Syllabus: GS3/Awareness in the fields of Space
Context
- A 500-kg metal object, believed to be space debris, crashed in Kenya, highlighting concerns about accountability and regulatory gaps in space governance.
About Space Debris
- It includes non-functional satellites, abandoned rocket stages, and smaller fragments from previous space missions.
- The UN Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UN-COPUOS) defines space debris as all man-made objects, including fragments and elements thereof, in Earth orbit or re-entering the atmosphere, that are non-functional.
- According to NASA, millions of pieces of debris orbit the Earth, ranging from tiny paint flecks to large satellite remnants.
Factors Causing Space Debris
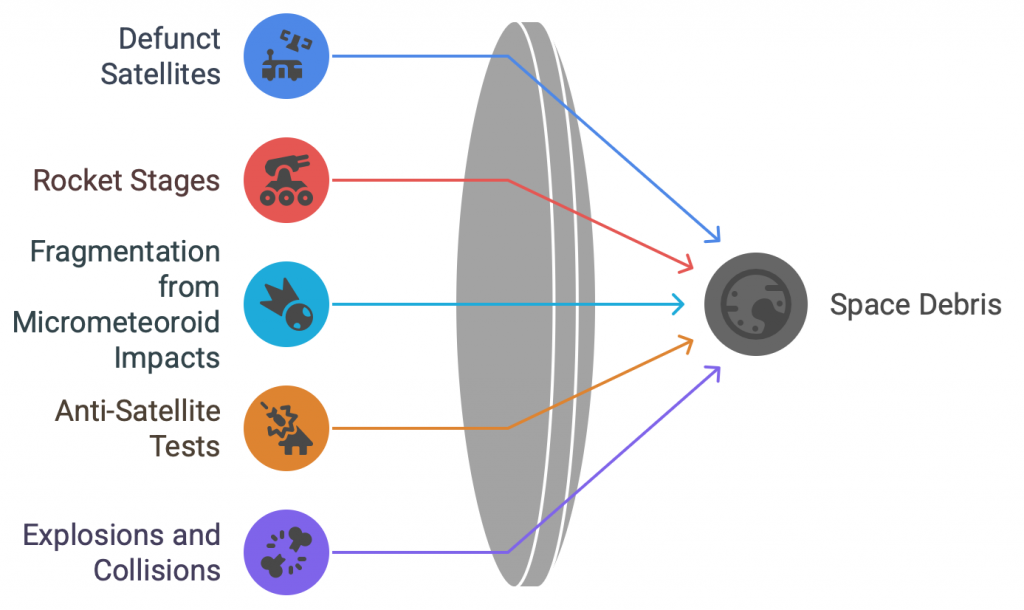
Examples
- 2022: Chinese Long March 5B rocket fell into the Indian Ocean, sparking concerns about uncontrolled re-entry.
- 2023: Parts of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket were discovered on a sheep farm in Australia.
- February 2024: Debris from a Russian satellite disintegrated over the United States, alarming residents.
