
Indian space missions, led by ISRO, testify to the progress of the nation in space exploration and technology. Initiating satellite launches for communication and remote sensing, and later stepping into lunar and interplanetary missions like Chandrayaan and Mangalyaan, it has truly distinguished itself as the global leader in cost-effective and innovative space exploration.
About India’s Space Missions
- The strategy of our Space programme is thus self-sufficiency, indigenisation, building exclusive satellites, and our own GSLVs, etc.
- A Space Vision 2025 was unveiled at the Indian Science Congress – 2003 at Bangalore. The vision document spells out the measures to bring the space programme onto a higher plane, the accent being on self-reliance in launch capabilities and therefore alienation from foreign agencies for the same.
- Of course, self-sufficiency has been attained in the fabrication of satellites. The mission to the moon is also a part of the vision.
- With its constant efforts by the ISRO, India has been able to achieve huge accomplishments in space exploration and technological advancements.
- Starting with the launch of Aryabhata in 1975, ISRO has developed satellite programs for communication, weather monitoring, and navigation.
- Key missions are Chandrayaan (Lunar Exploration), Mangalyaan (Mars Orbiter Mission), and recently, with a great triumph, Chandrayaan-3 soft-landed on the south pole of the Moon. Gaganyaan is ISRO’s effort towards human spaceflight.
- Known for cost-effective missions, India contributes significantly to global space research, commercial satellite launches, and collaborative scientific projects.
India’s Early Satellites
Aryabhata
- On April 19, 1975, India entered the space age by launching their first-ever satellite, the Aryabhata. Built by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to gain experience in building and operating a satellite in space, it was actually launched by the Soviet Union. Aryabhata was built to conduct experiments in X-ray astronomy, aeronomics, and solar physics.
- Bhaskara -1
Bhaskara-1
- The First Experimental Remote Sensing Satellite built in India. The onboard TV camera imageries were used in the field of Hydrology and Forestry. Rich scientific data sent by Satellite Microwave Radiometer (SAMIR) was used for oceanographic studies.
Rohini
- Rohini Satellite RS-1 was a 35 kg experimental spin stabilized satellite designed with a power handling capability of 16W. It was successfully launched onboard SLV-3 from Sriharikota Range (SHAR) Centre on July 18, 1980.
Ariane Passenger Payload Experiment (APPLE)
- The Ariane Passenger Payload Experiment (APPLE) was ISRO’s first indigenous, experimental communication satellite. It was launched into GTO (Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit) by the third development flight of ESA’s Ariane vehicle from Kourou on June 19, 1981.
Communication and Educational Satellites
INSAT System
- The Indian National Satellite (INSAT) system is one of the largest domestic communication satellite systems in the Asia-Pacific region with nine operational communication satellites placed in Geo-stationary orbit.
Here are some applications of INSAT satellites:
| EDUSAT | launched by Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV-F01) in September 2004, is India’s first thematic satellite dedicated exclusively for educational services. |
| INSAT | INSAT is being used to provide Educational TV(ETV) service for primary school children in Tamil, Marathi, Oriya, Telugu and Hindi. INSAT provides a facility of tele-medicine which aims at providing Tele-medicine Technology & connectivity between remote/rural hospital and Super Speciality Hospital for Tele-consultation, Treatment & Training of doctors & paramedics. INSAT has been a major catalyst for the expansion of television coverage in India, presently 40 Doordarshan TV channels including news uplinks are operating through C-band transponders of INSAT-3A, INSAT-4B, INSAT-3C and INSAT-2E. |
Kalpana-1
- METSAT (renamed as Kalpana-1 on February 5, 2003 after the Indian born American Astronaut Dr. Kalpana Chawla, who died on February 1, 2003 in the US Space Shuttle Columbia disaster) is the first in the series of exclusive meteorological satellites built by ISRO.
CMS-01
- CMS-01 is a communication satellite envisaged for providing services in Extended-C Band of the frequency spectrum. The Extended-C Band coverage will include Indian mainland, Andaman-Nicobar & Lakshadweep Islands. CMS-01 is the 42nd Communication Satellite of India. Its mission life is 7 years and it was launched by PSLV-C50.
