Syllabus: GS2/IR, GS3/Economy
Context
- India has been excluded from the US-led Pax Silica initiative, a new US critical mineral diversification plan.
About
- Pax Silica is a US-led strategic initiative to build a secure, prosperous, and innovation-driven silicon supply chain from critical minerals.
- The inaugural Pax Silica Summit convenes counterparts from: Japan, Republic of Korea, Singapore, the Netherlands, The United Kingdom, Israel, United Arab Emirates, and Australia.
- Together, these countries are home to the most important companies and investors powering the global AI supply chain.
- Its objective is to reduce coercive dependencies, protect the materials and capabilities foundational to artificial intelligence, and ensure aligned nations can develop and deploy transformative technologies at scale.
- Countries will partner on securing strategic stacks of the global technology supply chain, including, but not limited to, software applications and platforms.
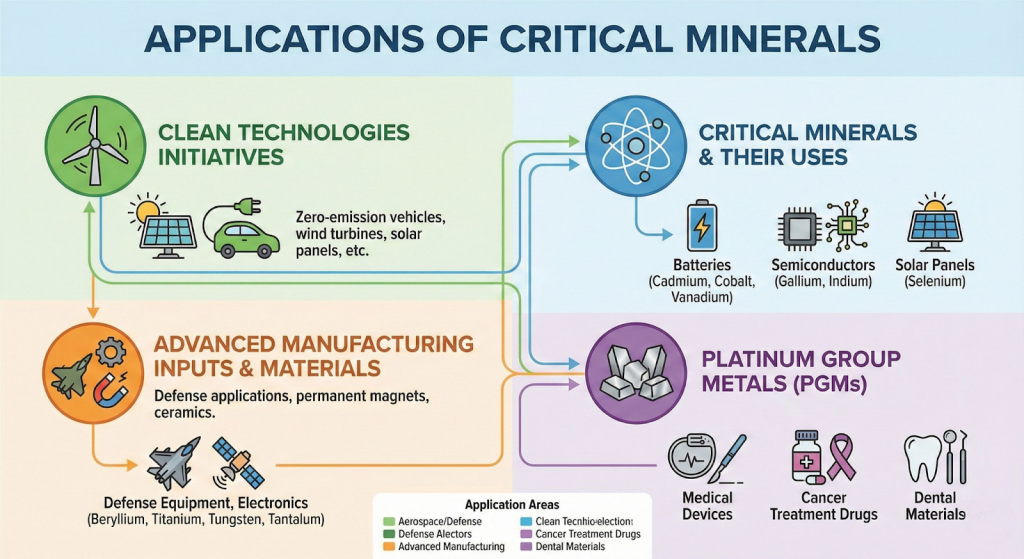
What are Critical Minerals?
- Critical minerals are elements that are the building blocks of essential modern-day technologies, and are at risk of supply chain disruptions.
- The lack of availability of these minerals or the concentration of extraction or processing in a few geographical locations could potentially lead to “supply chain vulnerabilities and even disruption of supplies”.
List of Critical Minerals
- Different countries have their own unique lists of critical minerals based on their specific circumstances and priorities.
- A total of 30 minerals were found to be most critical for India: Antimony, Beryllium, Bismuth, Cobalt, Copper, Gallium, Germanium, Graphite, Hafnium, Indium, Lithium, Molybdenum, Niobium, Nickel, PGE, Phosphorous, Potash, REE, Rhenium, Silicon, Strontium, Tantalum, Tellurium, Tin, Titanium, Tungsten, Vanadium, Zirconium, Selenium and Cadmium.
Source: IE
Next article
News In Short 13-12-2025