Syllabus :GS 3/Environment
In News
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) released Global Methane Tracker 2025.
The IEA’s Global Methane Tracker
- It is a vital tool for reducing methane emissions in the energy sector.
- It offers updated estimates of emissions using the latest satellite and ground-based data, alongside information on the costs and opportunities for reduction.
- The 2025 update will include new features such as country-level data on historical emissions, projections for 2030 and 2035, an interactive tool for exploring global methane initiatives, and estimates for emissions from abandoned fossil fuel facilities.
- Additionally, it provides an open-access model for exploring methane reduction options in oil and gas operations.
Key Points
- Methane is a greenhouse gas responsible for around 30 per cent of the rise in global temperatures since the Industrial Revolution.
- Its levels in the atmosphere are growing faster than other greenhouse gases, with its concentration being two-and-a-half times higher than the preindustrial era.
- The three main sources of methane include agriculture, energy and waste sectors.
- The energy sector — including oil, natural gas, coal and bioenergy — accounts for more than 35 per cent of methane emissions from human activity.
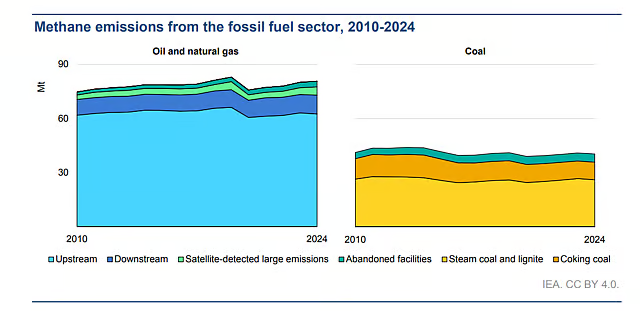
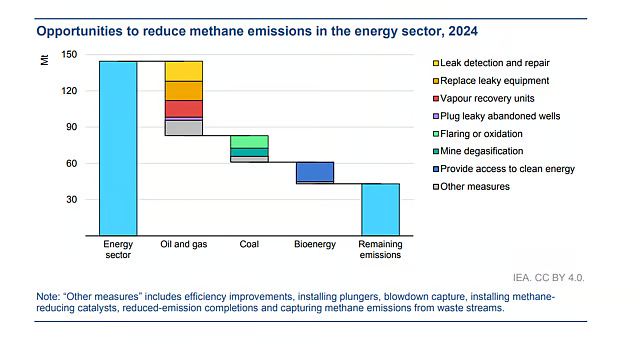
- The energy sector emitted about 145 million tonnes (Mt) of methane in 2024, with oil and gas facilities contributing over 80 Mt.
- The energy sector — including oil, natural gas, coal and bioenergy — accounts for more than 35 per cent of methane emissions from human activity.
- Top methane-emitting countries from fossil fuels include: China, the United States, Russia, Iran, Turkmenistan, India, Venezuela, and Indonesia.
Challenges
- The IEA also points out a major underreporting issue—actual methane emissions are 80% higher than reported to the UN.
- Only about 30 countries included methane reduction in their climate action plans (NDCs) for 2024, and just nine had measurable targets.
- A new round of NDCs is due in 2025, with a few nations like Brazil, Canada, UAE, and the UK already incorporating methane measures.
- Few countries and companies have shown verified reductions since initiatives like the Global Methane Pledge (GMP) and the Oil and Gas Decarbonization Charter began.
- Key emitters like China, India, and Russia, responsible for 45% of methane emissions, have not joined GMP.
Suggestions
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights key actions to reduce methane emissions, including sealing abandoned coal mines, plugging and monitoring closed wells, and capturing methane for energy or flaring when recovery isn’t viable.
- Bioenergy emissions can be reduced by promoting clean cooking, modern heating, and careful handling of biogas and biomethane to prevent leaks.
- The report reiterated that with current technologies, around 70 per cent of methane emissions from the fossil sector can be reduced.
- For oil and gas sectors specifically, around 75 per cent of emissions can be reduced through well-known measures like upgrading leaky and high-emitting equipment or plugging leaky wells.
Source :DTE
Previous article
National Technological Day
Next article
News In Short-12-05-2025