Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
Context
- A group of local farmers and volunteers, called water guardians, are attempting grassroots water restoration in the semi-arid Homokhátság region in Hungary.
The ‘Water Guardians’ Initiative
- Parts of Central Europe, particularly Hungary’s Great Hungarian Plain (Homokhátság), are witnessing rapid desertification, driven by climate change, falling groundwater levels, and unsustainable land and water management.
- The initiative aims to retain and redistribute water locally, rather than allowing it to drain away unused.
What is Desertification?
- Desertification refers to land degradation in arid, semi-arid and dry sub-humid areas, resulting from climatic variations and human activities.
- It is a gradual process of soil productivity loss and the thinning out of the vegetative cover because of human activities and climatic variations such as prolonged droughts and floods.
- Desertification is a worldwide problem directly affecting 250 million people and a third of the earth’s land surface or over 4 billion hectares.
Reasons for the Rise in Desertification
- Climate Change: Increasing global temperatures intensify evaporation, reducing soil moisture and drying surface layers.
- Erratic rainfall patterns, shorter monsoon periods and prolonged droughts weaken vegetation cover and soil regeneration.
- Declining Groundwater Levels: Excessive extraction of groundwater for agriculture and urban use leads to falling water tables. Further channelisation of rivers and drainage of wetlands disrupt natural flooding and recharge cycles.
- Unsustainable Agricultural Practices: Overgrazing removes protective vegetation cover, exposing soil to wind erosion.
- Monocropping and excessive use of chemical inputs degrade soil structure and fertility.
- Deforestation: Clearing forests for agriculture, infrastructure or mining reduces root systems that bind soil. Also Loss of tree cover increases surface runoff and accelerates land degradation.
Impacts of Desertification
- Environmental Impacts: Decline in biodiversity as grasslands, wetlands and forests degrade. It also leads to increased soil erosion, dust storms and reduced ecosystem services.
- Economic Impacts: Reduced agricultural yields affect farmer incomes and rural livelihoods leading to rising costs of irrigation, land reclamation and drinking water supply.
- Social Impacts: Food insecurity and nutritional stress, especially among marginal farmers.
- Climate Change: Loss of vegetation reduces carbon sequestration, accelerating climate change. Dry soils intensify heatwaves, creating a vicious cycle of warming and degradation.
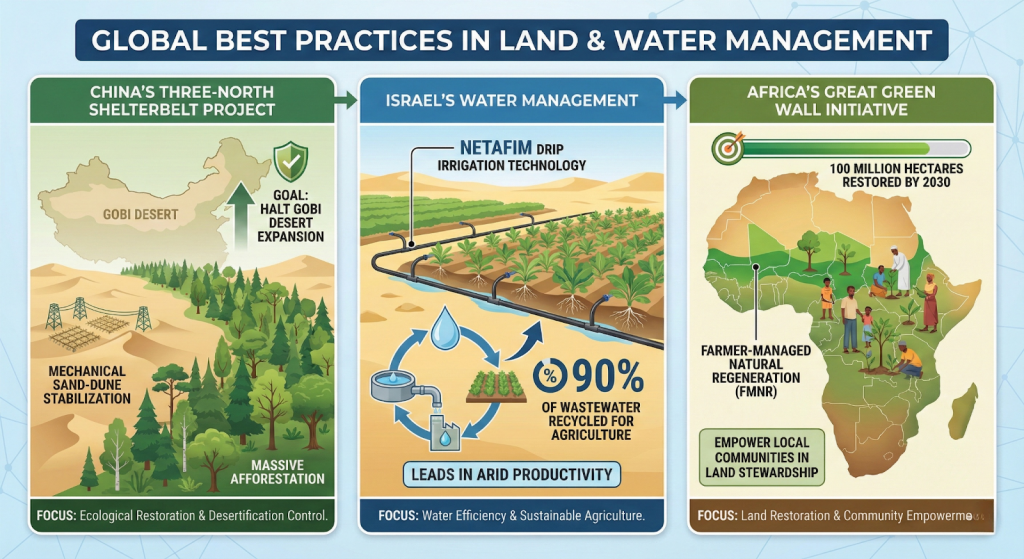
Steps Taken to Combat Desertification
- The UNCCD promotes Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN), aiming to balance land degradation with restoration by 2030.
- United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD):
- UNCCD was established in 1994 to protect and restore the land and ensure a safer, just, and more sustainable future.
- It is the only legally binding framework set up to address desertification and the effects of drought.
- There are 197 Parties to the Convention, including 196 country Parties and the European Union.
- Actions taken by India:
- National Afforestation and Eco-Development Board (NAEB) is implementing the National Afforestation Programme (NAP) for ecological restoration of degraded forests and adjoining areas through people’s participation.
- Aravalli Green Wall Initiative: The initiative aims to expand green cover in a five-kilometre buffer around the Aravalli range. It covers 29 districts across Gujarat, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Delhi.
- National Action Plan to Combat Desertification, 2023 is prepared taking due consideration of the country’s commitments for restoration of 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030.
Source: TH
Next article
The US Push to Redefine the WTO