Home Minister Calls for Establishing Common Anti-Terrorism Squad Structure
Syllabus: GS3/ Internal Security
In News
- Home Minister Amit Shah has called for establishing a common Anti-Terrorism Squad (ATS) structure across the country.
Significance of a Uniform ATS Framework
- Changing Nature of Terrorism: Terror groups increasingly use technology: encrypted communication, drones, cyber tools, online radicalisation.
- Standardised Preparedness: Same training modules, drills, and response timelines across India.
- This will reduce institutional weaknesses exploitable by terror groups.
- Federal Coordination Challenges: Terrorism often spans multiple States. Different ATS structures slow down real-time intelligence sharing and joint operations.
- Stronger Anti-Terrorism Grid: Contributes to an “impenetrable and future-ready” security architecture. Ensures readiness not only for present threats but emerging threats.
Source: AIR
Government Notifies Colliery Control (Amendment) Rules, 2025
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
Context
- The Government has amended the provisions governing approval for opening coal and lignite mines under the Colliery Control Rules, 2004.
About
- As per earlier provisions of Rule (9) of the Colliery Control Rules, 2004, a coal/ lignite mine owner was required to obtain prior permission from the Coal Controller’s Organisation (CCO) for opening a coal mine as well as for opening individual seams.
- Permission of CCO was also required for starting a coal/ lignite mine if a mine was not operational for a period of 180 days or more.
- Under the amended provisions, the authority to approve mine/ seam opening permission has now been entrusted/ vested with the board of the concerned coal company.
- Safeguards Provided: It has been provided that:
- the Board of the concerned coal company can approve mine/ seam opening after the requisite approvals from Central/ State Government and statutory bodies has been obtained,
- the company has to submit information about mine opening to CCO, and
- for entities other than companies, such approval will continue to be through CCO.
- Significance: The amendment removes procedural redundancies and enables faster operationalisation of mines, while ensuring continued regulatory oversight.
Source: PIB
Nitrate Contamination
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
Context
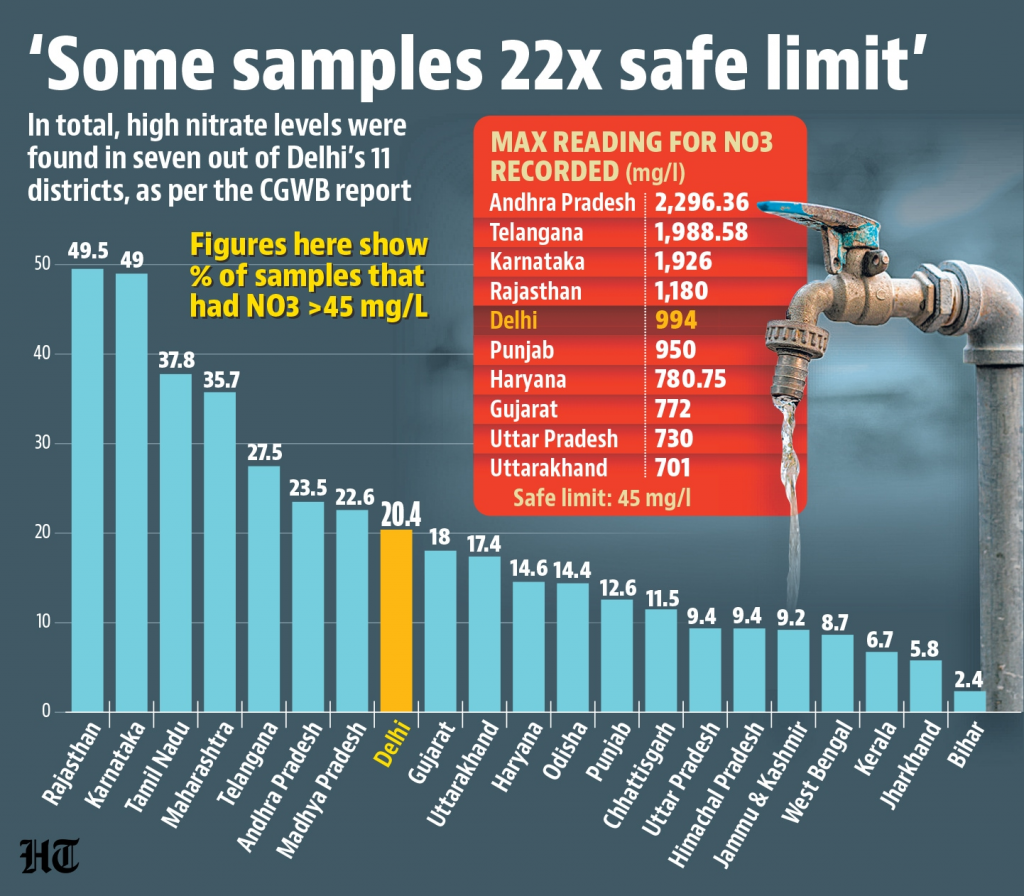
- According to data submitted by the Central Groundwater Board (CGWB) to the National Green Tribunal (NGT), over 20% of groundwater samples in Delhi exceed the permissible nitrate limit of 45 mg/l.
