
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
In News
- A Parliamentary panel has called on the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) to create a dedicated oversight body for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) issues.
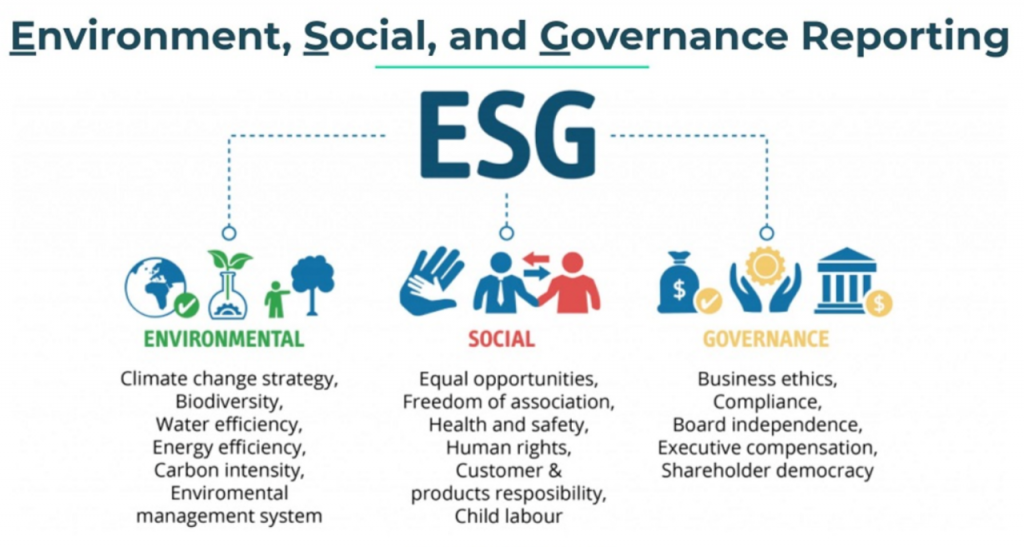
What is Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG)?
- It is a framework used to evaluate a company’s performance on non-financial factors. It has become a key consideration for investors, consumers, and other stakeholders who are concerned about a business’s impact on society and the environment.
Key Recommendations of the Parliamentary Panel
- Establishment of a Dedicated ESG Oversight Body: The panel urged the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) to create a specialized oversight authority for ESG. This body should have forensic expertise to proactively detect, investigate, and deter greenwashing, and develop sector-specific ESG guidelines.
- Strengthening Legal Mandate: The panel argued that current provisions under the Companies Act, 2013 (notably Section 166(2)) are too general and lack the robust framework necessary to ensure accurate and substantive ESG disclosures and actions.
- Developing MSME Support: The proposed oversight authority should offer targeted assistance and guidance to Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) for ESG compliance, addressing their unique capacity constraints.
Other Initiatives Related to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG)
- Companies Act, 2013: Mandates certain companies to spend at least 2% of their average net profits on CSR activities.
- Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR): SEBI has introduced BRSR for the top 1,000 listed companies, requiring disclosure of ESG parameters.
- International Alignment: India’s policy direction is evolving in response to global ESG trends, aiming for convergence with global best practices such as those from the EU and International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB).
Source: PIB
Previous article
15th Indian Organ Donation Day Ceremony