In-vitro fertilization is an assisted reproductive technology in which eggs are fertilized by sperm in a laboratory and embryos are then transferred into the uterus. It is necessary for various reasons of infertility and probably resulted in the millions of births since its inception in the late 1970s, working to improve access and success rates in reproductive healthcare.
What is In-Vitro Fertilization?
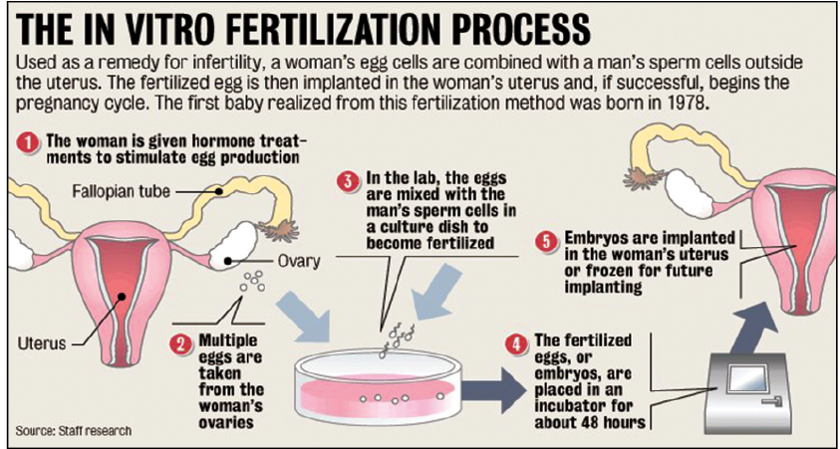
- It is an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART), commonly referred to as IVF. IVF is the process of fertilization by extracting eggs, retrieving a sperm sample, and then manually combining an egg and sperm in a laboratory dish. The embryo(s) is then transferred to the uterus.
Application of IVF
The domains in which In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) finds its application are varied in response to different reproductive challenges. The main applications include the following.
- Treatment of Infertility:
- IVF is mainly used to treat couples who are infertile due to factors such as blocked tubes, endometriosis, ovulatory disorders, or unexplained infertility.
- Advanced Maternal Age:
- In the case of women over 35, their fertility is on the decline. IVF comes to their aid to improve conception chances.
- Genetic Testing:
- Embryos-scope Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) may be carried out to eliminate embryos carrying genetic disorders for safer pregnancies.
- Same-Sex Couples or Single Parents:
- IVF treatment provides treatment options for same-sex couples and single women who wish to conceive through donor eggs or sperm.
- Donor Egg/Sperm IVF:
- IVF offers use of donor eggs or sperm in cases where an individual is infertile or has a genetic problem.
- Fertility Preservation:
- Egg or embryo freezing may be done with IVF to enable individuals to preserve their fertility before commencing medical treatments (such as chemotherapy).
- Repeated Pregnancy Loss:
- IVF may offer assistance to couples who undergo recurrent miscarriage by way of genetic testing of embryos before transfer.
- Surrogacy:
- IVF is used in surrogacy operations where embryos generated from the gametes of the intended parents are then implanted in a surrogate mother.
- Research and Development:
- IVF techniques help develop new reproductive technologies, genetics, and fertility treatments.
- Education and Awareness:
- Infertility and treatments have come into light due to IVF, and this has led to continuous discussion on reproductive health.
These applications highlight IVF’s role in addressing diverse reproductive challenges and its impact on modern reproductive healthcare.
Steps Involved in In-Vitro Fertilization
- Fertility medications are prescribed to stimulate egg production. Multiple eggs are desired because some eggs will not develop or fertilize after retrieval. A transvaginal ultrasound is used to examine the ovaries, and blood test samples are taken to check hormone levels.
- Eggs are retrieved through a minor surgical procedure that uses ultrasound imaging to guide a hollow needle through the pelvic cavity to remove the eggs. Medication is provided to reduce and remove potential discomfort.
- The male is asked to produce a sample of sperm, which is prepared for combining with the eggs.
