Syllabus: GS2/Governance
Context
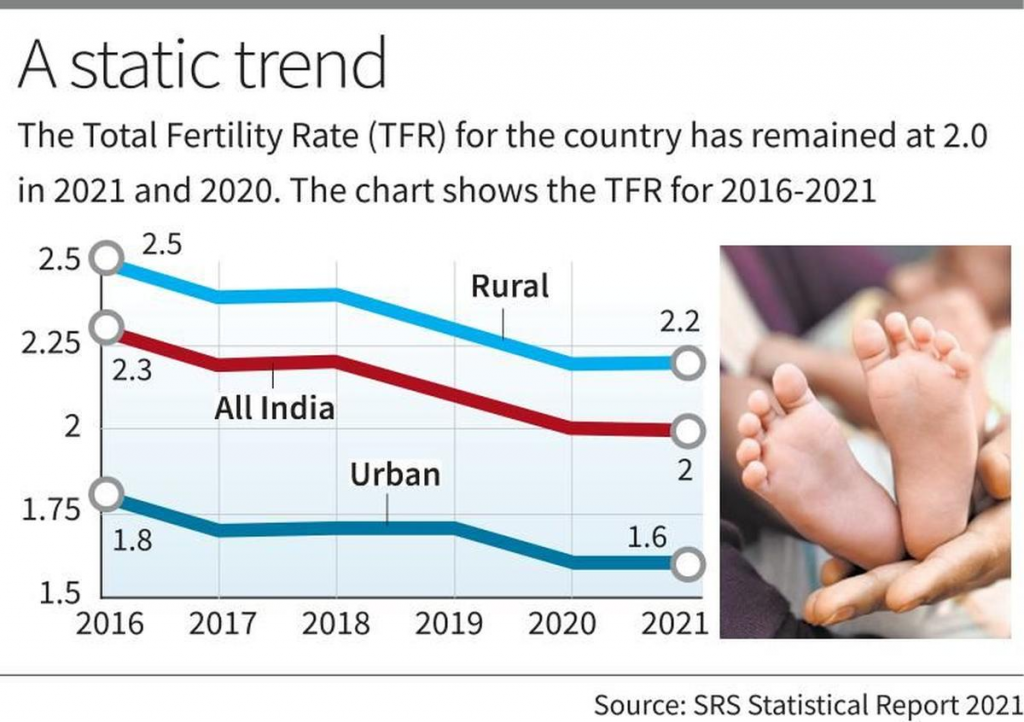
- The Sample Registration System (SRS) Statistical Report 2021, released by the Registrar General of India (RGI), highlights that India’s Total Fertility Rate (TFR) has remained constant at 2.0 in 2021, the same as in 2020.
- The survey was conducted in 8,842 sample units across all States, covering about 84 lakh sample population.
Sample Registration System (SRS)
- The Sample Registration System (SRS) is a large-scale demographic survey in India used to collect data on births and deaths, providing annual estimates of vital rates like birth rate, death rate, and infant mortality rate.
- Key features of SRS:
- Dual Record System: The system uses two sources of information: continuous enumeration by part-time enumerators and six-monthly retrospective surveys by supervisors.
- Sample-Based: SRS operates on a sample of villages and urban blocks, making it cost-effective and efficient.
| Total Fertility Rate (TFR) – The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years. – A TFR of 2.1 is considered the replacement level needed to maintain a stable population. |
Key findings of the report
- Bihar has reported the highest TFR at 3.0, while Delhi and West Bengal reported the lowest TFR of 1.4.
- Demographic Shifts (1971–2021):
- 0–14 age group: Declined from 41.2% to 24.8%, indicating a falling young population.
- 15–59 age group (working age): Increased from 53.4% to 66.2%, representing a demographic dividend window.
- The elderly population has gone up from 5.3% to 5.9% for the 65+ age group and 6% to 9% for the 60+ age group during the same period. Kerala reported the highest elderly population at 14.4%.
- The mean age at effective marriage for females has increased from 19.3 years in 1990 to 22.5 years in 2021.
Significance of the Findings
- Population Stabilization: A TFR of 2.0 indicates India is approaching population stabilization, which can ease pressure on natural resources, public services, and the environment.
- Demographic Dividend: A larger working-age population provides an opportunity for increased productivity, and economic growth.
- Improved Maternal health: Fewer childbirths per woman, coupled with delayed age of marriage, lead to reduced maternal mortality, better child care, and healthier families.
- Women Empowerment: Lower fertility rates reflect higher education levels, workforce participation, and greater autonomy among women, leading to better social and economic outcomes.
Negative Impacts of Declining TFR
- Ageing Population: A rise in the elderly population will increase the dependency on the working population, demanding increased focus on pension, healthcare, and social welfare systems.
- Potential for Skewed Sex Ratios: In certain areas, fertility reduction without tackling gender bias can exacerbate sex-selective practices, leading to imbalanced sex ratios.
- Demographic Imbalance: States with vast fertility differences, potentially leading to interstate migration, cultural shifts, and resource strain in low-TFR states.
Concluding Remarks
- The stabilization of India’s Total Fertility Rate reflects a significant demographic shift, signaling that the country is moving closer to achieving replacement-level fertility. However, the associated challenges must not be overlooked.
- A balanced approach that promotes equitable development, strengthens social security, and anticipates future demographic needs is essential to ensure that this transition supports a resilient and prosperous India.
Source: TH
Previous article
Magnetic Flip-Flop
Next article
IMF Loan to Pakistan