Syllabus: GS3/ Space
In News
- The recent Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla journey to ISS marks India’s ascent as a major space power, aligning with the vision of Viksit Bharat 2047 and embracing the philosophy of Vishwabandhu Bharat in the space sector.
Dimensions of India’s Space Programme
- Scientific & Technological Dimension:
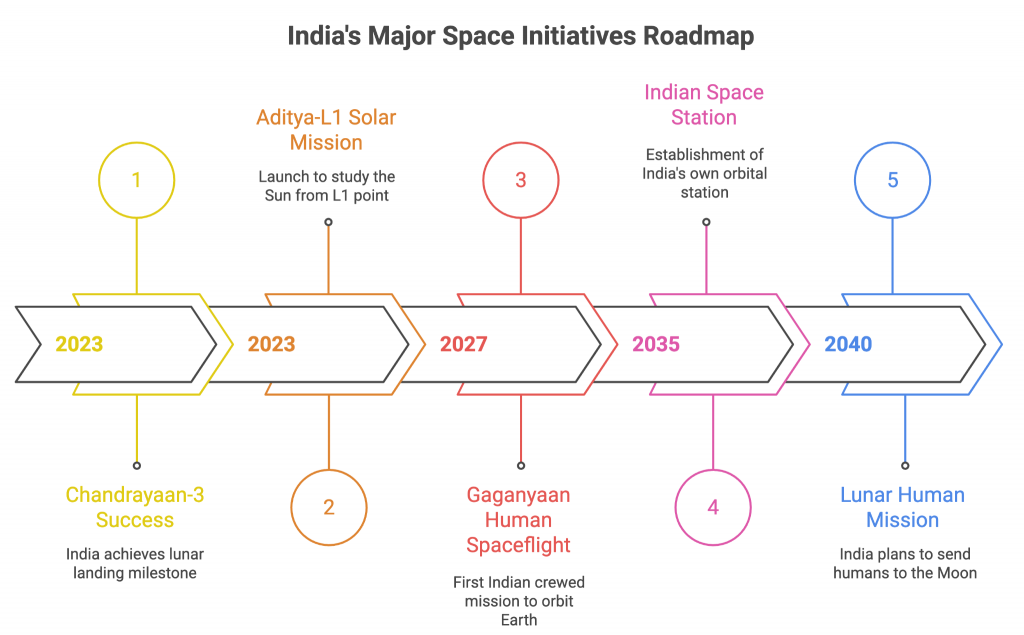
- Cost-effective innovation: India’s missions, such as Chandrayaan-3, succeeded in lunar landing at about 1/10th the cost of global peers; the ISS research mission was also completed at a fraction of international costs.
- Indigenous R&D: Development of launch vehicles (PSLV, GSLV Mk-III), navigation (NavIC), and cryogenic technology showcases India’s self-reliance.
- Economic Dimension:
- Space Economy: Currently worth ~$8 billion, India’s space sector is projected to reach $40 billion by 2040.
- Startup ecosystem: Home to over 300 startups like Skyroot Aerospace, Agnikul Cosmos, and Pixxel, supported by IN-SPACe and NSIL.
- Satellite services: Drive growth in broadband (OneWeb, Jio-Satellite), agriculture, logistics, and financial inclusion.
- Diplomatic & Global Dimension (Vishwabandhu Bharat):
- South-South cooperation: India provides satellites and launch services to African and Asian nations (e.g., GSAT-9 “South Asia Satellite”).
- International collaborations: Key projects with NASA (NISAR mission), Artemis Accords, and partnerships with France, Russia, SpaceX, and Axiom Space.
- Soft power: India is recognized as a responsible, affordable space launch provider fostering goodwill worldwide.
- Social & Developmental Dimension:
- Health & education: Telemedicine and tele-education programs connect rural India via INSAT satellites.
- Agriculture: Satellite-based yield forecasting, soil moisture mapping, and precision farming increase productivity.
- Disaster management: Real-time alerts and tracking (INSAT, RISAT) bolster climate resilience.
- Urban planning: Remote sensing and GIS underpin smart city development.
- Inclusivity: Spaces technology benefits extend beyond urban areas, supporting rural and marginalized communities.
- Security & Strategic Dimension:
- Indigenous navigation: NavIC ensures India is not reliant on foreign navigation systems.
- Military use: Development of military communication and surveillance satellites; dual-use technologies enhance security.
- ASAT Test (2019): Demonstration of anti-satellite capability established deterrence in space.
- Geopolitical leverage: Strategic autonomy enhanced vis-à-vis the US, China, and Russia.
Challenges
- Rising competition from private global giants (SpaceX, Blue Origin, etc.).
- Space debris and orbital congestion issues.
- Low R&D investment.
- Balancing commercialization with national security.
- Need for clear regulatory frameworks for startups and FDI.
Way Forward
- Increase R&D investment to meet global benchmarks.
- Facilitate private sector participation with simplified procedures.
- Enhance space diplomacy—especially with the Global South and major powers.
- Prioritize sustainability and responsible use of outer space.
Source: PIB
Previous article
The India-Africa-UAE Trilateral Framework
Next article
Public Accounts Committee on Toll Collection