Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- According to a report released by Meta, India’s start-up ecosystem has witnessed exponential growth over the last decade.
Key Highlights
- It identified six key levers of growth of India’s startups such as: AI adoption, cross-border expansion, omnichannel presence, Tier 2/3 market expansion, category diversification, creator-led brand building.
- Integration of AI: Over 70% of startups were integrating artificial intelligence into their business operations.
- Sectors such as healthcare, edtech, and beauty were leading in AI maturity, leveraging automation for customer service, predictive analytics, and personalisation.
- Tier 2 and 3 Market Focus: Emerging as the new growth area.
- Startups use vernacular content, regional influencers, and WhatsApp-based commerce for penetration.
- Service-based startups are entering these markets earlier than product-based ones.
India’s Startup Ecosystem
- India is home to one of the most vibrant startup ecosystems with close to 30,000+ tech startups, making it the 3rd largest startup ecosystem in the world after the US and China.
- The number of DPIIT-recognised startups has grown from around 500 in 2016 to 1,59,157 as of January 2025.
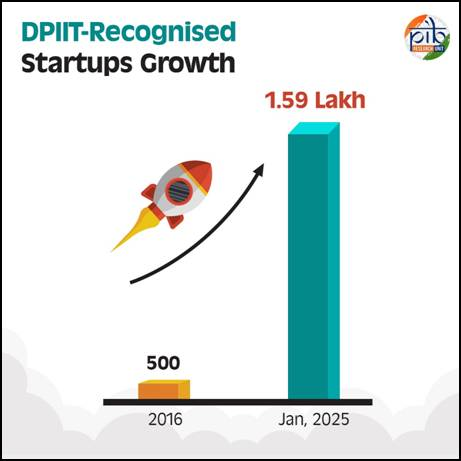
- From 2016-2024, recognised startups have reportedly created over 16.6 lakh direct jobs, significantly contributing to employment generation.
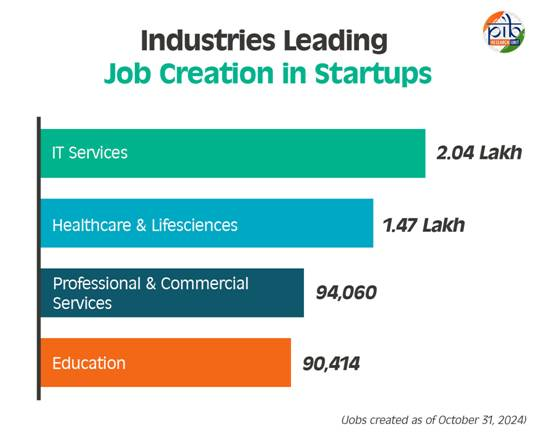
- India is ranked fourth after the US, UK and China in terms of total funding to tech startups.
- At present, the country has over 1.4 lakh startups. India minted six new unicorns in 2024 alone.
- Significance:
- Generated Employment: Startups have created over 1.6 million jobs across the country, demonstrating their role as significant employment generators.
- Boosted GDP Growth: Startups contribute directly to GDP through innovation-driven productivity and indirectly by fostering ancillary industries.
- Attracted Foreign Investments: India has become a magnet for global venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) investments.
- Promoted Inclusivity: Rural-focused startups and social enterprises are addressing critical gaps in healthcare, education, and agriculture, improving the quality of life for millions.
Government Initiatives
- Startup India: Launched in 2016, it is a flagship initiative by the Government of India to foster innovation and create a thriving startup ecosystem. Through various schemes, it aims to empower startups to scale and succeed.
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS): Launched in 2021, the SISFS supports startups at various stages, including proof of concept, prototype development, product trials, market entry, and commercialisation.
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS): It provides credit guarantees for loans to DPIIT-recognised startups from Scheduled Commercial Banks, NBFCs, and Venture Debt Funds.
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM): Launched in 2016 by NITI Aayog, it aims to promote innovation and entrepreneurship across India.
- It includes initiatives like Atal Tinkering Labs at the school level to foster creativity, Atal Incubation Centres to build a robust startup ecosystem, and Atal Community Innovation Centres to serve unserved and underserved regions.
- MeitY Startup Hub (MSH): It serves as a central hub, ensuring synergies among incubation centres, Centres of Excellence on Emerging Technologies, and other platforms supported by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- IndiaAI Mission (2024): It has a budget of ₹10,300 crore over five years.
- A key goal is the creation of a high-end common computing facility with 18,693 GPUs.
- India’s AI Models & Language Technologies: The government is facilitating the development of India’s own foundational models, including Large Language Models (LLMs) and problem-specific AI solutions tailored to Indian needs.
- AI Centers of Excellence: Establishing dedicated AI hubs and innovation centers across the country to support AI startups and research.
- India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI): Combines public funding with private sector innovation to drive digital transformation.
Conclusion
- Over the last 10 years, India’s startup ecosystem has experienced tremendous growth, becoming the third-largest in the world.
- India’s startup ecosystem is entering a new maturity phase, marked by:
- Smarter tech-led growth;
- Regional inclusivity;
- Global ambition;
- Focus on sustainability and consumer personalization.
- These shifts reflect not just a digital revolution but a strategic rethinking of entrepreneurship in India.
Source: TH
Previous article
News In Short-27-06-2025
Next article
India-US Trade Deal To Finalise Soon