EDUSAT
- GSAT-3, known as EDUSAT is meant for distant classroom education from school level to higher education. This was the first dedicated “Educational Satellite” that provide the country with satellite based two way communication to class room for delivering educational materials. This is a Geo-synchronous satellite developed on I-2K bus. GSAT-3 was co-located with METSAT (KALPANA-1) and INSAT-3C.
GRAMSAT Scheme
- Under “Gramsat Scheme”, ISRO’s contribution is to provide the necessary satellite bandwidth to respective State Governments. Generally, these programmes cover areas such as mass education, tribal culture, anganwadi workers’ training, fisheries, forest and environment.
Gyan Darshan
- It is an educational channel which carries programmes on IGNOU’s courses, general awareness programmes, and interactive sessions with subject experts and scholars besides promoting nationalism, harmony and peace.ce.
GSAT 31
- India’s telecommunication satellite, GSAT-31 was successfully launched in 2019 from Kourou launch base, French Guiana by Ariane-5 VA-247. GSAT-31 will provide continuity to operational services on some of the in-orbit satellites.
Earth Observation Satellites
- ISRO’s Earth Observation Satellites (EOS) support applications in agriculture, urban planning, water management, forestry, disaster management, and oceanography. The program began with IRS-1A in 1988 and includes satellites in Sun-synchronous (e.g., RESOURCESAT, CARTOSAT, RISAT, OCEANSAT) and Geostationary orbits (e.g., INSAT-3D, Kalpana).
- The CARTOSAT series provides imagery for cartographic and urban planning needs, while RESOURCESAT-2A monitors resources, crops, and water bodies. SARAL, a joint Indo-French mission, supports oceanographic research. EOS-01 aids agriculture and disaster management, and EOS-04, launched in 2022, provides radar imaging under all weather conditions for hydrology, forestry, and flood mapping.
Navigation Satellite Systems
- India’s navigation satellite systems, led by ISRO, provide accurate geospatial positioning and timing services.
NavIC
- NavIC is India’s indigenous system that offers Standard Positioning Service (SPS) for general use and Restricted Service (RS) for authorized users, each with an accuracy of better than 20 meters.
- NavIC’s constellation consists of eight active satellites in both geostationary and geosynchronous orbits that aid navigation-related applications, emergency management, vehicle tracking, and capture of geodetic data.
- GAGAN is a satellite navigation augmentation for civil aviation that ensures precise guidance and fuel-efficient air traffic management. It is the world’s first Satellite-Based Augmentation System (SBAS) to be incorporated in the equatorial region that provides uninterrupted navigation from Africa to Australia.
- The GEMINI device, developed using GAGAN, offers ocean state forecasting and disaster warning to fishermen upto 300 nm offshore, fostering their safety and productivity. GAGAN further aids location-based services and operational safety in railway, shipping, scientific research, and tourism sectors.
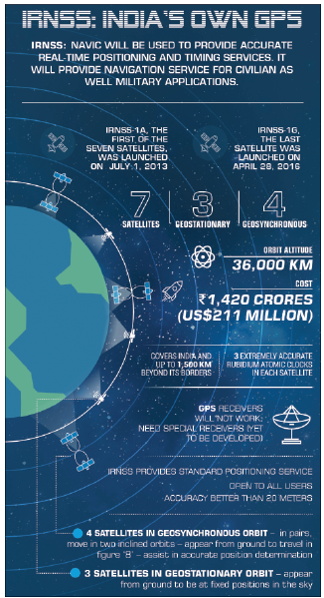
Read our detailed article on Navic
Positioning Satellite Systems of Foreign Countries
- The Global Positioning System, or GPS, is a satellite-based navigation system from the United States that provides uninterrupted PNT (Positioning, Navigation, and Timing) services worldwide, including for military and civilian users.
- Galileo is a European project for free services that are more accurate at providing performance metrics, especially at higher latitudes.
- China’s independent navigation system gives worldwide PNT services with positional accuracy between 2.6 and 3.6 meters and some telecommunication features, such as text messaging.
