Shaheed Udham Singh
Syllabus:GS1/History
In News
- The Prime Minister paid tribute to Shaheed Udham Singh on his martyrdom day.
Shaheed Udham Singh
- He was born in 1899 in Sangrur, Punjab and he lost his parents at an early age.
- He was hanged on July 31, 1940, for assassinating Michael O’Dwyer, the former Lieutenant Governor of Punjab, in London – an act of revenge for the 1919 Jallianwala Bagh massacre.
Legacy
- Udham Singh dedicated his life to self-respect and freedom. He launched an armed rebellion against British atrocities.
- The Jallianwala Bagh massacre deeply disturbed him, prompting him to travel to England to avenge the killings.
- Through the Ghadar Party, he inspired patriotism among Indians living abroad. His courage, bravery, and sacrifice gave greater strength to India’s freedom movement.
| Do you know? – The Jallianwala Bagh massacre took place on April 13, 1919, when British Indian Army troops under Colonel Reginald Dyer opened fire on a peaceful gathering of unarmed protesters and pilgrims in Amritsar, Punjab, on the occasion of Baisakhi. – The crowd had assembled to protest the arrest of nationalist leaders Satya Pal and Saifuddin Kitchlew. The indiscriminate firing led to massive casualties. – According to official British records, 379 people were killed and around 1,200 injured. 1. However, other estimates put the death toll at over 1,000. |
Source :PIB
Swachhata Pakhwada 2025
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
Context
- Recently, the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) observed Swachhata Pakhwada 2025.
About
- Swachhta Pakhwada is an initiative under Swachh Bharat Mission (Grameen).
- The programme was launched in 2016 with the objective of bringing about an intense focus on sanitation issues and practices by involving all Ministries and Departments of Government of India.
- It’s an annual observance aimed at spreading awareness and encouraging activities related to cleanliness and hygiene across various sectors of society.
- The Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS) acts as the nodal department, laying down suggestive activities for observing the Pakhwada each year.
Source: PIB
Nyaya Bandhu Legal Aid Programme
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
Context
- Till June, 2025, approximately, 14888 women beneficiaries have registered under the Nyaya Bandhu App.
About
- The Nyaya Bandhu (Pro Bono Legal Service) is one of the programmes under the scheme of “Designing Innovative Solutions for Holistic Access to Justice” (DISHA).
- It was launched in 2017 and is implemented by the Department of Justice under the Ministry of Law and Justice.
- It registers interested Pro Bono Advocates and connects them with the beneficiaries.
- Beneficiaries are entitled for free legal aid under Section 12 of the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987 through the Nyaya Bandhu Application.
- In order to avail the services of a Pro Bono lawyer, both the applicants and lawyers are required to register on the Nyaya Bandhu Mobile Application.
- To enhance the reach and effectiveness of the Nyaya Bandhu program in remote areas, Pro Bono Clubs (PBCs) in the Law schools are engaged in providing community care, legal assistance and legal awareness to the beneficiaries in the villages.
Source: PIB
Malaria Elimination
Syllabus: GS2/Health
In News
- India reduced its malaria burden by over 80% since 2015, but tribal areas still face high rates.
Malaria
- It is a life-threatening disease which spreads to people through the bites of some infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- Blood transfusion and contaminated needles may also transmit malaria.
- It is mostly found in tropical countries. It is preventable and curable.
- It is caused by a parasite and does not spread from person to person.
Symptoms
- It can be mild or life-threatening. Mild symptoms are fever, chills and headache. Severe symptoms include fatigue, confusion, seizures, and difficulty breathing.
Risk
- Infants, children under 5 years, pregnant women and girls, travellers and people with HIV or AIDS are at higher risk of severe infection.
- In 2023, malaria infected 294 million people globally, killing nearly 600,000.
Prevention
- Malaria can be prevented by avoiding mosquito bites and with medicines. Treatments can stop mild cases from getting worse.
Vaccines
- The R21/Matrix-M vaccine, developed by Oxford and the Serum Institute, showed up to 77% efficacy in Phase 3 trials winning World Health Organization (WHO) approval in 2023.
- Fewer doses, low cost, and Indian production make it especially promising.
- Whole-parasite vaccines like PfSPZ and dual-stage Indian candidate AdFalciVax show promising results.
