Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- Recently, the US President has announced a 25% tariff on all imports from India, effective August 1, 2025, along with an unspecified penalty for India’s continued purchases of Russian oil and military equipment.
Why the US Imposed a 25% Tariff on Indian Imports?
- High Indian Tariffs on US Goods: India’s high tariffs on U.S. goods, which the US President called ‘among the highest in the world’. The US has about a $40.8 billion trade deficit with India.
- India’s Non-monetary Trade Barriers: The US accuses India of maintaining high tariffs and other non-tariff barriers, particularly citing India’s agricultural subsidies and sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) measures related to food safety.
- India’s Energy and Defense Ties with Russia: India’s status as Russia’s largest energy buyer (accounts for 35–40% of India’s total oil imports), and its long-standing defense ties with Moscow.
- The penalty component of the tariff is reportedly linked to these purchases, though its exact nature remains unspecified.
- India’s BRICS Membership: The US views BRICS, the emerging markets bloc which India is part of, as an anti-dollar coalition that challenges US economic leadership.
- Failed Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA) Negotiations: A mini-deal to avoid retaliatory tariffs was not finalized before the August 2025 deadline, despite ongoing talks since February 2025.
- It is seen as a pressure tactic to accelerate negotiations.
Key Implications of the 25% U.S. Tariff on Indian Imports
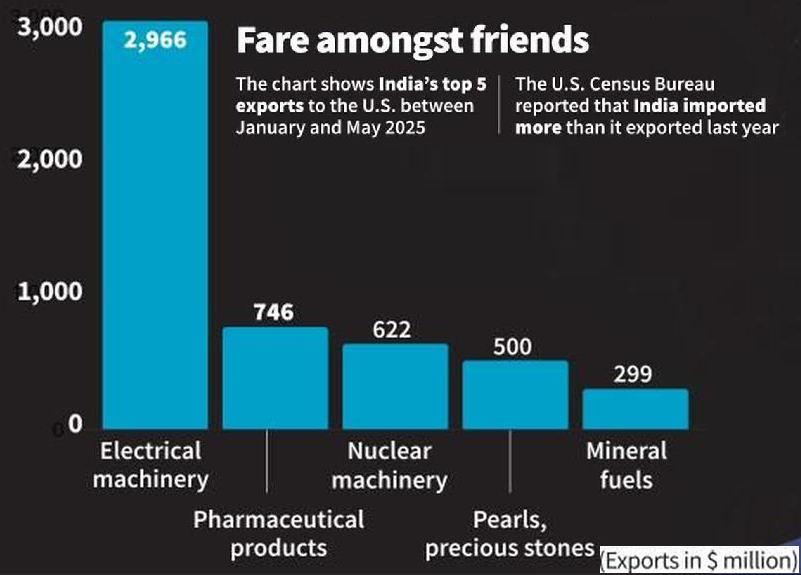
- Economic Impact on Indian Exports: The tariff affects $129 billion in annual bilateral trade, with India’s exports to the U.S. valued at $86.5 billion in FY25.
- Most Vulnerable Sectors:
- Pharmaceuticals: India is a major supplier of generic drugs to the U.S.
- Auto Parts & Engineering Goods: $2.2 billion worth of auto components exported in 2024 now face full tariffs.
- Textiles, Gems & Jewellery, Electronics, and Seafood: These export-heavy sectors may lose price competitiveness.
- Pressure on MSMEs and Labour-Intensive Industries: The tariff could disproportionately affect small manufacturers and exporters, especially in labour-intensive sectors like garments, leather, and handicrafts.
- Industry bodies like FICCI warn of immediate disruption to India’s export-intensive sectors.
- Geopolitical Undercurrents: The penalty component is linked to India’s energy and defense ties with Russia, making this tariff not just economic but geopolitical.
- India’s strategic autonomy in foreign policy — especially its stance on Russia — may face renewed scrutiny.
- Market Volatility and Investor Sentiment: Indian stock indices like Sensex and Nifty dropped sharply following the announcement.
- Analysts expect short-term volatility, especially in sectors dependent on U.S. demand.
India’s Response Strategy & Options
- Immediate Response: The Ministry of Commerce and Industry stated that it is ‘studying the implications’ of the tariff and remains committed to a fair and mutually beneficial trade agreement.
- India emphasized its priority to protect farmers, MSMEs, and entrepreneurs, signaling that domestic interests will not be compromised.
- Ongoing Trade Negotiations: India and the US have been negotiating a Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA) since February 2025.
- A US delegation is scheduled to visit India on August 25 for the sixth round of talks.
- India had finalized a pre-harvest deal, but it remained unsigned by the US before the August 1 deadline.
- Strategic Options Under Consideration:
- Market Diversification: Reduce dependence on U.S. markets by expanding exports to Europe, Southeast Asia, and Africa.
- Strengthen ties with countries that have already negotiated favorable tariff deals with the U.S., like Japan and the EU.
- Domestic Resilience: Boost Make in India initiatives to absorb external shocks.
- Provide support packages for affected sectors like pharmaceuticals, textiles, auto parts, and seafood.
- Market Diversification: Reduce dependence on U.S. markets by expanding exports to Europe, Southeast Asia, and Africa.
Previous article
Single-window System for Appointing State DGPs
Next article
Chile’s Coastal Erosion