Gum Arabic (Acacia Gum)
Syllabus: GS1/ Natural Resources
In News
- Smuggling of arabic gum (Acacia Gum) from war-torn Sudan is disrupting global supply chains.
- Sudan produces 80% of the world’s supply followed by Chad, Nigeria, and other Sahelian nations.
About Gum Arabic (Acacia Gum)
- It is a natural exudate obtained from Acacia trees, primarily Acacia senegal and Acacia seyal. It is a complex polysaccharide with excellent emulsifying, stabilizing, and thickening properties.
- Uses:
- Food Industry: Acts as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and thickener in soft drinks, baked goods, and confectionery.
- Cosmetics: Used in skincare products and lipsticks for texture and stability.
- Pharmaceuticals: Found in syrups, capsules, and tablet coatings.
Source: TH
Wallace Line
Syllabus: GS1/ Geography
Context
- The Wallace Line is a crucial concept in biogeography, explaining the striking differences in species distribution across continents.
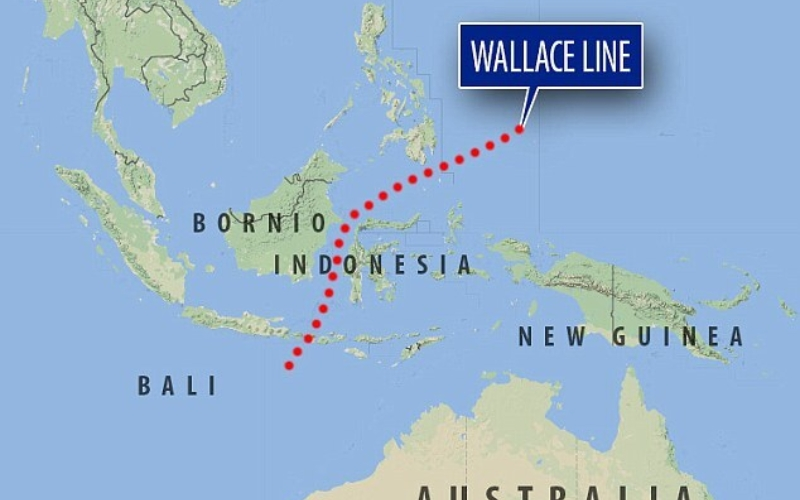
What is the Wallace line?
- The Wallace Line, first identified by British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace in the late 19th century, is an imaginary boundary that separates the distinct biogeographic regions of Asia and Wallacea (a transitional zone between Asia and Australia).
- On the western side of the line, species are primarily of Asiatic origin, whereas on the eastern side, species exhibit characteristics of both Asian and Australian descent.
- This stark contrast in fauna occurs despite the relatively short distances around (35 kilometers) between these regions.
Geographic extent of the Wallace Line
- It runs through the Lombok Strait between Bali and Lombok.
- It runs through the Makassar Strait between Borneo and Sulawesi.
- It extends eastward, south of Mindanao Island, into the Philippine Sea.
Findings on Sulawesi Island
- In 1876, it was noted that the island had affinities with Africa, India, Java, Maluku Islands, New Guinea, and the Philippines.
- Also there is a unique mix of species from both Asia and Australia.
- Examples of Sulawesi’s Unique Fauna
- Asian species: Tarsiers (family Tarsiidae), Lowland anoa (Bubalus depressicornis) and Mountain anoa (Bubalus quarlesi).
- Australian species: Dwarf cuscus (Strigocuscus celebensis).
Source: TH
Thorium Reserves
Syllabus: GS1/Geography/Mineral Resources
Context
- China’s geologists have found one million tonnes of thorium in the Mongolia region of China.
Thorium’s Potential
- Thorium generates 200 times more energy than uranium and is safer with no risk of meltdown, no need for water cooling, and minimal radioactive waste.
- Thorium molten-salt reactors (TMSRs) are seen as a game-changer for global energy production.
China’s Energy Projects
- China has approved the world’s first TMSR power plant, set to generate 10 megawatts by 2029.
- The country is exploring thorium-powered ships and lunar reactors for future moon bases.
India’s Thorium Reserves
- India has one of the largest reserves of thorium in the world.
- Major thorium deposits are found with large reserves in Kerala, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Together, Kerala and Odisha account for over 70% of India’s thorium.
- India has been developing a three-stage nuclear program, with thorium-based reactors being a critical part of the third stage.
