor various aspects in very high resolution.
- After a 90-day commissioning period, the mission will conduct a minimum of three full years of science operations with the L-band radar to satisfy NASA’s requirements,
- ISRO requires five years of operations with the S-band radar.
How NISAR Works?
- NISAR combines two types of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) systems:
- The L-band SAR (1.257 GHz) uses longer-wavelength radio waves that can penetrate thick vegetation and even soil, making it ideal for observing ground deformation beneath forests.
- The S-band SAR (3.2 GHz) uses shorter-wavelength radio waves that are more effective at detecting surface details such as crops, water surfaces, and urban infrastructure.
- The satellite also uses polarimetric radar technology, which involves sending and receiving radar signals in both horizontal and vertical polarizations.
- Satellite operations and commanding will be managed by ISRO, while NASA will provide the orbit maneuver plan and radar operations plan.
Objectives of the Mission
- NISAR can measure tectonic plate movements accurately. So a lot of geological, agricultural and water-related observations can be obtained from this satellite.
- It can study the water-stressing, climate change-related issues, agricultural changes through patterns, yield, desertification and continental movements precisely with respect to annual water cycle movements.
- NISAR’s data can help people worldwide better manage natural resources and hazards, as well as providing information for scientists to better understand the effects and pace of climate change.
Source: TH
Next article
News In Short 28-07-2025