Santhara
Syllabus: GS1/Culture
Context
- A three-year-old girl battling a brain tumour died after her parents initiated her into the Jain ritual of Santhara.
What is Santhara?
- Santhara—also known as Sallekhana or Samadhi Maran—is a solemn vow in Jainism, where one gradually gives up food and water to embrace death with spiritual detachment, believed to cleanse the soul of karma.
- Jain scriptures emphasize that this vow should only be undertaken when death is near, or in cases of extreme old age, incurable illness, or unavoidable hardship (like famine).
- For example, if someone’s worsening eyesight leads them to unknowingly harm living beings – violating the principle of ahimsa – they may choose Santhara.
- However, the recent death of a toddler has raised serious ethical and legal concerns. Child rights activists and medical professionals argue that a child cannot give informed consent for such a life-ending ritual, which is meant for spiritually aware adults.
Is Santhara Legal?
- The debate over Santhara in legal and religious circles intensified in 2015 when the Rajasthan High Court declared the practice a punishable offence under sections 306 (abetment to suicide) and 309 (attempt to suicide) of the Indian Penal Code.
- However, the Supreme Court later stayed the judgment following petitions by Jain religious bodies, upholding the community’s right to religious freedom.
Source: Mint
Mangar Bani
Syllabus: GS1/ Ancient History
In Context
- Archaeological research in Mangar has uncovered prehistoric tools and rock paintings dating back to the Lower Palaeolithic age (200,000–500,000 years ago).
About Mangar Bani
- Mangar Bani is a Paleolithic archaeological site and a sacred grove hill forest located in the Aravalli ranges along the Delhi-Haryana border.
- It lies within the only primary forest of the Delhi NCR region. Despite its forest-like features, Mangar Bani is not officially notified as a forest under the Forest (Conservation) Act.
- A primary forest is an ecologically mature ecosystem, naturally regenerated and minimally disturbed by human activity, comprising native tree species.
Source: HT
Rules for Obtaining Voter ID in India
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
Context
- Following the Pahalgam terror attack, several deported Pakistani nationals were found to possess Indian identity documents including Voter IDs.
Constitutional and Legal Framework
- Article 326 of the Constitution states that every Indian citizen aged 18 years or above has the right to vote in elections to the Lok Sabha and state/Union Territory Assemblies.
- Section 16 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950 disqualifies a person from being registered on an electoral roll if:
- They are not a citizen of India,
- Are of unsound mind, as declared by a competent court, or
- Are disqualified under any law relating to corrupt practices or offences in connection with elections.
Procedure for Voter Registration
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) mandates new voters to apply using Form 6.
- Applicants must submit:
- Self-attested proof of age and address (such as utility bills, passport, etc.)
- A declaration of Indian citizenship, which they must personally sign.
- Proof of citizenship (such as passport or birth certificate) is not strictly required unless the ERO suspects the applicant’s credentials.
- Electoral Registration Officers (EROs) and Booth Level Officers (BLOs) are responsible for verifying the applications. The process includes:
- Verification of documents,
- Hearings for claims and objections,
- Acceptance or rejection of the application.
- Section 31 of the RP Act, 1950 penalizes false declarations in voter applications.
Source: IE
OPEC and OPEC+
Syllabus: GS2/Important International Institutions
Context
- Oil prices plunge to multi-year low as OPEC+ plans to accelerate production hikes.
About OPEC
- The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is an intergovernmental organisation established in 1960 at the Baghdad Conference by Saudi Arabia, Iran, Venezuela, Kuwait and Iraq.
- Currently, it has 12 members, viz. Algeria, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and Venezuela.
- The objective of the organisation is to coordinate policies with respect to petroleum demand and supply to ensure fair and stable prices and ensure a steady income to oil producing countries.
- It is headquartered in Vienna, Austria, although Austria is not an OPEC member state.
OPEC+
- OPEC+ has 22 members, made up of 10 major oil producing countries (Russia, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, Brunei, Bahrain, Mexico, Oman, South Sudan, Sudan and Malaysia), along with the 12 OPEC members.