- In a process called insemination, the sperm and eggs are mixed together and stored in a laboratory dish to encourage fertilization. In some cases where there is a lower probability of fertilization, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be used. Through this procedure, a single sperm is injected directly into the egg in an attempt to achieve fertilization. The eggs are monitored to confirm that fertilization and cell division are taking place. Once this occurs, the fertilized eggs are considered embryos.
- The embryos are usually transferred into the woman’s uterus three to five days following egg retrieval and fertilization. A catheter or small tube is inserted into the uterus to transfer the embryos. This procedure is painless for most women, although some may experience mild cramping. If the procedure is successful, implantation typically occurs around six to ten days following egg retrieval.
Side Effects of IVF
- Passing a small amount of fluid (may be clear or blood-tinged) after the procedure.
- Mild cramping and Mild bloating can also occur in some cases.
- Constipation and Breast tenderness are also witnessed in some cases.
- The chance of a multiple pregnancy is increased with the use of fertility treatment. There are additional risks and concerns related to multiples during pregnancy including the increased risk of premature delivery and low birth weight.
- Assisted reproductive technology (ART) involves a significant physical, financial, and emotional commitment on the part of a couple. Psychological stress and emotional problems are common, especially if in vitro fertilization (IVF) is unsuccessful.
Latest Developments in In-Vitro Fertilization
- Improved Embryo Selection:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms represent one of the possibilities increasingly used to analyze embryo images and assist embryologists with selecting the most viable embryos for transfer.
- Time-Lapse Imaging: With time-lapse imaging, embryos may be monitored in a continuous manner, having embryo selection based on development patterns enhanced.
- Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT):
- With further advancements in PGT, embryos can be better screened for the likelihood of genetic disorders, thereby increasing chances of healthy pregnancies.
- Embryo Freezing and Storage:
- Improved cryopreservation techniques allow for better survival of frozen embryos, granting patients additional flexibility in choosing when to undertake pregnancy.
- Mitochondrial Replacement Therapy (MRT):
- This revolutionary technique aims to prevent mitochondrial diseases by substituting the defective mitochondria in an egg with healthy ones from a donor, hence giving women with mitochondrial disorders a chance of having healthy children.
- Optimized Ovarian Stimulation Protocols:
- New protocols and medications have been developed to improve ovarian response and reduce side effects while truly assuring better oocyte retrieval results.
- Non-Invasive Testing:
- Further studies on approaches to embryo health and viability, including the analysis of spent culture media, are being considered to avoid possible risks of invasive procedures.
- 3D Printing:
- Research on 3D printing for the creation of artificial ovaries and other reproductive structures continues to remain on track to supply those with better fertility interventions.
- Wider Access and Insurance Coverage:
- Expanding acceptance of infertility as a medical condition leads to wider access to IVF, with more insurance plans covering fertility treatment.
- Regenerative Medicine Approaches:
- Exploring the use of stem cells and regenerative medicine to enhance ovarian function and egg quality continues, presenting the possibilities for new avenues for women confronting age-related fertility decline.
- Public Awareness and Support:
- Rising consciousness of fertility issues and activism have provided a solid supporting system for individuals and couples attempting IVF, thus creating a better environment for emotional and psychological support.d
Such developments voice the ongoing status given to IVF to improve success and experience of people and couples barred to infertility.
Way Forward
Reproductive medical technology will always enjoy a high profile, simple because we are on the new frontier of medical science. But we must be sure that the practice is conducted under a system of licensing and regulation.
Conclusion
- One of the technological transformations of infertility management has given hope to millions. Such technology can finely control fertilization but also viable embryos for transfer. With the improvement in preimplantation genetic testing and embryo selection via AI, IVF success rates are getting higher, thus presenting benefits to different populations with genetic issues and advanced maternal age that receive help from IVF.
- But, IVF does have an emotional and financial downside to consider (on ethical grounds, too). Efforts are being made to make IVF and related procedures more affordable and easier to access. With this, we can say IVF is here to stay in the arena of reproductive health. Hence, IVF will hopefully end up being a solution for many hopeful parents out there.





