Syllabus: GS3/Infrastructure
Context
- The Union Cabinet increased the budgetary outlay for the flagship scheme Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY) by Rs 1,920 crore to Rs 6,520 crore to boost the food processing sector.
About
- Of the total outlay, ₹1,000 crore has been earmarked to set up 50 Multi-Product Food Irradiation Units under the component scheme Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure (ICCVAI).
- And 100 NABL-accredited Food Testing Laboratories under the Food Safety and Quality Assurance Infrastructure (FSQAI) component.
- These initiatives are in alignment with announcements made in the Union Budget.
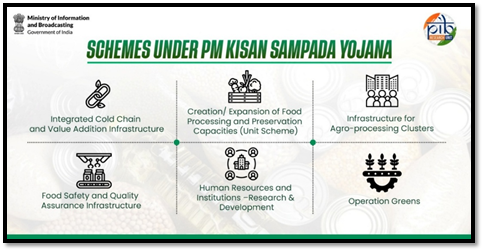
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY)
- SAMPADA- Scheme for Agro-marine processing and Development of Agro-processing Clusters is an umbrella Central sector scheme approved in 2017.
- Ministry: The Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI).
- Key Goals:
- A comprehensive package for modern infrastructure and efficient supply; chain management, from farm gate to retail outlet.
- Aims to boost the food processing sector in India.
- Helps farmers get better returns and supports doubling of farmers’ income.
- Creates huge employment opportunities, especially in rural areas.
- Reduces wastage of agricultural produce.
- Increases processing levels of food products.
- Enhances exports of processed foods.
What is Food Processing?
- Food processing can be defined as the use of methods and techniques involving equipment, energy, and tools to transform agricultural products such as grains, meats, vegetables, fruits, and milk into food ingredients or processed food products.
- This can include a wide range of activities, such as: Preparation, Cooking, Preservation, Packaging and Fortification.
- Formulations and processing techniques are scientifically developed to deliver food that is safe, eliminating the presence of any harmful chemical contaminants and micro-organisms that could cause food-borne illnesses.
Food Processing Industry in India
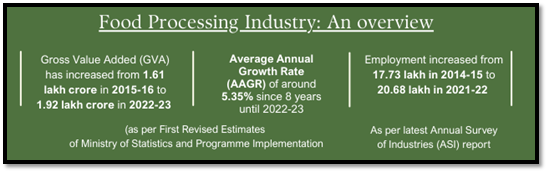
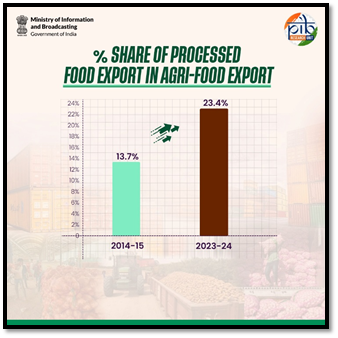
- Reasons for the Growth of Sector: India is the largest producer of milk and spices and one of the leading producers of fruits and vegetables, poultry, and meat.
- India has access to several natural resources that provides it with a competitive advantage in the food processing sector.
- Due to its diverse agro-climatic conditions, it has a wide-ranging and large raw material base suitable for food processing industries.
Challenges
- Cold Chain Logistics: Lack of adequate cold storage facilities leads to significant food wastage, especially for perishable items.
- Transportation: Poor road and transport infrastructure delay the movement of goods, affecting freshness and quality.
- Complex Compliance: Navigating various regulations and standards set by agencies like FSSAI can be challenging, particularly for small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
- Limited Adoption of Modern Techniques: Many small processors lack access to advanced processing technologies and machinery, which limit efficiency and scalability.
- Price Sensitivity: Consumers are often price-sensitive, which pressures margins for processors.
- Inconsistent Supply: Fluctuations in agricultural production due to weather conditions disrupt the supply chain, leading to shortages and price volatility.
- Health Consciousness: Increasing demand for healthier and organic options requires processors to adapt their offerings, which can be resource-intensive.
- Changing Tastes: Rapid shifts in consumer preferences necessitate constant innovation and product development.
Government Initiatives
- PLISFPI- Production Linked Incentive Scheme for Food Processing Industry: It was approved by the Union Cabinet in 2021, the Scheme is being implemented over a six-year period from 2021-22 to 2026-27.

- PMFME- Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme: It is providing technical, financial and business support for setting up/upgradation of 2 lakh Micro Food Processing Enterprises.

- National Food Processing Policy: This policy aims to enhance food processing capacity and encourage innovation in the sector.
- Market Access: Efforts are being made to improve market access for processed food products through various platforms, including e-commerce and direct selling.
Way Ahead
- The food processing sector in India has immense potential for growth and sustainability.
- The expansion of cold chain facilities, financial incentives, and skill development initiatives have further positioned India as a global food processing hub.
- With a focus on innovation, sustainability, and entrepreneurship, the sector is set to enhance farmer incomes, generate employment, reduce food wastage and boost exports.
Source: PIB
Previous article
Tamil Nadu’s Transgender Policy & Hindu Succession Act, 1956
Next article
Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021