Syllabus: GS2/ International Relations
In News
- The India–Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA) has completed three years of operation since its implementation in December 2022.
What is Ind-Aus ECTA?
- The Ind-Aus ECTA is a bilateral free trade agreement between India and Australia, signed on 2 April 2022 and implemented from December 2022.
- It is termed an “early harvest” or interim agreement, meaning it focuses on quick and high-impact liberalisation in goods trade, with limited but important commitments in services and investment.
- The ECTA serves as a foundation for a deeper and more comprehensive Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) in the future.
Key Features of the Ind-Aus ECTA
- Tariff Liberalisation in Goods:
- Australia’s commitments: Duty-free access for Indian exports on over 95% of tariff lines from day one.
- From 1 January 2026, 100% of Australian tariff lines will be at zero duty for Indian exports.
- India’s commitments: Gradual tariff reduction on Australian exports, with sensitivity for sectors such as agriculture, dairy, and wine.
- Phased liberalisation protects domestic producers while allowing adjustment.
- Australia’s commitments: Duty-free access for Indian exports on over 95% of tariff lines from day one.
- Rules of Origin and Trade Facilitation: Clearly defined Rules of Origin (RoO) prevent misuse and trans-shipment.
- Simplified customs procedures aim to reduce transaction costs and delays, particularly benefiting exporters and MSMEs.
- Services and Mobility: Limited but significant provisions for business visitors, contractual service suppliers, and professionals.
- Enhanced cooperation in IT, education, and professional services, though deeper liberalisation is reserved for CECA.
- Investment and Safeguards: Provisions for investment promotion and protection.
- Safeguard mechanisms to address sudden import surges that could harm domestic industries.
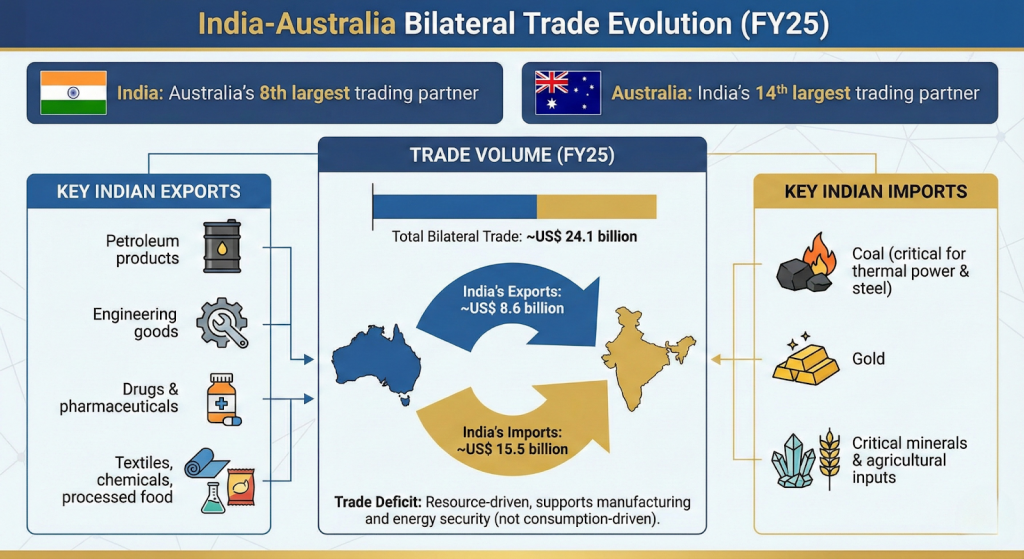
Significance of the India–Australia Relationship
- Strategic and Geopolitical Significance: India and Australia share a common vision of a free, open, and rules-based Indo-Pacific.
- Cooperation under initiatives like the Australia–India Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative Partnership (AIIPOIP) strengthens maritime governance and regional stability.
- Strategic Alliances: Both are core members of the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD) along with the US and Japan.
- ECTA adds an economic dimension to QUAD’s strategic and security cooperation.
- Defence and Security Cooperation: Mutual Logistics Support Agreement (MLSA) enables reciprocal access to military bases and logistics support.
- Joint military exercises between both nations like Malabar (naval, QUAD countries), AUSINDEX (bilateral naval exercise) enhances interoperability, maritime security, and trust.
- Multilateral Alignment: India and Australia work closely in global and regional forums such as G20, East Asia Summit (EAS) & Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
- Supply Chain Resilience: Both countries are partners in the Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) along with Japan.
- This would reduce dependence on single-country supply chains and promote trusted, resilient production networks.
- Critical Minerals Partnership: Australia is a major global supplier of lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements. These minerals are essential for India’s Electric Vehicle (EV) mission, battery manufacturing, and clean energy transition.
Challenges
- Services share: Services form ~55% of India’s GDP, but get limited coverage under ECTA.
- Domestic sensitivity: Dairy sector employs ~80 million rural households in India, a key reason for cautious liberalisation.
Way Forward
- Improve MSME utilisation rate of FTAs (currently estimated below 30% across Indian FTAs).
- Fast-track CECA negotiations focusing on services, digital trade, and investment protection.
- Expand cooperation in green hydrogen, critical minerals processing, and skill mobility.
Source: TH
Previous article
News In Short 29-12-2025