In News
- The ‘State of the Global Climate 2022’ report released by WMO highlighted that sea level is rising at an unprecedented rate.
More about Report
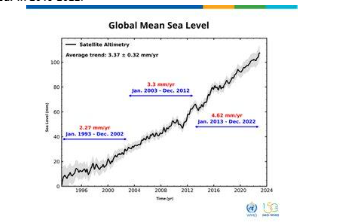
- The rate of global mean sea-level [GSML] rise has doubled in three decades i.e., rate of sea-level rise was 2.27 mm/year in 1993-2002, it shot up to 4.62 mm/year in 2013-2022.
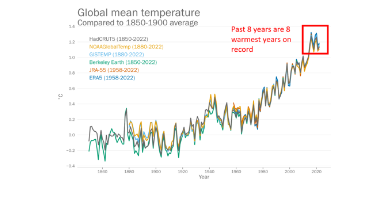
Global mean temperature in 2022 was 1.15 ± 0.13 °C above the 1850-1900 average. The years 2015 to 2022 were the eight warmest in the instrumental record back to 1850.
- Ocean Heat content (OHC) in 2022 touched a new record high. Around 90% of the energy trapped in the climate system by greenhouse gases goes into the ocean.
- In 2022, 58 percent of the ocean surface suffered at least one marine heatwave event and 25 per cent of the surface experienced at least one marine cold spell.
- Concentrations of the three main greenhouse gases – carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide – reached record observed highs in 2021.
- Earth’s ice cover known as cryosphere has thinned. The cumulative thickness loss since 1970 amounts to almost 30?m. Six of the ten most negative mass balance years on record (1950-2022) occurred since 2015
- Ocean Acidification: Global mean ocean pH has been steadily declining at rates not seen for at least the past 26,000 years.
What causes accelerated sea-level rise?
- According to the report during 2005-2019:

Impacts
- Increase inFrequency of cyclones: This will affect coastal communities and lead to large economic liabilities for tropical countries like India and South Africa, which have high population densities. For instance, South Africa was affected by five cyclones in over two months in 2022.
- Salinization of Groundwater: More seawater could seep into the ground, leading to the groundwater – which is usually freshwater – turning more and more saline. This in turn can exacerbate water crises in coastal areas as well as agriculture in adjacent regions.
- Forced migration: coastal ecosystems could be “completely changed”. In the Sundarbans delta in West Bengal, rising sea levels and coastal erosion has forced members of local communities to migrate.
- Record breaking rain: For instance, extensive flooding in Pakistan.
- Record breaking heat waves affected Europe during the summer. China had its most extensive and long-lasting heatwave since national records began
- Food insecurity: As of 2021, 2.3 billion people faced food insecurity, of which 924 million people faced severe food insecurity.
|
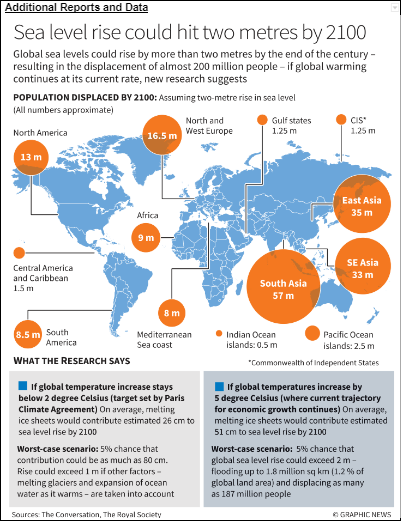
Additional Reports and Data |
|
About World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
|
Source: TH