
Mahatma Gandhi’s 156th birth anniversary on 2 October 2025 reminds us of his timeless values of truth, non-violence, and simplicity. In today’s world of conflicts, climate challenges, and social divides, Gandhi Jayanti inspires sustainable living, peaceful coexistence, and inclusive development, guiding humanity towards harmony and moral progress.
Why in the News?
- The 156th Mahatma Gandhi Jayanti (2 October 2025) is in the news as India, along with the global community, commemorates the birth anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi, celebrating his legacy of truth, non-violence, and sustainable living.
- This year, special emphasis is given to Gandhi’s principles in the context of rising social inequalities, environmental crises, and international conflicts, making his ideals especially relevant today.
- Nationwide, schools, colleges, and government bodies organize cultural programs, debates, cleanliness drives, and tributes at Raj Ghat to promote his message of peace and inclusive growth.
- The United Nations continues to observe this day as the International Day of Non-Violence, reinforcing Gandhi’s values for justice, ethical leadership, and harmony.
- Recent government initiatives and activities, including Seva Pakhwada and community summits, further highlight Gandhi’s enduring influence in shaping policy and social action in contemporary India.
Who was Mahatma Gandhi?
- Mahatma Gandhi, born Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi on 2 October 1869, was an Indian lawyer, social activist, and leader who played a pivotal role in India’s struggle for independence from British rule.
- Known as the “Father of the Nation,” he pioneered the philosophy and practice of non-violent resistance called Satyagraha, which became a powerful tool against colonial oppression.
- Gandhi’s ideology emphasized truth (Satya), non-violence (Ahimsa), swaraj (self-rule), rural development, social equality, and simplicity in life.
- He led significant movements such as the Champaran and Kheda agitations, Non-Cooperation Movement, Salt March, and Quit India Movement. Beyond freedom, he worked for the upliftment of the marginalized, promoting communal harmony and economic self-reliance.
- His principles continue to inspire global peace and justice movements. Gandhi’s 156th birth anniversary on 2 October 2025 reaffirms the relevance of his teachings in addressing contemporary challenges with ethics, peace, and inclusiveness.
Historical Significance of 156th Mahatma Gandhi Jayanti
- The 156th Mahatma Gandhi Jayanti on 2 October 2025 marks the remembrance of a towering figure in India’s freedom struggle and the global peace movement.
- Gandhi’s leadership in the non-violent struggle against British colonial rule revolutionized political resistance through satyagraha and civil disobedience, inspiring millions in India and worldwide.
- His emphasis on self-reliance (swaraj), rural upliftment, and social reform united diverse sections against oppression.
- This day commemorates his role as the Father of the Nation, celebrating his vision of a free, just, and equitable society.
- Gandhi Jayanti also reflects on his contributions beyond politics: promoting communal harmony, uplifting the marginalized, and pioneering ethical living.
- Historically, it marks India’s triumph through peaceful means, contrasting with violent revolutions.
- Observed as the International Day of Non-Violence by the UN, the 156th anniversary highlights the enduring legacy of Gandhi’s philosophy in shaping democratic values, human rights, and global peace, making this day a significant reminder of the power of non-violence and truth in societal transformation.

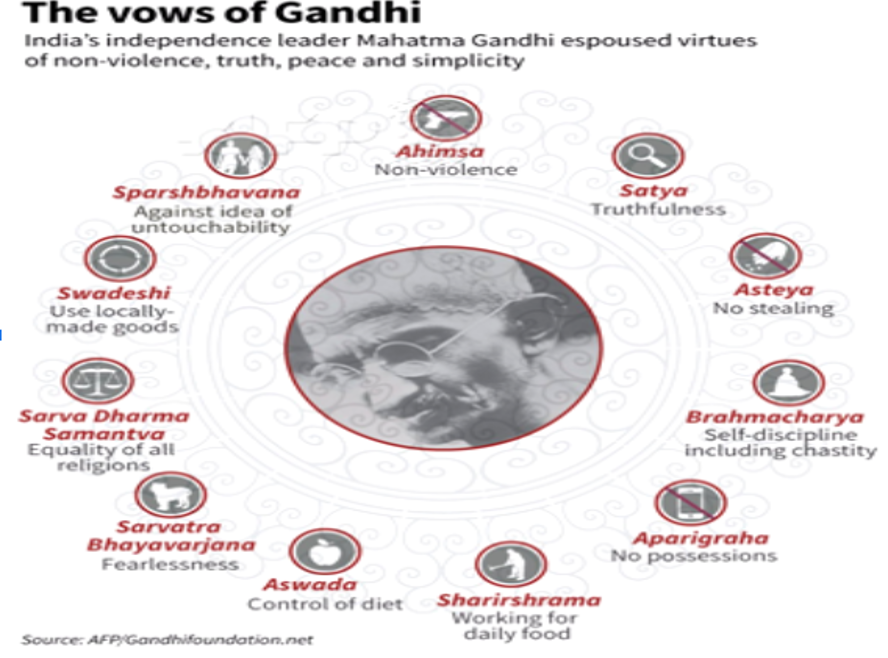
Core Principles of Mahatma Gandhi
- Mahatma Gandhi’s core principles shaped his life and India’s struggle for freedom, teaching lessons that endure today.