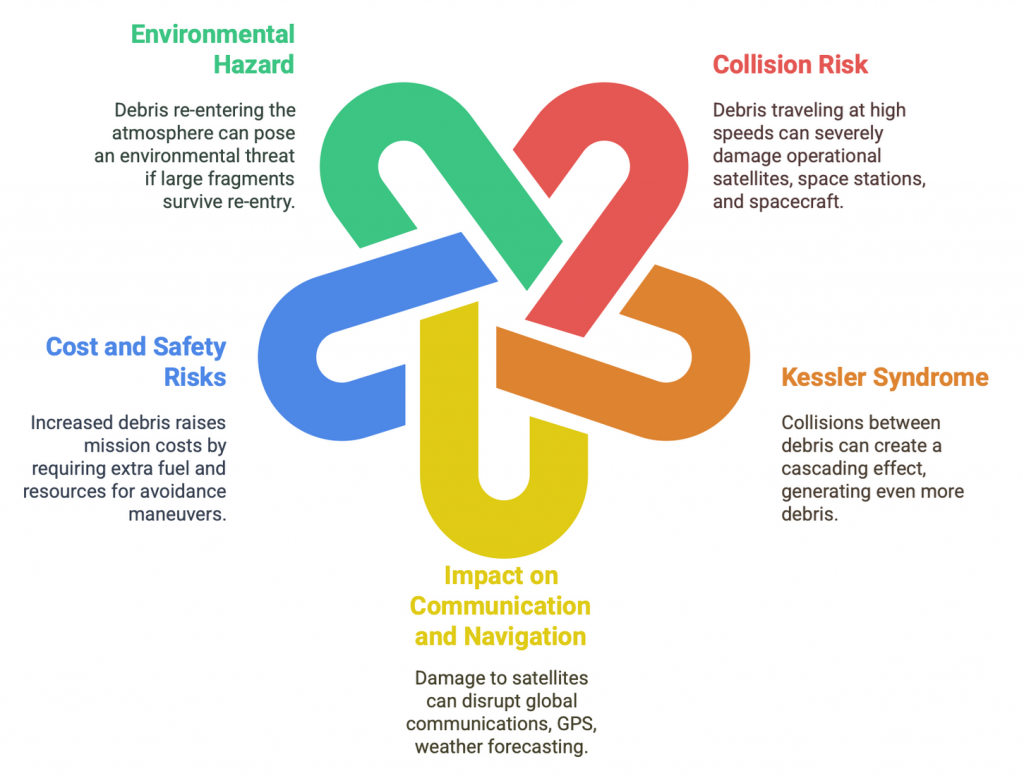
Threats from Space Debris
International Laws on Space Debris Responsibility
- United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA):
- Outer Space Treaty (1967): It does not specifically address space debris, it emphasizes that nations are responsible for activities conducted in outer space, including by private entities under their jurisdiction.
- Article VI of the treaty emphasizes that states bear responsibility for their space objects.
- Liability Convention (1972): It introduces the concept of ‘absolute liability’ for damage caused by space objects on Earth.
- Under this framework, launching states are automatically responsible for any harm caused by their debris, without the need to prove negligence.
- Outer Space Treaty (1967): It does not specifically address space debris, it emphasizes that nations are responsible for activities conducted in outer space, including by private entities under their jurisdiction.
India’s Initiatives in Space Debris Management
- ISRO adheres to internationally accepted space debris mitigation guidelines recommended by the UN-COPUOS and the Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC).
- ISRO System for Safe and Sustainable Space Operations Management (IS4OM): To focus on spaceflight safety and debris mitigation.
- Network for Space Object Tracking and Analysis (NETRA): For Space Situational Awareness (SSA) capacity building.
- Debris-Free Space Missions (DFSM) Initiative (2024) by ISRO: It aims to achieve debris-free space missions by all Indian space actors, both governmental and non-governmental, by 2030. The initiative focuses on:
- Avoiding Debris Generation;
- Collision Avoidance;
- Post-Mission Disposal;
Challenges in Holding Countries Accountable
- Difficulty in Tracing Ownership: Identifying the exact origin of debris is challenging, especially for small fragments.
- Bureaucratic and Political Hurdles: Diplomatic processes for compensation can be slow and politically sensitive.
- No Penalties for Uncontrolled Re-entry: While the Liability Convention requires countries to pay for damages, it does not penalize them for allowing uncontrolled re-entries to happen.
Mitigation and Future Solutions
- International Cooperation: Strengthening international cooperation like the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UNCOPUOS) and developing standardized procedures for debris removal can enhance accountability and enforcement.
- Mandatory End-of-Life Plans: Space missions should include clear deorbiting strategies to minimize debris risks.
- Technological Innovations: Investing in technologies for active debris removal, such as the ADRAS-J mission by Astroscale, can help mitigate the risks posed by space junk.
- Liability Insurance: Countries and private companies could be required to have insurance policies covering potential damage from space debris.
- National Regulations: Implementing and enforcing national regulations that align with international treaties can ensure that countries take responsibility for their space activities.
Previous article
RBI Announces Over US$21 Billion Liquidity Infusion