Kokborok
Syllabus: GS1/Culture
Context
- Kokborok day is celebrated by the Indigenous Tripuri people of the state of Tripura on 19th January each year.
About
- Significance: It commemorates the rich cultural heritage, history, and linguistic contributions of the Kokborok language, which is the mother tongue of the Tripuri people.
- It was first recognised as an official state language of Tripura in 1979.
- Other official languages of Tripura are Bengali and English.
- Tripura has rolled out a language mapping drive to boost Kokborok in schools.
Source: TH
Kuka Movement
Syllabus: GS1/ History
In Context
- The Kuka Movement, also known as the Namdhari Movement, emerged in the 19th century as a Sikh religious and socio-political reform movement.
About
- Origin: Namdhari sect was founded by Satguru Ram Singh on April 12, 1857, at Bhaini Sahib. He was the secular chief of Namdhari Sect.
- Followers were called “Kukas” due to their high-pitched recitation of Gurbani, referred to as “Kook” in Punjabi.
- Leadership: Led by Satguru Ram Singh, supported by Kuka Hira Singh and Lehna Singh.
- Core Objectives: Advocated for spiritual reform and social justice.
- Opposed British rule and promoted self-reliance through the boycott of British goods and institutions.
- Protested cow slaughter, reflecting their religious and cultural values.
Kuka Movement’s Escalation
- Clash with Authorities: On January 15, 1872, the Kukas attacked the Malaudh Fort in Ludhiana district, confronting British officials. Later, Britisher executed Kukas.
- Exile of Leaders: Satguru Ram Singh and other Kuka leaders were exiled to Rangoon (present-day Myanmar), where they remained until their deaths.
Post-Movement Contributions
- Publications: The Kukas launched ‘Satyug’ in 1920 and the daily ‘Kuka’ in 1922 to spread their ideology.
- Support for Non-Cooperation Movement: The Kukas aligned with Mahatma Gandhi’s Non-Cooperation Movement, contributing to the broader freedom struggle.
Significance
- Early Resistance: The Kuka Movement was among the first organized revolts against British rule in Punjab.
- Combination of social and freedom goals: Inspired self-reliance, civil disobedience, and social reform.
Source: TH
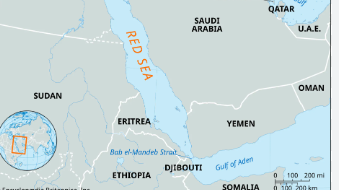
Gulf of Aden and Red Sea
Syllabus: GS1/ Geography
Context
- Rising threats in the Gulf of Aden, Red Sea, and East African waters have led the Indian Navy to enhance its presence and ensure secure sea routes.
Gulf of Aden
- It is a deepwater gulf located between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula and Somalia in the Horn of Africa.
- It connects the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea through the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
Red Sea
- It is a narrow, elongated sea separating the Arabian Peninsula from Africa.
- It extends from the Suez Canal in the north to the Bab el-Mandeb Strait in the south.
- Bordering countries: Djibouti, Egypt, Eritrea, Saudi Arabia, Sudan and Yemen.
Strategic Importance
- Global Trade Route: Together, they form a critical maritime route connecting the Indian Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea via the Suez Canal.
- Energy Supply Chain: Major pathway for oil and liquefied natural gas (LNG) shipments, with nearly 10% of global oil trade passing through the Bab el-Mandeb.
- Chokepoint Vulnerability: Bab el-Mandeb is a strategic chokepoint, and any disruption could impact global trade and energy security.
Source: TH
Bharathapuzha River
Syllabus: GS1/ Geography
Context
- In a tragic incident, members of a family drowned in the Bharathapuzha river at Cheruthuruthy.
About
- The Bharathapuzha River, also known as the Nila River or Ponnani River, is the second longest river in Kerala after Periyar.
- Length: 209 km (Approx).
- Origin: Anamalai Hills, Tamil Nadu.
- Tributaries: Gayathripuzha, Kannadipuzha, Kalpathipuzha, Thuthapuzha.
- Drainage Area: Covers parts of Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- Significance: Houses several ancient temples along its banks, including the Thiruvilwamala Temple.
- Known for the Kerala Kalamandalam, a center for traditional arts located on its banks.
Source: DH
Zombie Deer Disease (CWD)
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Tech
In News
- A recent study has concluded that humans are not at significant risk of contracting the deadly Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD), often referred to as Zombie Deer Disease.
Zombie Deer Disease (CWD)
- It is also known as Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD).
- It is a deadly, neurological illness that affects deer, elk, moose, reindeer, and muntjac.
- It may also affect some other members of the Cervidae family.
- Human Infection Risk: CWD is caused by prions, infectious proteins, and there are concerns about the disease potentially jumping to humans, particularly through the consumption of infected meat.
- However, no confirmed human cases have been reported.
- Transmission : CWD prions spread through body fluids such as saliva, blood, urine, and feces, either by direct contact or environmental contamination.
- Once present, prions remain infectious for years in soil, water, and plants.
- Impact : Infected animals may appear healthy for months or years, during which they can spread the disease. As the disease progresses, animals become debilitated and die.
- The speed of progression varies by species and the animal’s genetics.
Source: ET
National Sports Awards
Syllabus: Miscellaneous
In News
- The President of India recently presented the National Sports Awards 2024, honoring exceptional contributions to sports and adventure in India.
Award Categories
- Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award:
- India’s highest sporting honor, established in 1991-92.
- Recognizes outstanding performance over a period of four years.
- Named After: Major Dhyan Chand (1905–79), an iconic hockey legend who led India to three consecutive Olympic gold medals (1928, 1932, and 1936).
- 2024 Awardees:
- Gukesh D (Chess)
- Harmanpreet Singh (Hockey)
- Praveen Kumar (Para-Athletics)
- Manu Bhaker (Shooting)
- Arjuna Award:
- Established in 1961 for consistent performance over the past four years.
- Named After: Arjuna, the legendary warrior from the Indian epic Mahabharata.
- First Recipient: P.K. Banerjee (Football).
- Dronacharya Award:
- Instituted in 1985, this is India’s highest honor for coaches.
- Awarded for producing medal winners at prestigious international events.
- Named After: Dronacharya, the guru of Arjuna in Mahabharata.
- First Female Recipient: Renu Kohli (Athletics).
- Major Dhyan Chand Award for Lifetime Achievement:
- Instituted in 2002 for lifetime contributions to sports.
- First Recipients:
- Shahuraj Birajdar (Boxing)
- Ashok Diwan (Hockey).
- Maulana Abul Kalam Azad (MAKA) Trophy:
- The oldest National Sports Award, instituted in 1956–57.
- Named in honor of Shri Abul Kalam Azad, India’s first Education Minister and a freedom fighter.
- First Recipient: Bombay University.
- Rashtriya Khel Protsahan Puraskar:
- Instituted in 2009, awarded to organizations, corporates, and individuals for significant contributions to sports promotion and development over the past three years.
- Tenzing Norgay National Adventure Award:
- Introduced in 2004 to honor achievements in adventure sports.
- Recognizes contributions across land, water, air, and lifetime adventure categories.
Source: PIB
Previous article
Third launchpad at Satish Dhawan Space Center
Next article
Contract Farming