Syllabus: GS2/Governance; Government Policy and Intervention
Context
- A recent case study titled ‘From Gridlock to Growth: How Leadership Enables India’s PRAGATI Ecosystem to Power Progress’ by Oxford and Gates Foundation highlighted PRAGATI’s role in transforming India’s governance landscape, underscoring the platform’s success in bridging gaps in governance and driving national development.
Essence of PRAGATI
- India’s Digital PRAGATI (Pro-Active Governance And Timely Implementation) initiative is a multi-purpose and multi-modal platform aimed at addressing the common man’s grievances and simultaneously monitoring and reviewing important programs and projects of the Central Government as well as projects flagged by state governments.
- It leverages digital technology to enhance coordination, accountability, and efficiency in the execution of large-scale projects.
- It aims to enhance governance by integrating technology, fostering collaboration, and ensuring accountability by integrating three key aspects: digital data management, real-time tracking, and high-level coordination.
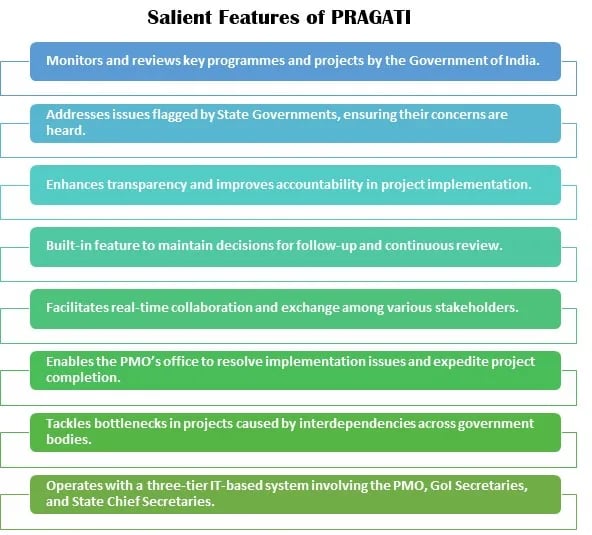
Key Features of PRAGATI
- Digital Data Management: PRAGATI uses a robust digital ecosystem to manage vast amounts of data related to various projects.
- It ensures that all stakeholders have access to up-to-date information, facilitating better decision-making and transparency.
- Real-Time Tracking: One of the standout features of PRAGATI is its ability to provide real-time updates on the progress of projects.
- It helps in identifying bottlenecks and addressing them promptly, ensuring that projects stay on track.
- High-Level Coordination: PRAGATI brings together officials from different departments and levels of government, fostering a collaborative approach to problem-solving.
- This high-level coordination is crucial for the timely and effective implementation of projects.
Key Findings of Case Study
- Accelerated Project Implementation: PRAGATI has reviewed over 340 critical projects worth $205 billion (₹17.05 lakh crore), significantly expediting their implementation.
- It includes the development of 50,000 kilometers of National Highways and doubling the number of airports, including the North Karanpura Thermal Power Plant.
- Enhanced Governance: PRAGATI integrates digital tools such as real-time data, video conferencing, and geo-spatial mapping to facilitate seamless collaboration between the Prime Minister’s Office, Central Ministries, and State Governments.
- This direct engagement ensures that issues are addressed in real time, fostering a culture of accountability and efficiency.
- Leadership from the Top: The Prime Minister’s active involvement (based on SWAGAT, a digital platform started by then Chief Minister Modi in Gujarat) has driven PRAGATI’s success, by directly reviewing progress, setting deadlines, and breaking bureaucratic bottlenecks.
- The study emphasizes the importance of top leadership in using technology to drive cross-collaboration and regular accountability reviews that has created a culture of efficiency and trust in public infrastructure projects.
- For instance, the Pakri-Barwadih Coal Mine in Jharkhand, delayed since 2006, saw swift progress after PM Modi’s intervention in 2016, leading to its completion in 2019.
- Collaboration Across States: PRAGATI has fostered collaboration across states, embodying the concept of ‘Team India’ – a unified approach to national development that transcends political divides.
- For the Ennore-Thiruvallur-Bengaluru Gas Pipeline, which faced land issues across three states, the Prime Minister urged creating a single implementing agency to resolve disputes.
- Economic and Social Impact: The platform has driven significant economic growth, with studies indicating that for every rupee spent on infrastructure, India gains 2.5 to 3.5 rupees in GDP.
- Additionally, fast-tracked projects providing essential services like roads, railways, water, and electricity have improved the quality of life for millions.
- Sustainable Development: PRAGATI incorporates green technologies and streamlined environmental clearances, ensuring that India’s development remains sustainable and inclusive.
- Model for Global Governance: The study commends PRAGATI as a beacon of modern governance, urging other nations to learn from India’s innovative approach to project monitoring and resolution, and setting a standard that other emerging economies can emulate to overcome the Middle-Income Trap.
Concerns and Suggestions Highlighted in Study
- Project Delays: Many of the 340 projects reviewed were significantly delayed, ranging from three to twenty years overdue.
- PRAGATI has been instrumental in reducing these delays from years to months.
- Accountability and Collaboration: The platform has driven accountability at the highest levels and fostered unprecedented federal and regional collaboration.
- Ensuring seamless coordination among these entities can be challenging, leading to delays and inefficiencies.
- Collaboration across government organisations is crucial in accelerating project completion and cutting through bureaucratic red tape.
Other Concerns
- Digital Governance: The platform integrates several key technologies and the success of PRAGATI heavily relies on these technologies.
- Any technical glitches or lack of technological infrastructure, especially in remote areas, can hinder its effectiveness.
- Data Accuracy: PRAGATI platform depends on accurate and timely data for monitoring and decision-making. Inaccurate or outdated data can lead to poor decision-making and ineffective governance.
- Resistance to Change: Implementing new governance models often faces resistance from within the bureaucracy that can slow down the adoption of PRAGATI’s processes and tools.
- Resource Constraints: Adequate resources, both financial and human, are essential for the successful implementation of PRAGATI. Resource constraints can limit its reach and effectiveness.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuous monitoring and evaluation are crucial for the success of PRAGATI. However, establishing robust monitoring mechanisms can be complex and resource-intensive.
Conclusion and Way Forward
- India’s digital PRAGATI is a shining example of how technology can be harnessed to improve governance and accelerate development. By fostering transparency, accountability, and efficiency, PRAGATI is paving the way for a more robust and resilient infrastructure landscape in India.
- Recent findings underscore PRAGATI’s role as a model of cooperative federalism and innovative governance, making it a valuable example for other developing countries aiming to enhance their infrastructure development strategies.
| Daily Mains Practice Question [Q] Critically analyze the effectiveness of the PRAGATI platform in achieving its intended goals of improving governance and development outcomes in India. Discuss the challenges faced in its implementation and suggest potential solutions to enhance its impact. |
Previous article
India’s Manufacturing Sector: Challenges, and Opportunities
Next article
Household Rooftop Solar Scheme Needs Refinement