
Syllabus: GS2/ Health, GS3/ Environment
Context
- The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Water Resources raised concern over the continued presence of uranium contamination in drinking water sources in Punjab and called for urgent solutions to safeguard public health.
What is Uranium Contamination?
- Uranium contamination refers to the presence of excessive levels of uranium in the environment, primarily in water and soil, exceeding safe limits.
- Safe Limits Prescribed:
- World Health Organization (WHO): Uranium safe limit: 0.03 mg/L.
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS): Also follows 0.03 mg/L as permissible limit.
- Health Impacts: Uranium contamination poses risks due to both its radioactivity and chemical toxicity.
- Ingestion of contaminated water or food can lead to Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), skeletal damage, cancers, reproductive health issues.
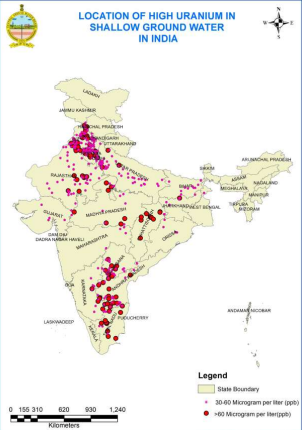
Uranium Contamination in India
- According to the Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) survey of 2019–20, out of nearly 16,000 groundwater samples, around 450 exceeded the World Health Organization’s (WHO) permissible limit.
- Uranium contamination is reported to be more prevalent in northwest India’s alluvial aquifers and in southern India’s hard-rock aquifers.
- The states of Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat were found to be the most affected.
Sources of Contamination
- Natural Sources: Uranium is a naturally occurring radioactive element found in the Earth’s crust.
- Geogenic processes, such as the weathering of uranium-bearing rocks and the movement of groundwater, can release uranium into water sources.
- Anthropogenic Sources:
- Groundwater depletion: Lowers the water table and alters aquifer chemistry, leading to uranium release.
- Industrial Processes: Some industrial processes, like those involving phosphate fertilizers and nuclear facilities, can also release uranium.
- Mining and Milling: Uranium mining and processing can release uranium into the surrounding environment.
Government Measures
- The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) have developed hybrid membrane techniques and Reverse Osmosis (RO) plants, which have been installed in affected areas of Punjab and Haryana on a pilot basis.
- Under the National Aquifer Mapping and Management Programme (NAQUIM), CGWB is generating scientific data to understand aquifer behavior and provide site-specific solutions to mitigate contamination risks.
- The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) has been engaged in developing low-cost adsorbents and nanomaterials to filter uranium from groundwater.
- India has collaborated with the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) for capacity building and technical expertise in monitoring uranium levels in drinking water and strengthening laboratory infrastructure.
Judicial Intervention
- In 2015, the Punjab and Haryana High Court took notice of uranium contamination in the region’s groundwater and directed the state governments to take remedial steps.
- In Subhash Kumar v. State of Bihar and Others (1991), the Supreme Court of India ruled that the right to life under Article 21 of the Constitution includes the right to pollution-free water and air.
Way Ahead
- The government should formally recognize uranium as a major groundwater contaminant, similar to arsenic and fluoride, so that dedicated funding and interventions can be streamlined.
- Public awareness campaigns must be conducted to educate rural communities about health risks of uranium contamination and safe water usage practices.
- Low-cost, decentralized treatment technologies such as adsorption filters, ion-exchange systems, and community-level RO plants should be deployed widely in affected villages.
Source: TOI
Previous article
Off Budget Borrowings
Next article
Soaps and Detergents