- Challenges: Extracting thorium from ores requires high amounts of energy and creates significant waste.
- While India has large thorium reserves, extracting it for nuclear energy use has faced challenges, including the need for advanced reactor technology and economic viability.
Source: BT
Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA)
Syllabus :GS 3/Economy
In News
- The Supreme Court expressed disappointment over the functioning of the Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA) describing it as a “rehabilitation centre for former bureaucrats.”
About
- Land and Colonization is a State subject, but to protect homebuyers and ensure transparency in the real estate sector, Parliament enacted the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 (RERA).
- It is a landmark legislation aimed at reforming India’s real estate sector.
- It established the Real Estate Regulatory Authority for regulation and promotion of the Real Estate sector.
Key Provisions of RERA
- Establishment of Regulatory Authorities:
- State Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA)
- Registers real estate projects and maintains a public database.
- Protects interests of buyers, promoters, and agents.
- Ensures compliance with regulations.
- Promotes affordable and sustainable housing.
- Real Estate Appellate Tribunal
- Handles appeals against RERA decisions.
- Ensures speedy dispute resolution.
- State Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA)
- Financial Safeguards:
- Escrow Account Mandate:
- 70% of buyers’ funds must be deposited in an escrow account, used only for construction.
- Advance Payment Cap:
- Developers cannot take more than 10% of the total cost as advance without a written agreement.
- Escrow Account Mandate:
- Protection for Homebuyers:
- Defined Carpet Area:
- Buyers will be charged based on net usable floor area, not super built-up area.
- Timely Project Completion:
- Developers must complete projects on time, failing which penalties apply.
- Structural Defect Liability:
- Developers are liable for five years to fix any structural defects.
- Defined Carpet Area:
- Penal Provisions & Legal Compliance:
- Equal penal interest for delays from both developers and buyers.
- Imprisonment:
- Up to 3 years for developers violating RERA provisions.
- Up to 1 year for agents and buyers for non-compliance with tribunal orders.
Source: TH
Rise in India’s R&D Spending
Syllabus: GS3/ S&T
Context
- India’s Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD) has more than doubled in the past decade, rising from ₹60,196 crore in 2013-14 to ₹1,27,381 crore.
DISHA Program: Driver of Technological Growth
- The DISHA Program, an initiative aimed at Developing Innovations, Successful Harnessing, and Adoption, is a step towards building a knowledge-based economy where research-driven solutions transform industries.
- The program is designed to support faculty members and students working on disruptive technologies across disciplines, ensuring that India remains at the forefront of global innovation.
- Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF), seeks to create a unified research ecosystem bridging science, humanities, and social sciences.
Other Government Initiatives to Boost R&D
- National Research Foundation (NRF): Aims to enhance research funding and collaboration between academia and industry.
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM): Encourages startups, entrepreneurship, and innovation among students and professionals.
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme: Supports high-tech manufacturing through incentives for R&D-driven industries.
- Startup India and Make in India: These initiatives foster innovation by providing funding and policy support for startups.
Challenges in India’s R&D Ecosystem
- Private Sector Participation: The private sector contributes only about 36% of GERD, whereas in developed nations, it exceeds 60-70%.
- Insufficient Funding: Despite growth, India’s GERD as a percentage of GDP (~0.7%) remains lower than countries like China (2.4%) and the US (3.1%).
- Limited University-Industry Collaboration: Weak links between academia and industry hinder commercialization of research.
Source: AIR
Solar Maximum
Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- NASA has launched the Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere (PUNCH) Mission, aligning with the solar maximum phase of the Sun’s cycle.
What is the solar cycle?
- The Sun, like a bar magnet, possesses a magnetic field with north and south poles.
- This magnetic field is generated by the movement of electrically charged particles within the Sun.
- Approximately every 11 years, the Sun’s magnetic field completely flips, switching its north and south poles—a phenomenon known as the solar cycle.
Solar Maximum
- Solar maximum is the peak phase of the Sun’s 11-year cycle, characterized by heightened solar activity.
- During this period, the Sun emits more energy, radiation, and light and experiences an increased number of sunspots.
- The transition occurs when the Sun’s magnetic field undergoes a complete flip.
- Duration: Solar Maximum lasts between one and two years. The time between two solar maxima can vary from 9 to 13 years.
Impacts of Solar Maximum on Earth
- Solar Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs): The release of magnetic energy leads to massive solar storms that send bursts of radiation and particles into space.