About
- Causes of Nitrate Contamination:
- Excessive use of nitrogen-based fertilizers in agriculture.
- Animal waste and agricultural runoff entering aquifers.
- Leaching from poorly managed septic tanks and sewage systems, especially in urban and peri-urban areas.
- Environmental Impacts: Excess nitrates cause explosive growth of algae in lakes and ponds, leading to oxygen depletion (dead zones) that kill aquatic life.
- Public Health Concerns: High nitrate levels can cause methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome) in infants. Long-term exposure is linked to;
- Increased risk of certain cancers.
- Thyroid dysfunction.
- Reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of blood in adults.
Key Findings from CGWB Data
- Andhra Pradesh has recorded the highest level in the country. Nitrate concentrations there have reached 2,296.36 mg/l.
- Rajasthan is the worst on the scale of pervasiveness, with 49.52% of its 630 samples exceeding safe limits.
Source: HT
Narasapuram Lace Craft
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
In News
- The Prime Minister recently highlighted Narasapuram (Narsapur) lace craft as a powerful example of women’s empowerment, self-reliance, and grassroots economic progress.
About Narasapuram Lace craft
- Location: Narasapur / Narsapur, West Godavari district, Andhra Pradesh
- Origin: Introduced in the 19th century by Christian missionaries
- Alternate Name: Crochet lace craft
- Technique & Material: Handcrafted using fine cotton threads
- Made with crochet needles
- Products: Bedspreads, table covers, cushion covers
- Curtains, mobile covers, decorative items
- Design Features: Intricate floral, geometric, and paisley patterns.
- Motifs inspired by nature and traditional art
- Social Significance: Around 60% artisans are women
- Promotes women’s empowerment through home-based livelihoods
- Economic Importance: Source of supplementary income for rural households
- Supports traditional artisanal economy
- Recognition: Granted Geographical Indication (GI) tag
- Selected under One District One Product (ODOP) scheme.
Source: TH
INS Vagsheer
Syllabus: GS3/ Defence
In News
- President Droupadi Murmu created history by undertaking a dive and operational sortie aboard the indigenous Kalvari-class submarine INS Vaghsheer.
About INS Vaghsheer
- It is the sixth and final submarine of the Indian Navy’s Kalvari-class (Scorpène-class) under Project 75, built by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited with French technology transfer.
- Other submarines of this class are Kalvari, Khanderi, Karanj, Vagir and Vela.
- It is named after the sandfish, it enhances India’s underwater combat capabilities with advanced stealth features.
Source: TH
Magnetic Levitation Technology
Syllabus: GS3/ Science & Technology
In News
- China has set a new world record in magnetic levitation by accelerating a one‑ton superconducting maglev test vehicle from 0 to 700 km/h in about 2 seconds on a 400‑metre track.