- The OPEC+ was formed in 2016 after the adoption of the ‘Algiers Accord’ by OPEC countries in September 2016 and signing of the ‘Vienna Agreement’ in November 2016 between OPEC and other major oil exporting countries.
- The move was largely a response to sharply falling oil prices caused by a surge in U.S. shale oil production.
Source: IE
NAMASTE (National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem) Scheme
Syllabus :GS 2/Social Justice
In News
- A NAMASTE scheme event was held in Budaun, Uttar Pradesh and sanitation workers were honored.
The NAMASTE (National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem) scheme
- It was launched in July 2023 by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment in collaboration with the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- It is a Central Sector Scheme.
- It aims to ensure the safety, dignity, and rehabilitation of sanitation workers.
- It focuses on eliminating hazardous manual cleaning of sewers and septic tanks by promoting mechanized, safe, and skilled sanitation practices.
- The components includes profiling of Sewer and Septic Tank Workers (SSWs); Health Insurance coverage under AB-PMJAY; Occupational safety training of SSWs; upfront Capital Subsidy for procurement of Sanitation related Vehicles/ Equipments; PPE kits to SSWs; safety devices to Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs) and IEC Campaign for awareness of safety and dignity of SSWs.
- In 2024, waste pickers were added under the scheme to support safe, dignified, and sustainable livelihoods
Source :PIB
Israel Cabinet Approves Plan for Gaza Conquest
Syllabus :GS2/IR
In News
- Israel’s security Cabinet approved an expansion of military operations in Gaza, including the potential conquest and occupation of the territory.
- The Israeli army has called up tens of thousands of reservists for the offensive.
The Gaza Strip
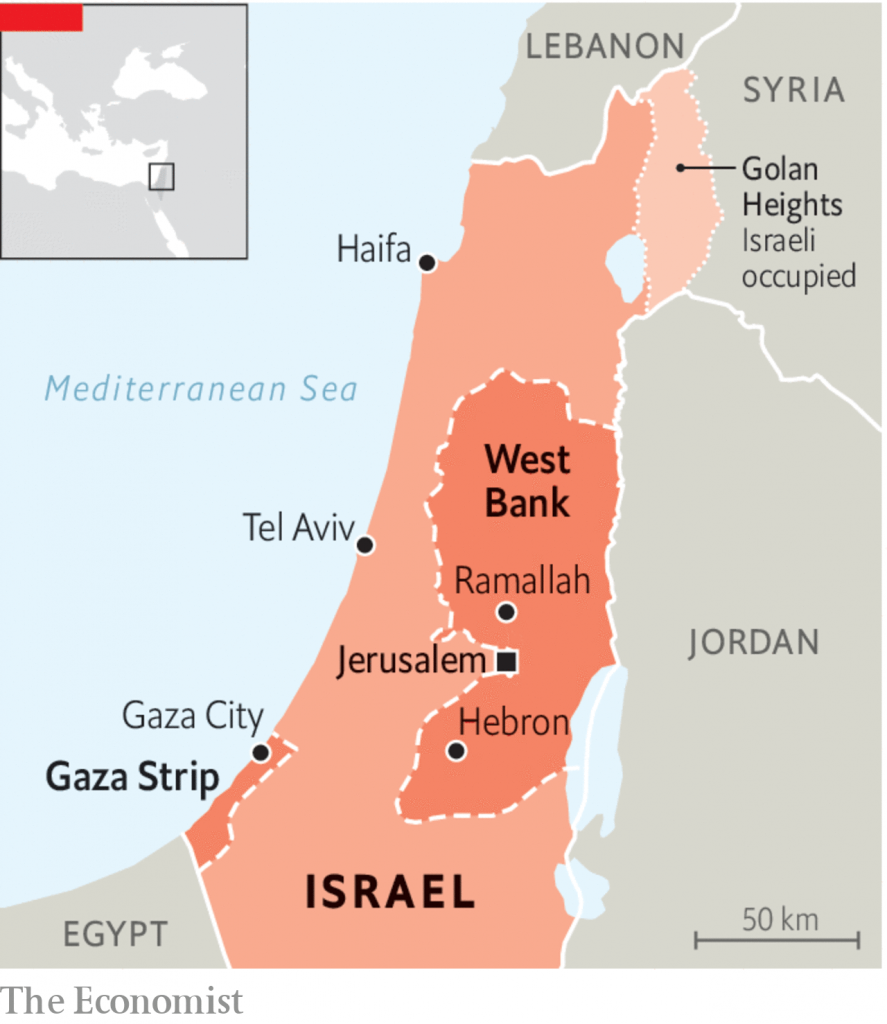
- It is a small piece of land in the Middle East
- It is located on the Mediterranean Sea between Israel and Egypt.
