
Syllabus: GS2/International Relations
Context
- As Israel’s military campaign in Gaza intensifies, a growing divide has emerged within the Western world over how to respond – a rift that could reshape global diplomacy, humanitarian policy, and the future of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Overview of the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict

- Historical Background: The Zionist movement (Late 19th Century) emerged in Europe, advocating for a Jewish homeland in Palestine – then part of the Ottoman Empire.
- Jewish immigration increased, especially after World War I.
- British Mandate (1920–1948): Britain took control of Palestine and supported the creation of a Jewish national home through the Balfour Declaration (1917), sparking tensions with the Arab majority.
- UN Partition Plan (1947): UN proposed dividing Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab states.
- Jews accepted the plan; Arabs rejected it.
- Arab-Israeli War (1948): Following Israel’s declaration of independence, neighboring Arab states invaded.
- Over 700,000 Palestinians were displaced – an event known as the Nakba (‘Catastrophe’).
- Six-Day War (1967): Israel captured the West Bank, Gaza Strip, East Jerusalem, and other territories, intensifying the occupation and settlement issues that persist today.
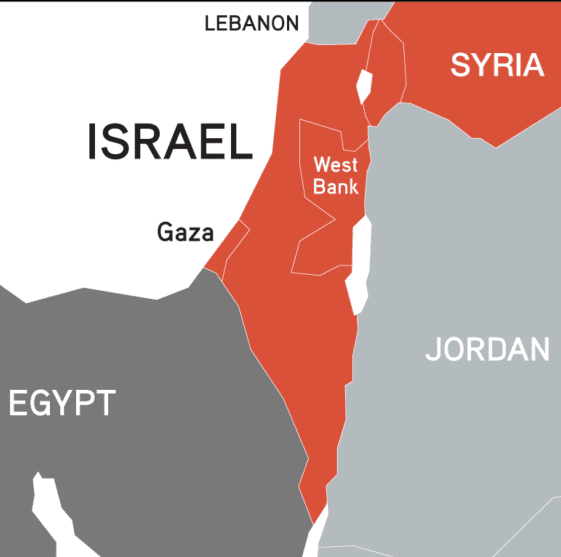
Root Causes of the Conflict
- Territorial Claims: Both Israelis and Palestinians claim historical and religious ties to the same land.
- Displacement and Refugees: The 1948 and 1967 wars led to mass displacement of Palestinians, many of whom still live in refugee camps.
- Jerusalem: A city sacred to Jews, Muslims, and Christians – both sides claim it as their capital.
- Security and Violence: Repeated cycles of violence, including suicide bombings, airstrikes, and rocket attacks, have deepened mistrust.
- Political Fragmentation: The Palestinian leadership is divided between Fatah (West Bank) and Hamas (Gaza), complicating negotiations.
- International Involvement: U.S. support for Israel and Arab backing of Palestine have globalized the conflict, often polarizing diplomatic efforts.
- Other Causes of the Crisis include the prolonged blockade and siege by Israel; destruction of aid supplies; dangerous aid distribution system; collapse of civil infrastructure; malnutrition and famine risk.
Concerns & Challenges:
- Global Rift & Western Division Over Gaza:
- United States: It has withdrawn from ceasefire negotiations and continues to support Israel’s military and political objectives, including its controversial plan to relocate Gaza’s population into a ‘humanitarian city’ – described by some experts as resembling a concentration camp.
- European Pushback: Western leaders, including the UK’s Keir Starmer, Canada’s Mark Carney, and Australia’s Anthony Albanese, have issued strong public rebukes of Israel’s actions.
- The recent Declaration of Palestinian statehood by the French President faced criticism from both the US and Israel.
- Joint Statement of Dissent: Recently, 25 countries including the UK, France, Italy, Japan, Canada, and the EU issued a joint statement declaring: ‘The war in Gaza must end now’.
- Global South and Arab States: Nations in the Global South and the Arab League overwhelmingly call for an immediate ceasefire and a return to negotiated two-state talks.
- However, these states have limited leverage, and most have refrained from punitive actions like sanctions or diplomatic isolation of Israel.
- Two-State Solution Under Pressure: Recently Israel has passed resolutions rejecting Palestinian sovereignty and approved 22 new settlements in the West Bank.
- France and Saudi Arabia are co-chairing a UN conference to revive the two-state framework, but the US and Israel remain resistant.
- Humanitarian Crisis Escalates: Over 1,000 Palestinians have died since the Israeli-American Gaza Humanitarian Foundation began operations in May 2025.
- The World Food Program reports that a third of Gaza’s population is going multiple days without food.
- Aid convoys have become deadly zones, with civilians reportedly shot while lining up for supplies.
Implications of the Global Rift
- Diplomatic Realignment: Countries like France and Canada may recalibrate their Middle East policies, potentially leading to new coalitions that challenge US-Israeli dominance.
- UN Dynamics: Growing support for Palestinian statehood could pressure the UN to take more assertive action, though veto powers remain a hurdle.
- Global South Influence: The rift highlights the rising influence of non-Western nations in shaping global narratives around justice and sovereignty.
- US Isolation: Continued American support for Israel may deepen its diplomatic isolation, especially among younger democracies and civil society movements.
Diplomatic Efforts and Reactions
- Ceasefire talks, mediated by Qatar and Egypt with U.S. backing, have stalled repeatedly.
- The U.S. envoy is currently pushing for a 60-day truce.
- France announced it will recognize Palestine as a state at the UN in September, joining over 140 countries in support of Palestinian statehood.
- A joint statement from 28 Western-aligned nations condemned Israel’s aid policies and civilian casualties, signaling a growing rift among traditional allies.
India’s Role in the Gaza Conflict
- Immediate Ceasefire & Humanitarian Access: At the UN Security Council, India’s Permanent Representative urged an ‘immediate ceasefire’, safe aid corridors, and release of all hostages, stressing that ‘ongoing human suffering must not be allowed to continue’.
- Two-State Solution: India supports ‘a sovereign, independent, viable Palestine’ alongside Israel within secure, recognized borders.
- The Palestinian Ambassador to India accused Israel and the U.S. of committing genocide and highlighted the destruction of schools and libraries funded by India.
Way Forward
- Immediate Humanitarian Relief: Open border crossings and restore UN-run aid networks.
- India, Egypt, and other regional powers must pressure Israel to comply with international law.
- Revive the Two-State Solution: Despite setbacks, the two-state framework remains the most viable path.
- A reformed Palestinian Authority, backed by international monitors, could govern Gaza and the West Bank.
- Global Accountability: International courts must investigate alleged war crimes. Countries must condition military aid on compliance with humanitarian norms.
- Reconstruction and Recovery: A UN-led multi-year plan should rebuild Gaza’s infrastructure, homes, and schools. India could play a key role through development aid and technical expertise.
| Daily Mains Practice Question [Q] To what extent does the growing division among Western nations over the Gaza conflict challenge the traditional notions of collective diplomacy, and what implications might this have for global humanitarian accountability? |
Previous article
On India-United Kingdom Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement
Next article
Decoding India’s Energy Transition