
Syllabus: GS3/ S&T
In Context
- During World War I, shortages of animal fats and oils spurred chemists to find alternatives. This led to the development of synthetic cleaning agents: the first commercial “soap-like” detergents emerged in the mid-1930s.
What are Soaps & Detergents?
- Soaps: Naturally derived, made from fatty acids and alkali; work through surfactant action.
- Detergents: First widely made in the 1930s; synthetic surfactants; effective in hard water.
- Composition: Sodium (Na) or Potassium (K) salts of fatty acids (RCOONa or RCOOK).
- Raw Materials: Derived from vegetable oils (coconut, palm, olive) or animal fats.
Historical Background
- 2800 BC (Mesopotamia): Earliest recorded use of soap-like substances.
- Ancient India: Soap nuts, tree bark, leaves, and flowers were used as natural cleansers.
- Industrial Revolution: Mass production of soap began in Europe, though soaps remained luxury goods taxed heavily until the 19th century.
- World War I: Shortage of natural oils led to the birth of synthetic detergents, with commercial-scale detergent production beginning in the 1930s.
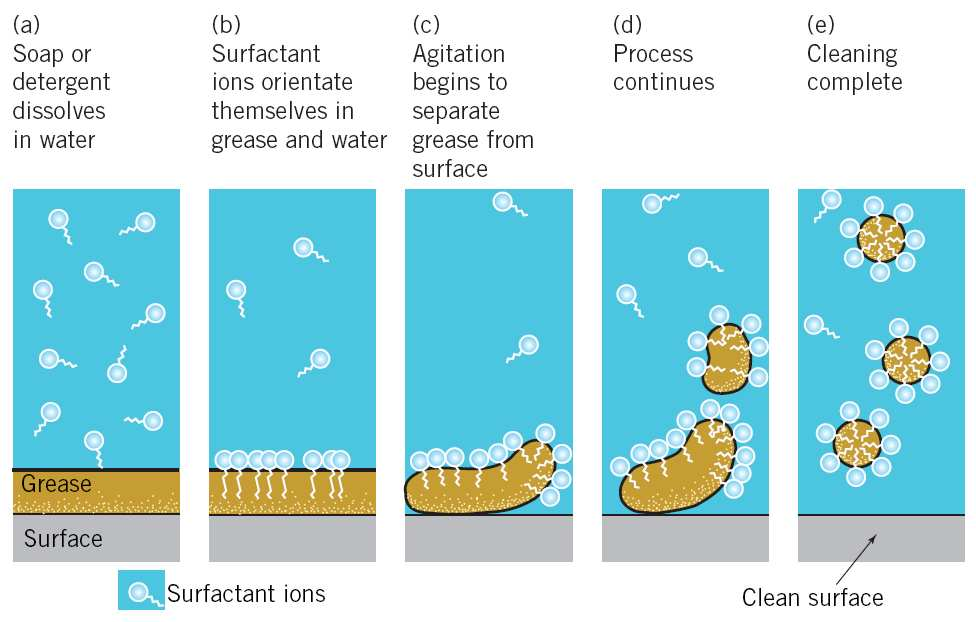
Working Mechanism of Soaps and Detergents
- Amphiphilic Nature:
- Hydrophilic (water-loving) end attracts water.
- Hydrophobic (water-repelling) end embeds into grease/dirt.
- Surfactants: Reduce water’s surface tension and dirt dislodges when scrubbing/rinsing.
- Detergents: Soap-like but formulated with stronger surfactants, bleach, and fragrances; more effective in hard water.
Economic and Social Dimension
- Industrial Significance: Large-scale global industry worth billions of dollars, employing millions.
- Public Health: Widespread use of soap linked to reduced infectious diseases, especially diarrhoea and skin ailments.
- Soap penetration in India is high (~98% households), reflecting its role in sanitation (Swachh Bharat Abhiyan).
Environmental Concerns
- Soaps are generally biodegradable (natural fatty acids) however, some surfactants (sulphonates) persist in the environment. Phosphates in detergents cause eutrophication (nutrient pollution, algal blooms).
Source: TH
Previous article
Radioactive Contamination in Punjab’s Groundwater