Syllabus: GS1/ Geography, GS3/ Science and technology
Context
- Recent studies indicate that Earth’s magnetic field is weakening and shifting, raising concerns over possible magnetic excursions or even a full-scale polarity reversal.
Earth’s magnetic field
- It is generated by the complex flow of molten metallic material in the outer core of the planet.
- The flow of this material is affected both by the rotation of Earth and the presence of a solid iron core, which results in a dipolar magnetic field where the axis roughly aligns with the rotational axis of the planet.
Cause of magnetic field reversal
- Short-term variations (milliseconds to days) are caused by solar activity and interaction with charged particles in space.
- Long-term changes, such as reversals and excursions, result from turbulent flows in the outer core, driven by heat released from the inner core and modulated by planetary rotation.
- A reversal happens when the flow of molten material in the core changes direction—for instance, from clockwise to anticlockwise—altering the magnetic field’s orientation.
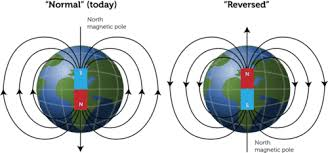
Magnetic Reversals and Excursions
- Magnetic reversal is a phenomenon where the magnetic north and south poles swap places. It occurred 183 times in the past 83 million years.
- The last major reversal was the Brunhes-Matuyama reversal, about 780,000 years ago.
- It can take thousands of years to complete, estimated at 22,000 years.
- Magnetic excursions are temporary and incomplete shifts in the magnetic field direction. It occurs 10 times more frequently than full reversals. Theexamples are as:
- Norwegian-Greenland Sea event (64,500 years ago),
- Laschamps and Mono Lake (34,500 years ago),
- Bagwalipokar excursions ( Uttarakhand): researchers found evidence of two excursions—15,500–14,700 years ago and 8,000–2,850 years ago.
Concerns Arising from Field Instability
- Atmospheric Vulnerability: During weak-field phases, Earth’s atmosphere is more exposed to harmful solar wind and cosmic rays.
- Technological Impacts: It could disrupt power grids, satellite operations, and communication systems.
- Biological Impact: Many animals, such as birds, sea turtles, and whales, rely on Earth’s magnetic field for navigation. A flip or fluctuation could disrupt migratory patterns and breeding cycles.
Concluding Remarks
- Though Earth’s magnetic field has reversed and fluctuated many times in geological history, the precise timing and triggers of such events remain uncertain.
- However, as human society grows increasingly dependent on electromagnetic infrastructure, understanding and predicting the behavior of the magnetic field becomes vital.
Source: DTE
Previous article
News In Short-10-05-2025
Next article
Total Fertility Rate Remains Constant at 2.0 in 2021