
Biotechnology is an interdisciplinary field that leverages the functionalities of cells and molecules to foster the advancement of health-related matters. Humans have been using microorganisms for food production and preservation for a long time. Today, biotechnology spans the large-scale manufacture of biopharmaceuticals and biological products, including the use of genetically engineered microorganisms, fungi, plants, and animals, all aimed at solving health-related issues. This article intends to shed light on the overview of Biotechnology, its Branches, and Benefits.
What is Biotechnology?
- This is a technology inspired by biology—it utilizes cellular and biomolecular functions to create technologies and products that enhance our quality of life and promote the health of our planet.
- We have microorganisms in use for centuries as they have a role in food production, such as with bread and cheese, which also serves to preserve dairy.
- It also pertains to the industrial-scale manufacturing of biopharmaceuticals and biologics through the use of genetically engineered microorganisms, fungi, plants, and animals.
Branches of Biotechnology
There are some important branches that are given below:
Blue Biotechnology
- Blue biotechnology relates to the study and use of marine and other aquatic life forms. Its functions include protecting marine life from dangerous underwater diseases, augmenting the seafood supply, and uncovering new active compounds.
Green Biotechnology
- It has been defined as the use of biological methods on plants to enhance the nutritional value, quantity, and yield.
- The most advanced use of biotechnology in this field is genetic modification (GM), which is also known as genetic engineering, gene technology, genetic manipulation, and recombinant DNA technology.
- In scientific literature and especially in regulatory documents, the term “Genetically Modified Organisms” (GMO) is used to collectively describe plants, animals, and microorganisms modified through genetic engineering.
- The Green Revolution in India was successful in increasing the food supply threefold. Increased yields have partly been due to the use of improved crop varieties and mainly due to better management practices and the use of agrochemicals.
- Plants, bacteria, fungi, and animals whose genes have been altered by manipulation. GM plants have been useful in many ways. Genetic modification has:
- Made crops more tolerant to abiotic stresses (cold, drought, salt, heat),
- Reduced reliance on chemical pesticides (pest-resistant crops);
- Helped to reduce post-harvest losses;
- Increased efficiency of mineral usage by plants (this prevents early exhaustion of fertility of soil);
- Enhanced nutritional value of food, e.g., Vitamin ‘A’ enriched rice.
White Biotechnology
- White biotechnology is the application of microorganisms or enzymes in the manufacturing of products that are biodegradable, require less energy, and generate less waste than products derived from traditional chemical processes.
- For many years, white biotechnology has been used in industrial applications to produce food nutrients, washing powders, and other products.
- The recent advancements in genomics, molecular genetics, metabolic engineering, and catalysis have, alongside the enhanced environmental concerns, energy security worries, heightened energy costs, and other related external factors, increased the importance of white biotechnology.
Red Biotechnology
- Also known as medical biotechnology, red biotechnology focuses on the application of biological techniques to develop and improve healthcare and medicine.
- The developments in this and related scientific areas have completely changed modern medicine.
- We now have advanced and simpler diagnostic methods to detect diseases, genetic and proteomic technologies to enable the prevention of diseases, and the opportunity of gene therapy to treat diseases that were once incurable.
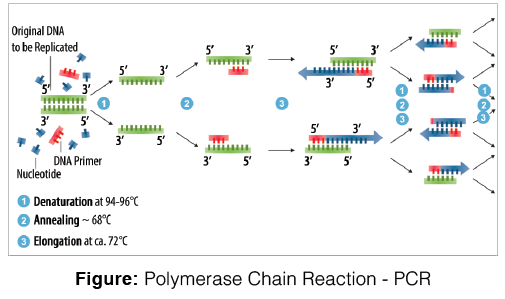
- It has been most productive in diagnostics. Recombinant DNA technology, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), and enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) are some of the techniques that serve the purpose of early diagnosis. Apart from this, producing upgraded and better pharmaceuticals is also a significant application.
Advantages of Biotechnology
- Enhanced Healthcare:
- New vaccines, medicines, and gene therapies are flowering on the horizon.
- Business is genetic testing, which allows us to diagnose problems early and treat them effectively.
- Advances in Agriculture:
- GM crops that yield more and resist pests.
- Crops that resist drought and are nutritious, designed to fight hunger.
- Protecting the Environment:
- Using bio-remediation to remove contaminants in the soil and water.
- Making biofuels that are kind to the planet in order to lower carbon emissions.
- Applications in Industry:
- Food and textile industries to transform and add value, using their enzymes to streamline their chemical operations.
- Creating biodegradable plastics which help to alleviate plastic waste..
- Geographical Economic Development:
- The advent of new sectors and employment in the field of biotechnology.
- Innovations in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and even energy give these industries a strong push.
Conclusion
Biotechnology takes biology and tech and blends them together to craft solutions for the most challenging issues out there. Through healthcare, agriculture, environmental science, and even industrial applications, biotechnology provides treatment for diseases, enhances the sustainability of food supply, offers eco-friendly technologies, and streamlines industrial processes. With continual advancements in genetic engineering and bio-manufacturing, biotechnology stands to offer solutions for climate change, food shortages, medical care, and healthcare for future generations, as well as guiding sustainable development for the world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who is the father of biotechnology?
Károly Ereky (1878-1952) is regarded as the “father of biotechnology” for introducing the term in 1919.
Who is the Indian father of biotechnology?
Professor V. L. Chopra is recognized as the father of biotechnology in India and played a key role in enhancing wheat production in the country.
What are the achievements of India in the biotechnology sector?
1. Market authorization was granted in July 2022 to CERVAVAC—the first quadrivalent Human Papilloma Virus (qHPV) vaccine developed in India—directly targeting cervical cancer, with the support of DBT and BIRAC.
2. The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation has approved the first gene therapy clinical trial for Hemophilia A in India.
3. Under the Genome India project, which spans the entire country, participant enrollment has reached 14,529, and phenotyping as well as blood biochemistry has been evaluated.
4. Indian TB Genomic Consortium: Funded by MoS&T and MoH&FW, and managed by DBT, this project aims to conduct Whole Genome Sequencing of 32,500 TB strains and use AI techniques to predict drug resistance, strain lineage, and more. This project supports the ‘TB Mukt Bharat’ initiative of the Government of India. There is even more.





