Bharat Forecasting System Launched
Syllabus :GS 1/Geography
In News
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences has launched the Bharat Forecasting System (BFS).
Bharat Forecasting System
- Developed by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, to deliver highly localized weather forecasts with a 6 km resolution—the most advanced globally.
- It allows for more precise prediction of small-scale weather events.
- It is powered by the supercomputer Arka (11.77 petaflops, 33 petabytes).
- The previous supercomputer ‘Pratyush’ used to take up to 10 hours to run the forecasting model.
- It covers the tropical region (30°S to 30°N), including all of India, and surpasses global models from the U.S., UK, and Europe, which operate at 9–14 km resolution.
Importance
- It significantly improves processing speed over the previous system, reducing model run time from 10 hours to 4.
- It uses data from 40 Doppler Weather Radars, with plans to expand to 100, enabling both detailed local forecasts and nowcasts (2-hour forecasts).
- It marks a major advancement in India’s meteorological self-reliance, with benefits for disaster management, agriculture, water resources, and public safety down to the panchayat level.
- Supports India’s commitment to the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.
Source :TH
Iran Slams Trump’s Plan to Rename Persian Gulf
Syllabus: GS2/IR/GS1/Places in News
Context
- US President Donald Trump’s now-aborted move to rename the Persian Gulf as the ‘Arabian Gulf’ or ‘Gulf of Arabia’ stirred sharp condemnation from Iranian officials.
About
- Iran saw it as a politically charged attack on its national identity and historical legacy.
- The suggestion reportedly emerged ahead of Trump’s visit to Saudi Arabia, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates.
Persian Gulf
- The Persian Gulf is a strategically important and economically vital body of water in Western Asia.
- A gulf is a large part of the ocean or sea that is partially enclosed by land, typically with a narrow opening to the sea.
- It opens into the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea via the Strait of Hormuz.
- The countries that surround the Persian Gulf are Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar, and UAE.
- All these nations, except Iran, use the names ‘Arabian Gulf’ or just ‘Gulf’ to refer to the body of water, and have debated for long that it must be renamed.
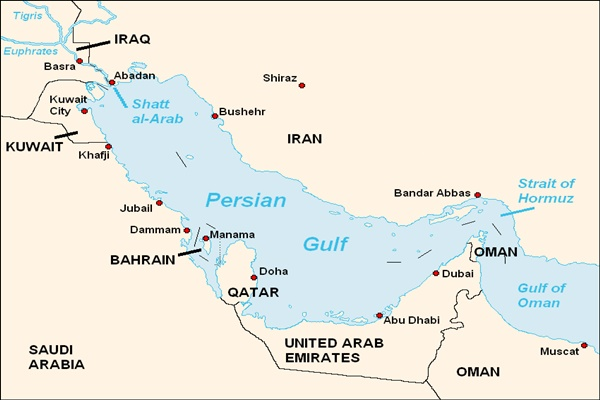
- Background: The Persian Gulf gets its name from Persia, which was the former name for Iran.
- Persia was officially renamed Iran in 1935 after Reza Shah Pahlavi, then Shah of Iran, felt that ‘Persia’ was an exonym – a historical name given by outsiders.
- He decided that the country deserves to be known by its endonym – a name given by its natives.
Source: AIR
Moringa
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
In News
- PKM1, a variety of Moringa oleifera, has created a global impact, especially in countries such as Senegal, Rwanda and Madagascar in the African continent.
About Moringa (Moringa oleifera)
- Origin and Distribution:
- Native to India, especially the foothills of the Himalayas.
- Now widely cultivated in South Asia, Africa, and tropical regions of Central and South America.
- Agricultural Requirements:
- Prefers deep sandy loam soil with pH between 6.5–8.0.
- Thrives in semi-arid and tropical climates. Optimal temperature: 25–30°C.
- Drought-resistant and fast-growing — can be harvested multiple times a year.
- Medicinal & Health Uses:
- Used in Ayurveda to treat over 300 conditions.
- Known for anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anti-diabetic properties.
- Seeds are used to purify water due to their coagulating ability.
Source: TH
NAMASTE Yojana
Syllabus :GS 2/Welfare Schemes
In News
- Recently, a special event was held in Madhya Pradesh to highlight the National Action Plan for Mechanized Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) scheme.
NAMASTE Yojana
- The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment in convergence with the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs have launched the National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) scheme in July 2023 to ensure safety and dignity of sanitation workers.
- The focus is on prevention of hazardous cleaning and promotion of safe cleaning practices through trained and certified sanitation workers.
- It aims to ensure safety and dignity of sanitation workers in urban India and enhance their occupational safety through capacity building and improved access to PPE Kits, safety devices and machines.
Source :TH
One Big Beautiful Bill Act
Syllabus: GS2/ International issues
Context
- The United States House of Representatives has passed the One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBBA) of 2025, aimed at reshaping the nation’s economic and immigration framework.
