Syllabus: GS3/ Energy
Context
- As the world moves towards sustainable transportation, Hydrogen Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) present an alternative to the battery electric vehicles (BEVs) currently dominating the market.
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
- BEVs are powered by electricity stored in rechargeable batteries.
- They require regular charging from external power sources, typically through the electric grid.
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
- FCEVs use hydrogen gas to generate electricity through a chemical process in fuel cells.
- They emit only water vapor as a byproduct, making them environmentally friendly.
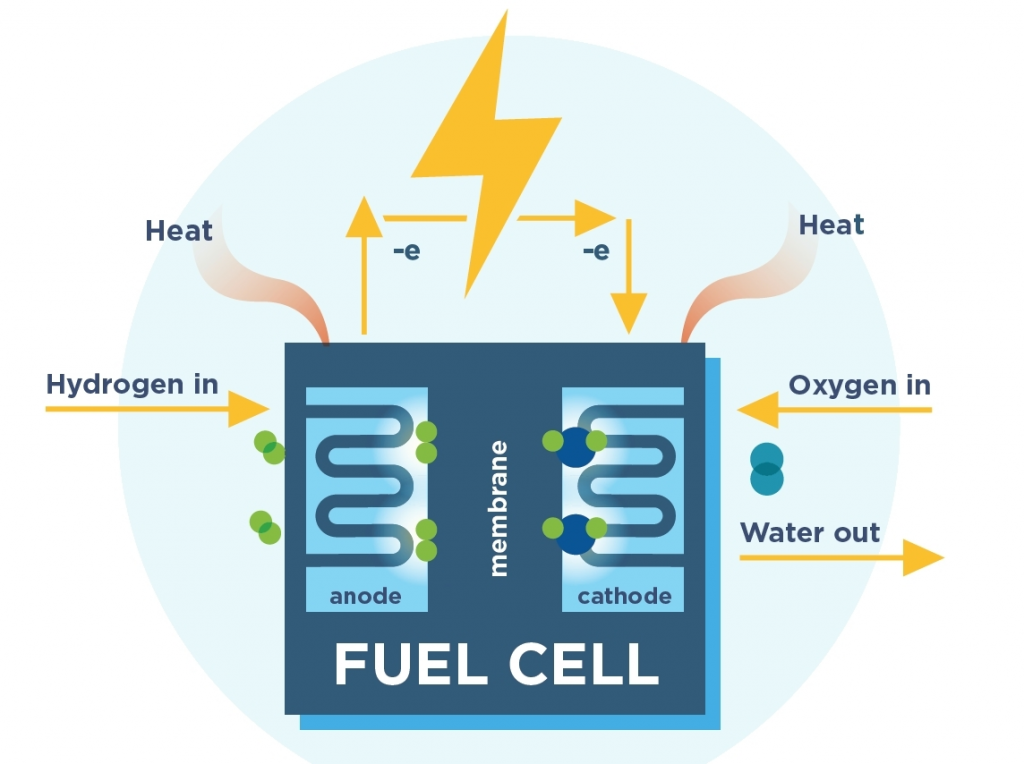
Hydrogen Versus Battery as Fuel Source
| Feature | Battery Electric Vehicles | Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles |
|---|---|---|
| Refuelling Time | Hours (depending on charger) | 5–15 minutes |
| Range | Moderate | Long |
| Weight | Heavier (due to batteries) | Lighter |
| Terrain Suitability | Limited for off-road | Suitable for rugged conditions |
| Cold Climate Suitability | Performance drops | Performs better |
India’s Electric Vehicle Landscape
- EVs accounted for 5% of total vehicle sales in 2023.
- Electric 3-Wheelers: India became the world’s largest market for electric three-wheelers in 2023, overtaking China.
- India contributes to 60% of global sales in this segment.
- Electric 2-Wheelers: India is the second-largest global market with 0.88 million units sold in 2023. China remains far ahead with 6 million units sold.
- India, China, and ASEAN nations lead in this domain; other regions make up less than 5% of the global two- and three-wheeler market.
Source: TH
Previous article
‘One Day One Genome’ Initiative to Harness the Microbial Potential
Next article
News In Short-6-05-2025