- GLONASS, Russia’s version of GPS, functions better at northern latitudes; it was initially intended for military purposes but has now been open for civil use.
- Thus these systems are used worldwide for various activities requiring accurate navigation, from military to commercial to civilian uses.
Satellites for Military Purposes by ISRO
- India has around 15 military satellites supporting defense operations. Key ones include GSAT-7 (Rukmini), launched in 2013 for naval communication, covering the Indian Ocean Region. GSAT-7A, launched in 2018, enhances Air Force capabilities, and GSAT-7R will replace Rukmini for naval use.
- EMISAT, developed by ISRO-DRDO, is India’s first ELINT satellite, aiding electronic surveillance and tracking hostile radars.
- Microsat-R, launched in 2019, provided imaging services and served as a target for the Mission Shakti anti-satellite test, showcasing India’s space defense capability.
India’s Recent Space Missions
- India’s recent space missions have given evidence to ISRO’s growing capabilities.
- Chandrayaan-3 soft-landed successfully on the south pole of the Moon in 2023.
- The Aditya-L1 mission was launched to study the Sun in 2023 itself.
- And then came Gaganyaan, the first crewed space mission of India, soon to be launched to mark the milestone in human spaceflight.
- EOS-04, launched in 2022, provides enhanced radar imaging for agriculture and disaster management. Commercial missions such as PSLV-C57, in which satellites were deployed for clients worldwide, were also conducted by ISRO, which firmly put India on the map of space research and exploration.
Way Forward
- With ISRO in pursuit of ambitious goals, India’s space missions are just about to witness exciting developments. The Gaganyaan mission will mark India’s entry into human spaceflight, thus setting in motion the future crewed exploration. The stages for Chandrayaan-4 are arranged for more lunar studies, with interplanetary missions of sorts envisioned with Mangalyaan-2 to Mars and Shukrayaan to Venus.
- ISRO also keenly wishes to build its satellite constellations for Earth observation, navigation, and communication. Collaborations with private players through Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) will foment innovation. India’s focus for space-related work remains sustainability, scientific discovery, global partnerships, and development of technologies for space exploration and commercialization.
Conclusion
Space missions of India stand for technology advancement in the country and aspirations for space exploration. From lunar and interplanetary missions to Earth observation and navigation systems, ISRO has made giant strides in cost-effective innovations. With the advent of Gaganyaan and associated missions, there can be several more developments that should place India in the serious considerations of global players in space research and commercial satellite services.
FAQs: India’s Space Programs
What is the primary focus of the ISRO astronaut mission?
Gaganyaan intended to demonstrate India’s capability in carrying humans into space by putting them into low Earth orbit, develop crucial technologies, enable scientific experiments, and lay the foundation for further crewed missions in the interest of scientific and technological development of the country.
What is the most expensive space mission of India?
Being ISRO’s costliest mission, Gaganyaan concentrates on human spaceflight technologies of higher complexity so that astronauts can train, the environment can be sustained, and the vehicle can be recovered after re-entry. In addition, it intends to place astronauts in low Earth orbit and bring them back safely; it will cost and be more big than previous flights. This is the first step in an autonomous human spaceflight program of India.
How many space missions has India done?
Since its inception in 1969, India has carried out over 100 space missions under ISRO. They include satellite launches, interplanetary missions of Chandrayaan and Mangalyaan, and ongoing projects of a more advanced nature, such as Aditya-L1 and Gaganyaan.
What is the latest space mission of India?
Aditya-L1 is a comprehensive solar observatory mission aimed at multi-messenger solar astronomy, advancing scientific understanding and space weather prediction through cutting-edge instruments and innovative technologies onboard.
Who is the father of the Indian space programme?
The father of the Indian space programme is Dr. Vikram Sarabhai. He is widely recognized as the visionary leader who laid the foundation for India’s space endeavors and established the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in 1969. Dr. Sarabhai’s vision and efforts were instrumental in initiating India’s journey in space technology and exploration.
Also Read: Achievements of India’s Space Programs
GS - 3




