Syllabus: GS3/Agriculture
Context
- Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) analysis of government data finds 64% of Indian soil samples low in nitrogen and nearly half low in organic carbon.
Major Findings
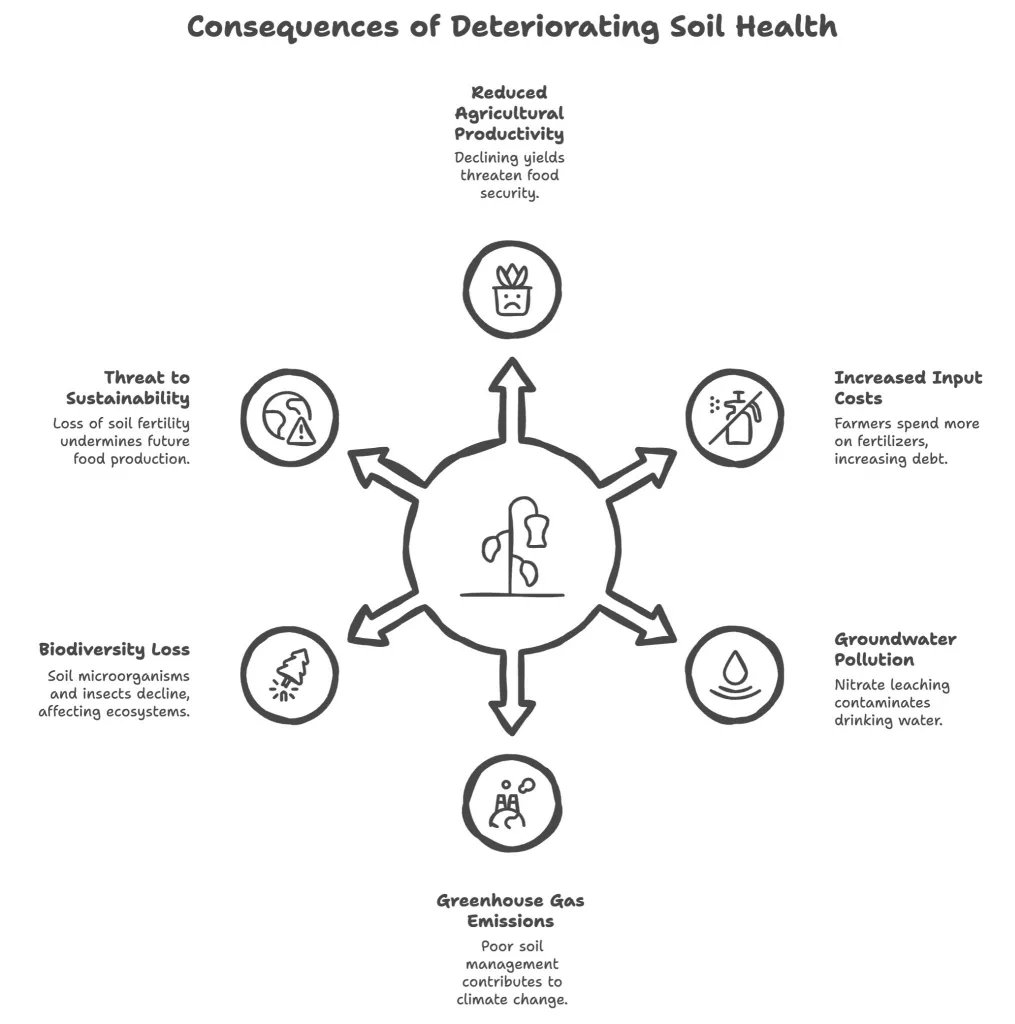
- India’s soils are severely deficient in essential nutrients such as nitrogen and organic carbon.
- These deficiencies have serious implications for both crop productivity and climate change mitigation.
- A critical function of healthy soil is its capacity to store organic carbon, which makes it essential for climate change mitigation.
- Indian soils can sequester an estimated 6-7 teragram of carbon annually.
- Limited scope of soil monitoring: Launched in 2015 under the National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture, the SHC scheme tests 12 chemical parameters in soil and issues nutrient-based recommendations to farmers.
- Experts at the conclave cautioned that the current monitoring framework is incomplete.
- Fertiliser inefficiency and policy gaps: The CSE analysis suggested that current fertiliser use fails to improve nitrogen or organic carbon levels in soil.
- This indicates inefficiency in application practices and calls for corrective policy measures.
- While organic farming schemes exist, their reach remains limited, the assessment underlined.
Soil Health and Its Significance
- Soil health is defined as the continued capacity of soil to function as a vital living ecosystem that sustains plants, animals, and humans.
- The soil on 96-120 million hectares out of India’s 328 million hectares of land, particularly in forests, croplands and pastures, is already classified as ‘degraded’ (NAAS 2010)(Space Application Centre, ISRO 2021).
- Nutrient availability: Healthy soils are rich in essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential for plant growth and development.
- Biodiversity: Healthy soils can host a vast diversity of organisms. They all play vital roles in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and soil formation.
- Soil structure: A “well-structured soil” embodies a vast amount of interconnecting pore spaces that allows the drainage of water, free movement of air and unrestricted growth of roots.
- Water retention: When soils have poor structure, they cannot hold water within the pore spaces, the water hits the compacted layers, and it cannot infiltrate.
- This leads to more runoff, and therefore, more erosion, flooding, more pollution, and less water held in the soil.
- Carbon sequestration: Healthy soils play a vital role in capturing and storing CO2.
- Soils with higher organic carbon content can support a richer population of microorganisms and contain more nutrients favoring the development of high-quality crops.
| Government Initiatives – Soil Health Card Scheme (2015): Provides farmers with soil nutrient status and fertilizer recommendations. – Neem Coated Urea (NCU): This scheme is initiated to regulate use of urea, enhance availability of nitrogen to the crop and reduce cost of fertilizer application. – Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY): Promotes organic farming. – National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA): Encourages soil and water conservation, and integrated nutrient management. – Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY): Supports state-level interventions for soil health. – National Project on Organic Farming (NPOF): Capacity building for composting and biofertilizer use. |
Way Ahead
- Biochar – produced through pyrolysis of biomass –is an emerging soil amendment that can enhance fertility, retain moisture and serve as a carbon sink by increasing the soil organic content.
- But India does not have any standardised production protocols for biochar.
- There is a need to strengthen soil testing infrastructure and farmer awareness.
- Regulate industrial effluent discharge and improve irrigation management.
- Foster climate-resilient agricultural practices.
- Encourage crop rotation and intercropping for nutrient restoration.
Source: DTE
Previous article
NITI Aayog Releases Reports on India’s Services Sector