- Transmission-blocking vaccines, mRNA platforms, and engineered antibodies are also under development.
India’s Targets
- India aims to eliminate malaria by 2030 but challenges include drug resistance, asymptomatic carriers, and relapse-prone P. vivax.
- Therefore, achieving the goal will require sustained scientific, political, and public health coordination — combining vaccines, vector control, and health system support.
Source :TH
India, Morocco Sign Agreement to Boost Judicial Cooperation
Syllabus: GS2/IR
Context
- India and Morocco have signed a Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty (MLAT) and a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to promote cooperation in judicial and legal spheres.
About
- The MLAT focuses on civil and commercial matters, enabling both countries to:
- cooperate in the service of judicial documents, the taking of evidence through Letters of Request, and the execution of judicial judgments, decrees, settlements, and arbitral awards.
- It also focuses on the exchange of legal expertise, training, and research.
- To ensure effective implementation, a joint coordination committee will be established to plan annual cooperation programmes.
Morocco
- Morocco is a mountainous country of western North Africa that lies directly across the Strait of Gibraltar from Spain.
- Morocco borders Algeria to the east and southeast, Western Sahara to the south, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north.
- It is the only African country with coastal exposure to both the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
Source: PIB
Grant in aid to National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC)
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- The Union Cabinet has approved the Central Sector Scheme “Grant in aid to National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC)” for four years from 2025-26 to 2028- 29.
About
- NCDC will be the implementing agency.
- It will provide loans to cooperatives either through state government or directly, as per NCDC guidelines.
- Loans will be provided for setting up/ modernization/ technology upgradation/ expansion of project facilities for various sectors and working capital to run their businesses efficiently and profitably.
Cooperatives
- A cooperative (or co-op) is an organization or business that is owned and operated by a group of individuals who share a common interest, goal, or need.
- These individuals, known as members, participate in the cooperative’s activities and decision-making process, typically on a one-member, one-vote basis, regardless of the amount of capital or resources each member contributes.
- The main purpose of a cooperative is to meet the economic, social, or cultural needs of its members, rather than to maximize profits for external shareholders.
- India has more than 8.25 lakh cooperatives with more than 29 crore members and 94% farmers are associated with cooperatives.
| National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) – It was established by an Act of Parliament in 1963 as a statutory Corporation under the Ministry of Cooperation. – Functions: 1. Planning, promoting and financing programmes through cooperatives, besides income generating streams of activities such as poultry, dairy, fishery, sericulture, handloom etc. 2. It also finances projects in the rural industrial cooperative sectors and for certain notified services in rural areas. 3. Loans and grants are advanced to State Governments for financing primary and secondary level cooperative societies. |
