Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- The Committee constituted for the Framework on Repairability Index (RI) in Mobile and Electronic Sector has submitted its Report to the Department of Consumer Affairs (DoCA), Government of India.
Background
- India ranks as the third-largest producer of electronic waste globally, following China and the United States.
- The surge in electronic consumption, coupled with limited repair options, has contributed significantly to this issue.
- Between 2022 and 2025, consumer complaints related to mobile phones and tablets increased from 19,057 to 22,864, underscoring the need for improved repair accessibility and transparency in post-sale services.
- In September 2024, the DoCA established a committee under the chairmanship of Bharat Khera to develop a framework for the Repairability Index.
Key Recommendations of the Committee
- Self-Declared Repairability Scores: Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) should self-assess and declare the repairability of their products based on standardized criteria, minimizing additional compliance burdens.
- Display of RI: The Repairability Index should be prominently displayed at points of sale, on e-commerce platforms, and via QR codes on product packaging to enable consumers to make informed choices.
- Scoring Parameters: Repairability is assessed on six core parameters.
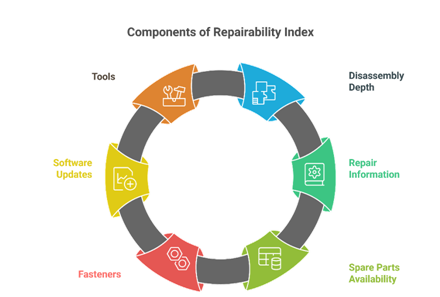
- Priority Components: The framework should focus on components prone to frequent failures and critical to device functionality, including batteries, display assemblies, microphones, and speakers.
- Stakeholder Engagement: The committee engaged with a wide array of stakeholders, including manufacturers, industry associations, consumer advocacy groups, and government representatives, to ensure a comprehensive and inclusive framework.
Significance of the Repairability Index
- Reduction in Electronic Waste: Enhancing repair options will extend product lifespans, thereby reducing the volume of e-waste generated.
- Circular Economy: The RI supports the principles of a circular economy by encouraging the reuse and repair of products, reducing the need for new resource extraction.
- Local Repair Industries: Improved access to repair information and parts will bolster local repair businesses, contributing to economic growth and job creation.
Global Scenario in Right to Repair
- United Kingdom: Right to Repair Regulations 2021, covers home appliances (e.g., fridges, washers, TVs).
- Manufacturers must supply spare parts for up to 10 years.
- France: Introduced a mandatory Repairability Index on five categories: smartphones, laptops, washing machines, TVs, and lawnmowers.
| Right to Repair Portal India – Launched in 2022, the Right to Repair Portal serves as a centralized platform providing consumers with information on repair services across four sectors: 1. Farming Equipment 2. Mobiles and Electronics 3. Consumer Durables 4. Automobile Equipment |
Challenges
- Technical Complexity: Modern electronic devices often feature compact and intricate designs, making repairs more challenging and necessitating specialized tools.
- Manufacturer Resistance: Some OEMs express concerns over intellectual property rights and the potential impact on product security and performance.
Concluding remarks
- The introduction of the Repairability Index in India’s mobile and electronics sector marks a significant step towards sustainable consumption and consumer empowerment.
- By promoting transparency and facilitating repairs, the initiative has the potential to reduce electronic waste, stimulate local economies, and align with global sustainability goals.
Source: PIB
Previous article
India–UK Free Trade Agreement (FTA) Negotiations