- At the heart is Truth (Satya)—complete honesty in thought, word, and deed, like his unwavering commitment during the Salt March.
- Non-violence (Ahimsa) means avoiding harm to all beings, inspiring global peace movements such as Martin Luther King’s civil rights efforts.
- Gandhi practiced Non-Stealing (Asteya), respecting others’ possessions, and Chastity (Brahmacharya), practicing self-control for spiritual strength.
- Non-Possession (Aparigraha) encouraged simple living, reducing desire for material goods, evident in Gandhi’s minimal lifestyle.
- He championed Fearlessness, urging courage in facing injustice, and Sarvodaya (welfare of all), focusing on uplifting marginalized communities. His principle of Swadeshi promoted using local goods, empowering communities.
- These timeless values guide ethical living, promoting love, harmony, and justice worldwide, proving relevant to personal and social transformation today.
Current Relevance
- The current relevance of Mahatma Gandhi in 2025 is profound, as his timeless principles continue to address critical global and societal challenges.
- Gandhi’s core values—non-violence (Ahimsa), truthfulness (Satya), simplicity, self-reliance (Swaraj), compassion, and service—offer vital solutions in today’s complex world.
- Non-violence now expands beyond physical actions to digital interactions, promoting respectful discourse amid rising online hate and harassment.
- Truthfulness combats disinformation and fake news through media literacy and responsible journalism. Simplicity aligns with sustainable living, reducing environmental footprints and fostering minimalism.
- Self-reliance encourages local entrepreneurship within global interdependence, while compassion and service unify polarized societies through empathy and volunteerism.
- Additionally, Gandhi’s philosophies inspire ethical leadership, social justice, sustainable development, and conflict resolution, remaining indispensable for democratic governance and peace in the 21st century.
- His vision of inclusivity, interfaith harmony, and grassroots democracy is instrumental in addressing contemporary issues like social inequality, environmental crisis, and global tensions.
- Thus, Gandhi’s legacy is a guiding light for individuals and nations to embrace peace, justice, ethical governance, and sustainability for a harmonious future.
Timeline of Mahatma Gandhi’s Life
| Year | Event/Details |
|---|---|
| 1869 | Born on 2 October in Porbandar, Gujarat |
| 1876 | Attended primary school in Rajkot; betrothed to Kasturba |
| 1888 | Left for London to study law |
| 1891 | Completed law studies; returned to India |
| 1893 | Went to South Africa for legal work |
| 1894 | Founded Natal Indian Congress in South Africa |
| 1906 | Started first Satyagraha campaign in South Africa |
| 1915 | Returned to India; began active involvement in freedom struggle |
| 1917 | Led Champaran agitation (first major satyagraha in India) |
| 1919 | Launched nationwide protests against Rowlatt Act |
| 1920 | Led Non-Cooperation Movement |
| 1930 | Led Salt March (Dandi March); Civil Disobedience Movement began |
| 1942 | Launched Quit India Movement |
| 1947 | India gained independence |
| 1948 | Assassinated on 30 January in New Delhi |
Celebrations and Observances of Mahatma Gandhi Jayanti
- Gandhi Jayanti is observed annually on 2 October across all states and union territories of India as a national holiday, honoring the birth of Mahatma Gandhi, known as the Father of the Nation.
- Official ceremonies include prayer services and tributes at Raj Ghat, New Delhi, where Gandhi was cremated. Leaders, officials, and citizens participate in paying homage through floral wreaths and prayer meetings.
- Educational institutions and government offices organize commemorative activities such as debates, essay competitions, painting contests, and award presentations centered on Gandhi’s ideals of nonviolence, peace, and social justice.
- Gandhi’s favorite devotional song, “Raghupati Raghava Raja Ram,” is commonly sung during these events to remember him.
- Statues and portraits of Gandhi throughout the country are decorated with flowers and garlands; some people observe a dry day by refraining from drinking alcohol as a mark of respect.
- The day is popularly used to promote projects and initiatives related to nonviolence, cleanliness, and community service. For instance, the Swachh Bharat Mission was launched on Gandhi Jayanti in 2014, inspiring cleanliness drives on this day annually.
- Community and cultural programs including rallies, seminars, and virtual campaigns help spread Gandhi’s message to different generations, both in India and abroad.
- Gandhi Jayanti is recognized internationally by the United Nations as the International Day of Non-Violence, marking Gandhi’s global legacy.
Thus, the celebrations are a mix of solemn homage, educational activities, community engagement, and promotion of Gandhian principles of peace and nonviolence.
Mahatma Gandhi and Government Policies around India and World
Mahatma Gandhi’s impact on government policies in India and worldwide is profound, rooted mainly in his philosophy of nonviolence, self-reliance, and social justice. His influence shaped India’s path to independence and guided foundational policies in independent India, while his principles inspired global movements and governance ideas.
