Syllabus: GS1/Geography
Context
- Scientists warn that the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) could slow by about 20% by 2050 under a high carbon emissions scenario.
About
- ACC is the world’s strongest ocean current.
- It’s five times stronger than the Gulf Stream and more than 100 times stronger than the Amazon River.
- It forms part of the global ocean “conveyor belt” connecting the Pacific, Atlantic and Indian oceans.
- ACC’s Role: ACC moves clockwise around Antarctica and regulates global climate by influencing the ocean’s ability to absorb heat and CO2 and preventing warm waters from reaching Antarctica.
- The system regulates Earth’s climate and pumps water, heat and nutrients around the globe.
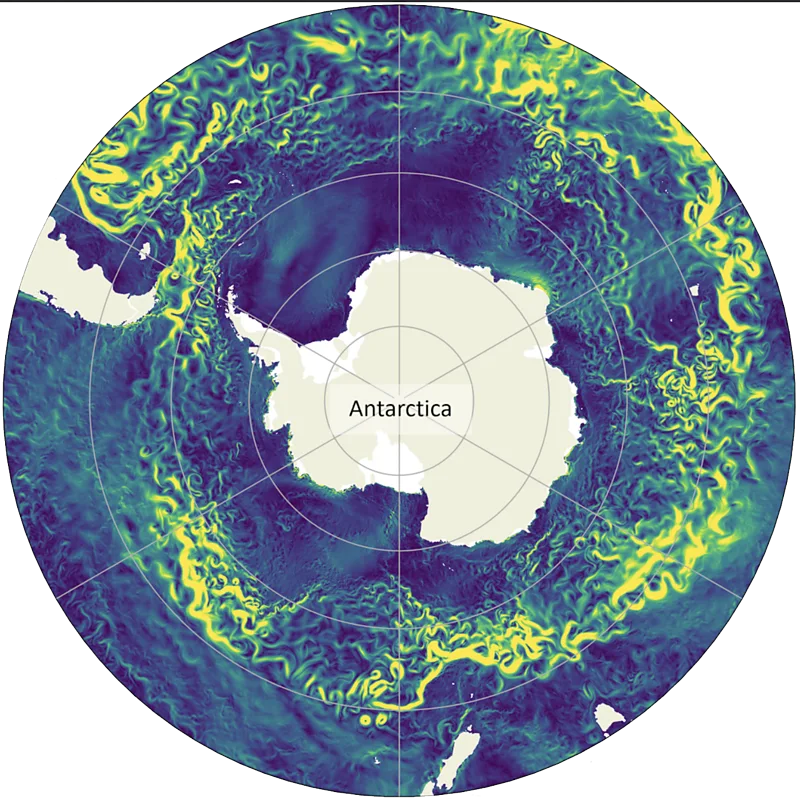
Impacts of Slowing down of ACC
- Impact on Climate and Carbon Absorption: If the ACC breaks down, it could lead to more climate variability, extreme weather in certain regions, and accelerated global warming due to reduced carbon absorption by the ocean.
- Threat to Antarctic Ecosystem: Slowing of the ACC could allow invasive species (e.g., southern bull kelp, shrimp, mollusks) to reach Antarctica, disrupting the local food web and affecting native species like penguins.
- Impact of Melting Ice Sheets: Melting ice shelves add fresh water to the ocean, altering its salinity, weakening the Antarctic Bottom Water formation, and reducing the strength of the ocean jet around Antarctica.
Ocean Currents
- Ocean currents are the continuous, predictable, directional movement of seawater driven by gravity, wind (Coriolis Effect), and water density.
- Ocean water moves in two directions: horizontally and vertically.
- Horizontal movements are referred to as currents, while vertical changes are called upwellings or downwellings.
- The system is responsible for the transfer of heat, variations in biodiversity, and Earth’s climate system.
Ocean Conveyor Belt
- The ocean conveyor belt, also known as the global thermohaline circulation (THC), is a large-scale ocean current system that moves water throughout the world’s oceans.
- The path starts in the North Atlantic, where cold water sinks, creating a flow of deep water that moves southward.
- It travels through the Southern Ocean, moves into the Indian and Pacific Oceans, and finally upwells in the Pacific and Indian Oceans, where the surface water returns toward the equator.
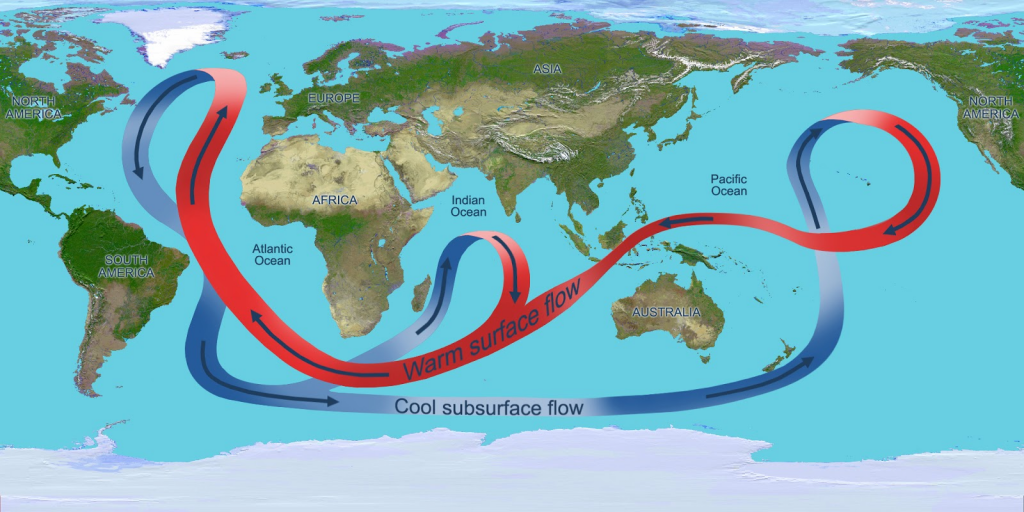
- This system plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate by redistributing heat, nutrients, and gases like carbon dioxide.
Role of Ocean Currents
- Climate Regulation: Transport heat from the equator to the poles and vice versa, helping to stabilize global temperatures.
- Supporting Marine Life: Distribute nutrients that support the growth of phytoplankton, forming the base of the ocean’s food chain.
- Influencing Weather Patterns: Affect weather systems and phenomena like El Niño and La Niña, influencing rainfall and storm activity.
- Carbon Sequestration: Help absorb and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, acting as a carbon sink.
- Fisheries and Economy: Influence fish distribution, affecting global fisheries, and provide efficient shipping routes.
- Ocean Mixing: Aid in mixing surface and deep ocean waters, regulating temperature, salinity, and oxygen levels.
- Sea Level and Coastal Erosion: Impact sea levels and contribute to coastal erosion through water movement.
Conclusion
- While our findings present a bleak prognosis for the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, the future is not predetermined.
- Concerted efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions could still limit melting around Antarctica.
- Establishing long-term studies in the Southern Ocean will be crucial for monitoring these changes accurately.
Source: ET
Previous article
News In Short-05-03-2025
Next article
India’s First Commercial Semiconductor Fab Unit