Syllabus: GS3/ Disaster Management, GS1/ Geography
Context
- A new study by researchers at IIT Gandhinagar has warned that flash floods are becoming more frequent and severe across India.
What Are Flash Floods?
- Flash floods are sudden, intense floods that occur within six hours of a heavy rainfall event, usually in regions with steep slopes, poor drainage, or saturated/dry soil.
- Unlike riverine floods, they offer little warning, making them particularly deadly.
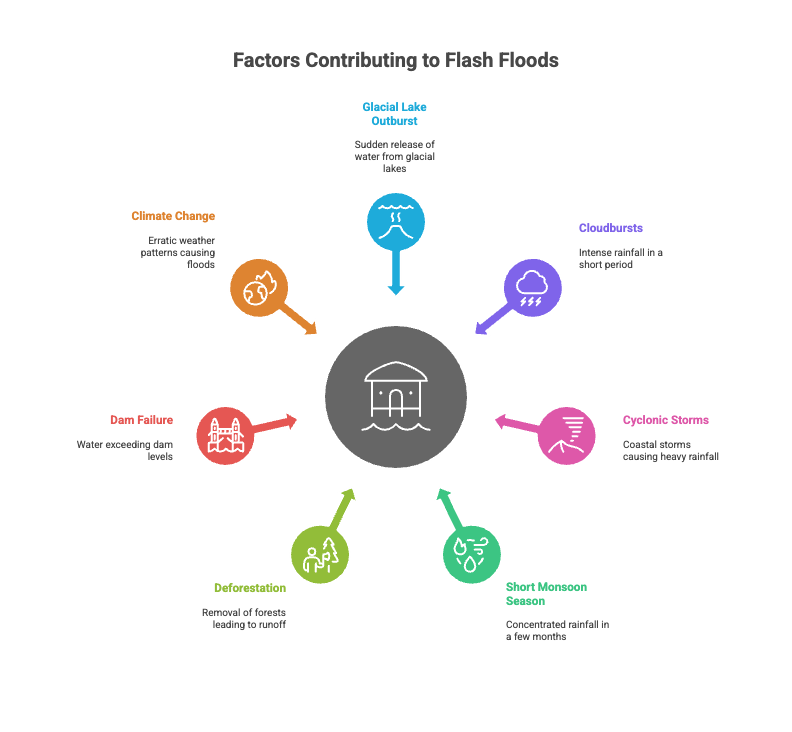
Impact of Flash Floods in India
- Human and Livelihood Impact: Flash floods lead to significant casualties due to their sudden onset.
- The 2023 flash floods in Himachal Pradesh claimed over 400 lives and displaced thousands.
- Damage to Public Utilities: Flash floods damage power lines, drinking water systems, and mobile networks, making post-disaster recovery slower and more expensive.
- Land Degradation: Torrential runoff erodes topsoil, degrades fertility, and increases sedimentation in rivers and reservoirs.
- Urban Challenges: Cities like Mumbai, Hyderabad, and Bengaluru experience rapid runoff due to concretised surfaces and encroached stormwater drains.
Initiatives taken by government
- Central Water Commission (CWC) is the nodal organisation entrusted with the task of flood forecasting & early flood warnings in the country.
- Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) in joint collaboration with the US National Weather Service, has developed a Flash Flood Guidance System (FFGS) for the South Asian region.
- The Central Government has approved the National Glacial Lake Outburst Flood Risk Mitigation Programme (NGRMP) in four Himalayan States viz. Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh with a total budget of Rs.150.00 crore.
Recommendations and Adaptation Strategies
- Flash Flood Forecasting: Integrate terrain, drainage, soil data, and real-time weather.
- Early Warning Systems: Develop region-specific models that consider soil moisture and topography.
- Promote community-level alerts in vulnerable districts.
- Land-Use and Urban Planning: Ban construction in high-risk zones (e.g., floodplains, steep slopes). Build climate-resilient infrastructure in elevated roads, permeable pavements, and stormwater drains.
- Disaster Preparedness: Update flood risk maps regularly and conduct mock drills in urban and rural areas.
- Climate Adaptation in Policy: Integrate climate models into national and state disaster management frameworks. Promote nature-based solutions like wetland conservation, afforestation, and catchment restoration.
Source: IE
Previous article
News In Short 31-07-2025
Next article
Supreme Court on Anti-Defection Law