Syllabus: GS2/Governance
Context
- The Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) has approved 56 new Watershed Development Projects across 10 high-performing states, with a budget of Rs. 700 crore.
Watershed Development Component of PMKSY (WDC-PMKSY)
- The Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP) was launched in 2009-10.
- IWMP was later merged with Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) in 2015-16 as WDC-PMKSY.
- The Government continued WDC-PMKSY as ‘WDC-PMKSY 2.0‘ from 2021-26 with a physical target of 49.50 lakh hectares and a financial outlay of Rs. 8,134 crore.
- WDC-PMKSY 2.0 will be implemented in Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Assam, Nagaland, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Sikkim.
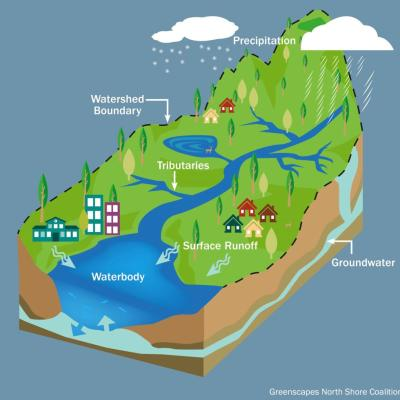
What is Watershed?
- A watershed is an area of land that channels rainfall, snowmelt, and runoff into a common body of water.
- Watershed development refers to the management and conservation of water resources within a defined watershed, to improve water availability, enhance soil fertility, and promote sustainable land use.
Significance of Watershed Development
- Improved Water Availability: By focusing on enhancing groundwater recharge through rainwater harvesting, as well as increasing the capacity for surface water storage in ponds, check dams, and other structures, the project helps improve water availability.
- The World Bank watershed management projects in Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Karnataka have been successful in arid zones, rain-fed lowlands, and higher elevation sites.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Watershed development helps in curbing soil erosion and improving soil fertility, which are vital for maintaining healthy agricultural ecosystems.
- Economic Upliftment: It creates opportunities for livelihood generation through activities like afforestation, fisheries, water harvesting, and agro-based industries.
- Resilience to Climate Variability: Climate change has made rainfall patterns increasingly erratic, leading to unpredictable droughts and floods. Watershed development plays a critical role in building resilience to such climate-induced challenges.
Way Ahead
- Better Integration of Technology: The use of modern technologies such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Remote Sensing (RS), and drones for mapping watersheds enhance the efficiency and impact of watershed management.
- Collaboration Between Stakeholders: Effective coordination among central and state governments, local bodies, NGOs, and farmers is crucial for the successful implementation of watershed development projects.
- Public-private partnerships, where corporations, research institutions, and local governments collaborate, could further enhance the scope and impact of watershed development initiatives.
Source: PIB
Previous article
National Broadband Mission 2.0
Next article
Discovery of Semi-Dirac Fermion