Source: PIB
Kavach 4.0
Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology; Infrastructure
Context
- Indian Railways has commissioned indigenous railway safety system Kavach 4.0 on the Mathura-Kota section of high-density Delhi-Mumbai route.
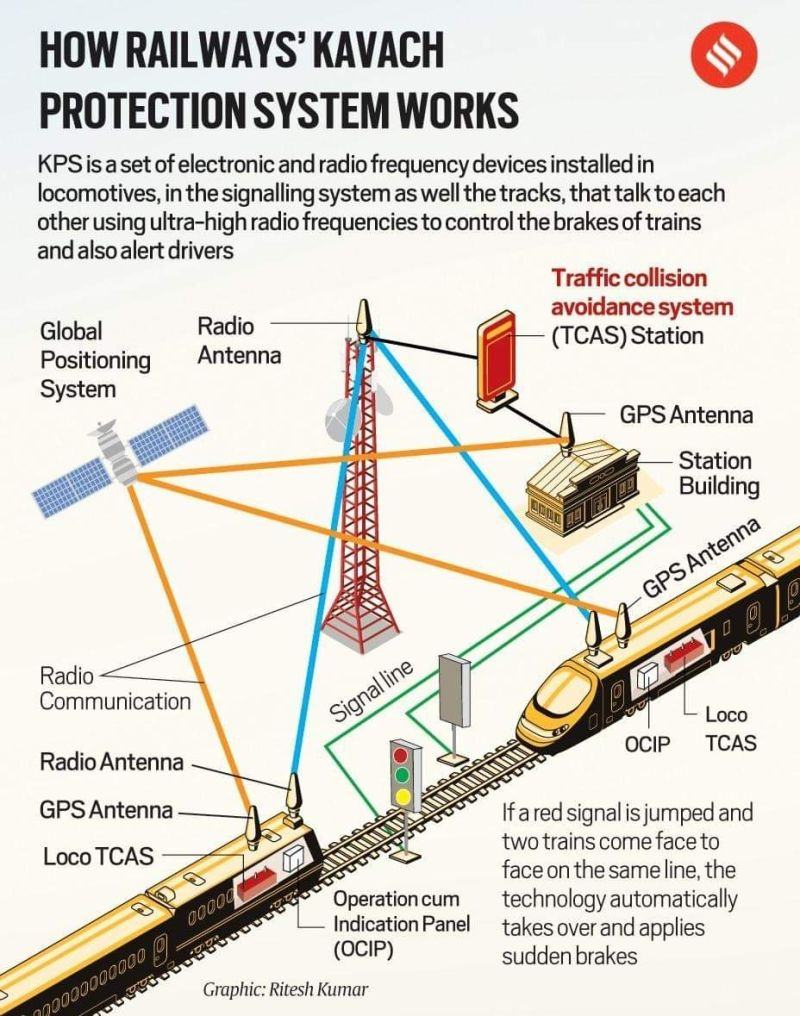
What is Kavach?
- It is an indigenously developed Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system by the Research Designs and Standards Organisation (RDSO) in collaboration with Indian industry.
- Kavach aids the Loco Pilot in running of trains within specified speed limits by automatic application of brakes in case Loco Pilot fails to do so and also helps the trains to run safely during inclement weather.
- It is designed to the highest safety standard — Safety Integrity Level 4 (SIL-4) — where the probability of failure is just 1 in 10,000 years.
- The advanced version ‘Kavach 4.0’ approved in May 2025 for speeds up to 160 kmph.
Source: PIB
India’s First 1 MW Green Hydrogen Plant Commissioned at Kandla Port
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- India’s first indigenously developed 1 MW Green Hydrogen Power Plant is inaugurated at the Deendayal Port Authority (DPA) in Kandla, Gujarat.
About
- The plant is capable of producing approximately 140 metric tonnes of green hydrogen annually.
- The Deendayal Port Authority has previously introduced India’s first Made-in-India all-electric green tug, further reinforcing its leadership in eco-friendly port operations.
What is Green Hydrogen?
- Green Hydrogen: The hydrogen produced via electrolysis, the splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen with electricity generated from renewable energy sources such as solar or wind, is known as Green hydrogen.
- MNRE defines Green Hydrogen as having a well-to-gate emission (i.e., including water treatment, electrolysis, gas purification, drying and compression of hydrogen) of not more than 2 kg CO2 equivalent / kg H2.
About Kandla Port
- Kandla Port, officially known as Deendayal Port Authority, is a major seaport located in the Kutch district of Gujarat, India.
- It’s situated on the Kandla Creek, about 90 km from the mouth of the Gulf of Kutch.
- Kandla Port was constructed in the 1950s to serve as the primary seaport for western India after the partition of India and Pakistan.
Source: TOI
Himgiri
Syllabus :GS3/Defence
In News
- The Indian Navy received the advanced guided-missile frigate Himgiri built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) in Kolkata.
Himgiri (Yard 3022)
- It is the third Nilgiri-class (Project 17A) frigate and the first built by GRSE.
- The Project 17A frigates are versatile multi-mission platforms, designed to address current and future challenges in the maritime domain.
- It is a reincarnation of the erstwhile INS Himgiri, a Leander-class frigate, that was decommissioned on May 6, 2025
- It is a modern, multi-mission warship designed by the Warship Design Bureau and launched in December 2020.
Features
- It features BrahMos and Barak 8 missiles, advanced AESA radar, and state-of-the-art combat systems.
- It is capable of anti-air, anti-surface, and anti-submarine warfare.
Importance
- The ship symbolizes India’s defence self-reliance with high indigenous content.
- It offers modular design, enhanced survivability, and full aviation facilities for helicopters, accommodating up to 225 personnel.
Source :TH
Previous article
White Paper on Blue Economy