Key Provisions of OBBBA
- Permanent Tax Cuts: The bill makes permanent the tax cuts introduced under the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), which had increased standard deductions and lowered tax brackets.
- Excise Tax on Remittances: A 3.5% excise tax on remittances sent by non-citizens, aiming to disincentivize undocumented immigration and generate federal revenue.
- Raising the Debt Ceiling: It authorizes an increase in the US debt ceiling.
- The debt ceiling is a legislative cap on the amount of national debt the US Treasury can incur.
- Fiscal Prudence: There are measures to cut government spending by targeting “waste, fraud, and abuse” in federal programs.
Implications
- For the US Economy:
- Offers tax relief to middle-income households.
- Aims to boost consumer spending and stimulate growth.
- Raises concerns over long-term fiscal sustainability, especially with simultaneous tax cuts and defence spending increases.
- The remittance tax could impact countries like Mexico, India, Philippines, etc., where remittances form a crucial part of household incomes and foreign exchange reserves.
Source: IE
Tianwen-2 Mission
Syllabus :GS 3/Space
In News
- China is set to launch its first asteroid sampling mission called Tianwen-2.
About Tianwen-2 Mission
- The mission will investigate 469219 Kamo‘oalewa, a near-Earth asteroid that orbits the Sun close to Earth.
- It aims to collect samples from Kamo‘oalewa using a “touch-and-go” technique or possibly an “anchor and attach” method.
- It aims to advance scientific understanding of asteroids and demonstrate China’s growing capabilities in deep-space exploration.
- If successful, China will join the ranks of the U.S. and Japan as one of the few countries to have collected and returned asteroid samples.
Kamo‘oalewa
- It is a small quasi-satellite asteroid of Earth and it was discovered in 2016 by the Pan-STARRS 1 telescope in Hawaii.
- It orbits the Sun but appears to follow Earth due to its unique, elliptical path.
- It has been in its current orbit for about 100 years and is expected to remain for another 300 years.
Source :IE
Pumped Storage Hydropower
Syllabus: GS3/ Energy and Infrastructure
Context
- The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) has identified Greenko, Adani Green, and JSW Energy as key players in India’s ambitious plan to add 51 GW of pumped storage hydropower (PSH) capacity by 2032.
What is Pumped Storage Hydropower (PSH)?
- Pumped storage hydropower is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by power grids for load balancing.
- It involves two reservoirs at different elevations:
- During low demand: Excess renewable energy (mainly solar) pumps water from a lower to an upper reservoir.
- During peak demand: Water is released to generate electricity, thus functioning like a battery.
Current Status in India
- Installed Capacity: Less than 5 GW (as of 2024)
- Planned Capacity by 2032: 51.24 GW (39 projects)
- Under Construction: ~10 GW, with 3 GW likely to be commissioned in FY25
- Major States: Andhra Pradesh (16 GW) and Maharashtra (13 GW) together will host 57% of new capacity.
Significance of Pumped Storage in India
- Grid Balancing for Renewables: Integration of variable solar and wind energy requires stable, dispatchable power sources. PSH provides this flexibility, helping maintain grid stability.
- Higher Economic Returns: Internal Rate of Return (IRR) for PSH is slightly higher than for standalone solar or wind projects.
Pumped Storage Hydropower vs Battery Energy Storage Systems
| Parameter | Pumped Storage (PSH) | Battery Energy Storage (BESS) |
| Environmental Impact | Requires more land and water | Resource-intensive (minerals, chemicals) |
| Scalability | High, with multi-GW potential | Modular, best suited for short-duration use |
| Supply Chain Risk | Low (local resources) | High (dependence on Chinese batteries) |
| Response Time | Moderate | Instantaneous |
| Gestation Period | ~5 years | 1–2 years |
Source: IE
Matryoshka
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
- Google’s annual I/O developer conference in 2025 showcased AI Matryoshka.
About
- AI Matryoshka is Google’s strategic framework for layering AI models and capabilities across its entire ecosystem—mirroring the structure of Russian nesting dolls (matryoshkas) where each layer supports the next.
- AI Matryoshka represents Google’s strategic vision to interlace AI throughout its entire product and service lineup.
- By nesting AI functionalities within each layer of its ecosystem, Google aims to deliver seamless, intelligent experiences that adapt to users’ needs across various platforms and devices.
Significance
- AI Matryoshka reflects how each AI capability is nested inside another, allowing:
- Tight integration between hardware and software;
- Reusability and specialization at different levels (from cloud to edge);
- Seamless transitions between on-device and cloud-based intelligence.
- This creates a unified AI experience, where different AI “layers” work together depending on the task’s complexity and device capability.
Source: TH
Previous article
Oil Spill off Kerala Coast