- Damage to Power Grids: Intense geomagnetic storms can disrupt electrical infrastructure, leading to power outages.
- Satellite Malfunctions: Increased solar radiation affects satellite operations, potentially causing communication and navigation failures.
| PUNCH Mission – PUNCH is a NASA Small Explorer (SMEX) mission to better understand how the mass and energy of the Sun’s corona become the solar wind that fills the solar system. – The mission consists of a constellation of four small satellites in Sun-synchronous, low Earth orbit that together will produce deep-field, continuous, 3D images of the solar corona. |
Source: IE
Offshore Mining
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- The Kerala Assembly unanimously passed a resolution, opposing the Central government’s plans to permit offshore mining along the Kerala coast.
About
- 2023 Amendment: Amendments to the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act, 2002, allows the Union Ministry of Mines to auction deep-sea mineral blocks.
Offshore Mining
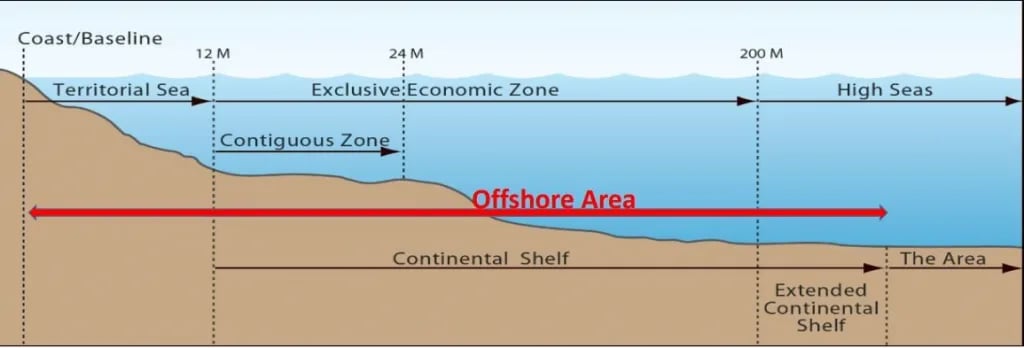
- Offshore mining is the process of retrieving mineral deposits from the deep seabed, at a depth of more than 200 metres.
- Types of Resources:
- Oil and Gas: Extracted from offshore oil rigs or platforms.
- Minerals: Includes precious metals, polymetallic nodules, and other rare minerals found on or beneath the seafloor.
- Sand and Gravel: Used for construction and other purposes.
Concerns
- Disruption of Habitats: Mining robots destroy the ocean floor, harming over 5,000 species and fragile ecosystems.
- Sediment Plumes: Sediment clouds smother marine life, disrupt feeding, and reduce water quality.
- Technical Challenges: Deep-sea mining technology is underdeveloped; equipment repair is difficult due to extreme pressure.
- Ethical Considerations: Companies (SAP, BMW, Google, etc.) oppose using seafloor materials, citing environmental concerns.
| United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) – UNCLOS was adopted in 1982, and came into force in 1994. – It lays down a comprehensive regime of law and order in the world’s oceans and seas establishing rules governing all uses of the oceans and their resources. – It establishes the International Seabed Authority to regulate mining and related activities on the ocean floor beyond national jurisdiction. The International Seabed Authority (ISA) – The International Seabed Authority (ISA) is an autonomous international organization established under 1. The 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and 2. The 1994 Agreement relating to the Implementation of Part XI of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. – All States Parties to UNCLOS are members of ISA. 1. As of May 2023, ISA has 169 Members (India is also a member), including 168 Member States and the European Union. – Headquarters: Kingston, Jamaica |
Source: TH
Vantara
Syllabus :GS 3/Environment
In News
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated Vantara.
Vantara
- It is a unique wildlife conservation, rescue, and rehabilitation initiative in Jamnagar, Gujarat.
- It is the world’s largest wildlife rehabilitation centre.
- It is home to over 1.5 lakh rescued, endangered, and threatened animals, offering them a home away from home and a second chance at life.
- Awards and Recognition : The Central government awarded Vantara the prestigious ‘Prani Mitra’ National Award under the ‘Corporate’ category, recognizing the exceptional contributions of the Radhe Krishna Temple Elephant Welfare Trust (RKTEWT) for elephant rescue, treatment, and care.
Source :TH
Previous article
Designing India’s AI Safety Institute