Syllabus: GS3/Inclusive Growth
Context
- Recently, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) released the Human Development Report (HDR) for 2025, highlighting India’s progress in life expectancy, education, and income levels.
- It is titled as ‘A Matter of Choice: People and Possibilities in the Age of AI’, and explores AI’s role in shaping future development.
| Human Development Index (HDI) – Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq created the HDI in 1990 and was further used by UNDP in creating a report on the nation’s socio-economic achievement. – It evaluates three key dimensions and is calculated using a geometric mean of these three indices: 1. Health is measured by life expectancy at birth (SDG-3). 2. Education is assessed through mean years of schooling for adults (SDG-4.4) and expected years of schooling for children (SDG-4.3). 3. Standard of Living is evaluated using Gross National Income (GNI) per capita (SDG-8.5), adjusted for income distribution. – Human Development Index (HDI): It categorizes countries into four development levels based on their HDI values: 1. Low Human Development: HDI value below 0.550 2. Medium Human Development: HDI value between 0.550 and 0.699 3. High Human Development: HDI value between 0.700 and 0.799 4. Very High Human Development: HDI value 0.800 and above Limitations and Complementary Indices – While HDI is a valuable tool, it does not capture inequality, poverty, human security, or empowerment. To address these gaps, UNDP provides additional indices, including: 1. Inequality-adjusted HDI (IHDI) 2. Gender Inequality Index (GII) 3. Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) |
Human Development Index: Current Status
- Iceland (HDI value of 0.972), ranked at the top of the Index, followed by Norway and Switzerland.
- South Sudan was at the bottom at 193 with 0.388.
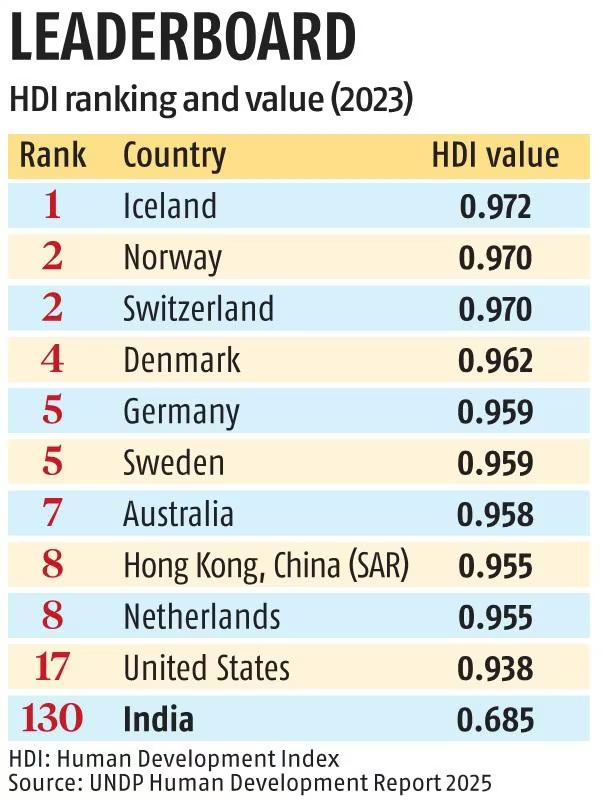
- India improved its HDI value from 0.676 in 2022 (133th) to 0.685 in 2023 (130th), remaining in the medium human development category.
- India’s HDI value has increased by over 53% since 1990, growing faster than both the global and South Asian averages.
- Among India’s neighbours, China (75th), Sri Lanka (78th) and Bhutan (127th) are ranked above India, while Bangladesh (130th) is ranked at par.
- Nepal (145th), Myanmar (149th), Pakistan (168th) are ranked below India.
Highlights of India’s HDI Progress
- Improved Life Expectancy: India’s life expectancy has risen from 58.6 years in 1990 to 72 years in 2023, marking its highest level since the index began.
- National health programs like Ayushman Bharat, Janani Suraksha Yojana, and Poshan Abhiyaan have contributed to this growth.
- Advancements in Education: The average years of schooling have increased from 8.2 years in 1990 to 13 years in 2023.
- Policies like the Right to Education Act, Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan, and National Education Policy 2020 have played a crucial role.
- Economic Growth and Poverty Reduction: India’s Gross National Income (GNI) per capita has risen over four times, from $2,167 in 1990 to $9,046 in 2023.
- 135 million Indians escaped multidimensional poverty between 2015-16 and 2019-21.
Key Challenges & Suggestions Made in Report
- AI and Human Development: HDR 2025 argues that AI should enhance human capabilities rather than replace them.
- It calls for bold policy decisions to ensure AI-driven growth benefits all communities.
- Widening Inequalities: Global inequalities are increasing, slowing human development progress, despite technological advancements.
- Income inequality reduces India’s HDI by 30.7%, one of the highest losses in the region.
- Gender disparities continue to affect education, employment, and healthcare access.
- The report urges inclusive AI policies to bridge the gap between developed and developing nations.
- Three Key Action Areas:
- Building a complementarity economy where humans and AI work together.
- Driving innovation to expand human capabilities.
- Investing in inclusive education, healthcare, and social protection systems.
Previous article
News In Short-6-05-2025
Next article
Supreme Court Publishes Assets of 21 Judges