Influence on Indian Government Policies
- Economic Self-Reliance (Swadeshi Movement): Gandhi promoted the boycott of British goods and advocated use of Indian-made products, especially khadi (homespun cloth), to cripple British economic dominance. This inspired policies encouraging cottage industries and local entrepreneurship in independent India.
- Directive Principles in Indian Constitution: Many of Gandhi’s ideas were incorporated in the Directive Principles of State Policy, which guide government policies on social welfare, economic equity, prohibition of intoxicants, rural self-governance (village panchayats), and promotion of cottage industries. Articles like 39, 40, 43, 46, and 47 reflect Gandhian vision for inclusive and ethical development.
- Panchayati Raj System: Gandhi’s emphasis on Gram Swaraj (village self-rule) led to constitutional provisions for Panchayati Raj institutions, empowering local self-government for rural development, which became key to India’s democratic decentralization.
- Nonviolence and Peaceful Protest as Political Tools: Gandhi’s nonviolent resistance (Satyagraha) became a model for civil disobedience, influencing India’s legislative approach and governance based on democratic participation and ethical statecraft.
Gandhi’s Influence on Global Government Policies and Movements
- Inspiration to Civil Rights and Freedom Movements: Gandhi’s methods inspired leaders like Martin Luther King Jr. in the American civil rights movement, Nelson Mandela in South Africa, and other global freedom struggles against colonialism and racial segregation.
- Nonviolent Political Philosophy: His emphasis on moral politics and nonviolence pushed many governments and international organizations to recognize peaceful conflict resolution as a viable political tool. The UN declared Gandhi’s birth anniversary the International Day of Nonviolence, promoting peace worldwide.
- New Paradigms of State and Development: Gandhi’s critique of industrialization and advocacy of sustainable, human-scale development influenced modern policy debates on environment-friendly governance and social equity in various countries.
- Influence on India’s Foreign Policy: Post-independence leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru adopted Gandhian principles to shape an inclusive, non-aligned foreign policy pursuing peace and cooperation in international relations.
In summary, Gandhi’s legacy in government policies spans promoting ethical governance, grassroots democracy, economic self-sufficiency, and global peace efforts, establishing him as an enduring symbol of political philosophy and transformative action.
Some Important Speeches & Famous Quotes by Mahatma Gandhi
| Speech/Event | Key Points / Famous Quotes |
|---|---|
| Quit India Speech (1942) | “Do or Die. We shall either free India or die in the attempt.” |
| Speech at Round Table Conference (1931) | Advocated peaceful negotiation for Indian self-rule. |
| Message of Non-violence and Truth | “My religion is based on truth and non-violence.” |
| General Inspirational Quotes | “Be the change that you wish to see in the world.” “An eye for an eye only ends up making the whole world blind.” “The weak can never forgive. Forgiveness is the attribute of the strong.” “Live as if you were to die tomorrow. Learn as if you were to live forever.” “In a gentle way, you can shake the world.” |
| On Self-reliance and Ethics | “There is a sufficiency in the world for man’s need but not for man’s greed.” |
| On Peace and Human Values | “Where there is love there is life.” |
| On Courage and Willpower | “Strength does not come from physical capacity. It comes from an indomitable will.” |
Way Forward
On this 156th Gandhi Jayanti, renew commitment to his principles of nonviolence, truth, and social justice. Promote peaceful coexistence, sustainability, and community service. Use digital platforms to spread his timeless message, inspiring a harmonious, inclusive, and equitable society for future generations.
Conclusion
The 156th Mahatma Gandhi Jayanti on 2 October 2025 is a powerful reminder of Gandhiji’s timeless values of truth, nonviolence, and harmony. It inspires renewed commitment to his ideals amid modern-day challenges of social inequality and global tensions. Honoring his legacy urges all to promote peace and justice for a sustainable future.
FAQs: Gandhi Jayanti 2025
When is Mahatma Gandhi Jayanti 2025 celebrated?
Gandhi Jayanti 2025 will be celebrated on 2 October, marking the 156th birth anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi.
Why do we celebrate Gandhi Jayanti?
Gandhi Jayanti honors Mahatma Gandhi’s contribution to India’s freedom struggle and his principles of truth, non-violence, and simplicity.
What is the significance of Gandhi Jayanti in 2025?
The 156th Gandhi Jayanti highlights the relevance of his values in tackling global challenges like inequality, climate change, and conflicts.
How is Gandhi Jayanti celebrated in India?
Gandhi Jayanti is marked by prayer meetings at Raj Ghat, cultural programs in schools, cleanliness drives, and UN observance as the International Day of Non-Violence.
What are Mahatma Gandhi’s core principles?
Gandhi’s principles include truth (Satya), non-violence (Ahimsa), self-reliance (Swaraj), simplicity, and service to humanity.
Read this article in Hindi: 156वीं महात्मा गांधी जयंती 2025 (2 अक्टूबर)