- The territory is 25 miles (40 kilometers) long and 4–5 miles (6–8 kilometers) wide.
- It is named for the ancient city of Gaza, which lies near the northeastern end of the strip.
- The area has been a source of conflict for many years.
Source :TH
Civil Defence Drills
Syllabus :GS2/Governance/GS 3/Internal Security
In News
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has directed states to conduct nationwide mock drills to strengthen civil defence preparedness in response to heightened tensions with Pakistan following a terrorist attack in Pahalgam
‘Civil Defence’ drills
- The drills are part of India’s passive defence strategy amid continued cross-border firing and rising geopolitical tensions.
- The drills will be carried out in 244 identified districts, including village-level operations.
- It will involve operationalising air-raid warning signs, crash blackout measures, camouflaging vital installations, evacuation plans, establishing hotline with the Indian Air Force and training civilians on the aspects of civil defence measures in the event of a “hostile attack.”
- States have been asked to activate control rooms, firefighting and warden services and undertake cleaning of bunkers and trenches among others.
- Bunkers are prevalent in border villages mostly in Jammu and Kashmir to shield civilians from cross-border firing.
- States have been asked to activate control rooms, firefighting and warden services and undertake cleaning of bunkers and trenches among others.
Civil Defence Framework in India
- The Civil Defence Act, 1968 was enacted in the aftermath of the 1962 India-China War and the 1965 India-Pakistan War.
- It provides for protective measures for people, property, and infrastructure against hostile attacks from air, land, or sea.
- The Act also authorises:
- Formation of Civil Defence Corps.
- Framing of rules and regulations for implementation.
- Civil Defence Corps consists of trained civilian volunteers, mobilised during war or disaster for relief and support.
- School, college students, National Cadet Corps (NCC), members from Nehru Yuva Kendra Sangathan (NYKS) will also be involved in the exercise.
Source :TH
Executive Director of IMF
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
In News
- Parameswaran Iyer, former Niti Aayog CEO and current World Bank director, takes interim charge as India’s executive director at the IMF after K V Subramanian’s early exit.
About IMF’s Executive Board
- The Executive Board of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) is the primary decision-making body responsible for conducting the day-to-day business of the IMF.
- The Executive Board is composed of 25 Executive Directors elected by individual member countries (with large quotas) or groups of countries (constituencies).
- A core function of the Board is to approve IMF financing to member countries facing temporary balance of payments problems, ensuring macroeconomic stability and preventing spillover crises.
Source: FE
Multi-Influence Ground Mine (MIGM)
Syllabus: GS3/ Defence
In News
- India recently achieved a major milestone by successfully test-firing the Multi Influence Ground Mine (MIGM).
About Multi Influence Ground Mine (MIGM)
- It is an advanced indigenously-developed underwater naval mine designed to detect and counter modern stealth ships and submarines, incorporating multi-influence sensing technology.
- It can track acoustic, magnetic, and pressure signatures, making it highly effective against a wide range of naval threats.
- Technologically, the MIGM features FRP (Fibre Reinforced Plastic) composites, advanced electronics, high-density power packs, and sophisticated software algorithms.
- The MIGM has been developed by the Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL), Visakhapatnam, with support from other DRDO labs.
Source: TH
Previous article
Hydrogen Versus Battery as Fuel Source
Next article
Human Development Report 2025: UNDP