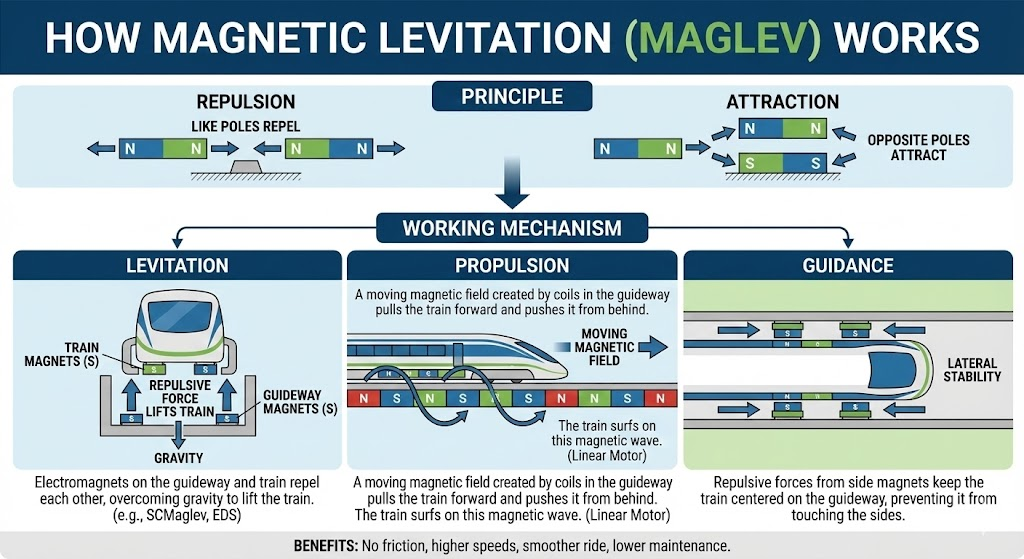
About Magnetic Levitation Technology
- Magnetic levitation (maglev) technology uses magnetic fields to suspend, guide, and propel objects like trains without physical contact, reducing friction for ultra-high speeds.
- Maglev operates on magnetic repulsion (like poles repel) or attraction, often combined with electromagnetic forces.
Source: TOI
K-4 Missile
Syllabus: GS3/Defence
Context
- India recently tested the K-4 submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) from the nuclear-powered submarine INS Arighaat in the Bay of Bengal.
- INS Arighaat, the country’s second nuclear-powered submarine with nuclear-tipped ballistic missiles (called SSBN in naval parlance), was commissioned in 2024.
About the K-4 Missile
- With a strike range of around 3,500 km, the DRDO-developed K-4 missile substantially enhances India’s sea-based nuclear deterrence.
- Earlier, the first nuclear-powered submarine, INS Arihant, commissioned in 2016, was equipped with K-15 missiles limited to a 750-km range.
- Derived from the Agni-III missile, the K-4 is India’s longest-range sea-launched strategic weapon and can carry a 2.5-ton nuclear warhead.
- The K-4 programme, along with future K-5 and K-6 missiles in the 5,000–6,000 km range class, is critical for narrowing India’s strategic gap with major nuclear powers, as the US, Russia, and China already deploy SLBMs with ranges exceeding 5,000 km.
Do you know?
- The ‘K’ in the K-series of missiles is a tribute to APJ Abdul Kalam (Scientist and former President of India), who played a key role in India’s Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP).
Source: HT
Frequency Combs
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
- Frequency combs are emerging as a key precision tool in modern physics, with important applications in atomic clocks, spectroscopy, and high-precision measurements of light.
About Frequency Combs
- A frequency comb is a special type of laser that produces a spectrum of many evenly spaced and highly stable frequencies, resembling the teeth of a comb. Unlike conventional lasers that emit light at a single frequency, frequency combs generate multiple frequencies with extremely regular spacing.
- They are typically produced using mode-locked lasers, which emit ultra-short pulses of light at fixed intervals, creating a precise frequency pattern.
- Frequency combs allow scientists to measure an unknown light frequency by comparing it with the nearest comb frequency and determining the exact offset, enabling extremely accurate measurements.
Source: TH