Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- Economic reforms in 2025 reflect a maturing phase of India’s governance, where the emphasis shifted decisively from “expanding regulatory frameworks” to “delivering measurable outcomes”.
Key Reforms Shaping Growth and Opportunity

Income Tax Reforms
- The Union Budget 2025-26 exempted the annual incomes up to ₹12 lakh from income tax under the new regime, with the effective exemption rising to ₹12.75 lakh for salaried taxpayers on account of the standard deduction.
- The Government announced a comprehensive overhaul of the Income-tax Act, 1961, resulting in the New Income Tax Act, 2025.
- The Act strengthens digital-first enforcement, faceless tax administration, consolidates compliance provisions such as Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) under a single section etc.
Rural Employment Reforms
- Rural employment reforms anchored in the enactment of the Viksit Bharat – Guarantee for Rozgar and Ajeevika Mission (Gramin) Act, 2025, replacing the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA).
- Extended Employment Guarantee: 125 days of wage employment per rural household in a financial year.
- Strengthened Administrative Capacity: The administrative expenditure ceiling has been increased from 6% to 9%, strengthening staffing, training, technical capacity, and field-level support to improve institutional delivery and outcomes.
Ease of Doing Business Reforms
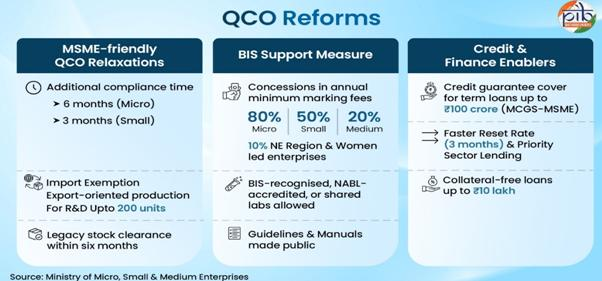
- To ensure that Quality Control Orders (QCOs) do not disrupt domestic production, the Government has implemented them in a phased and MSME-friendly manner through the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
GST 2.0 Reforms
- Simpler Tax Structure: The move to a two-slab GST regime (5% and 18%) reduces complexity, classification disputes, and compliance costs.
- MSME and Startup Enablement: Faster refunds, simplified registration and returns, and lower input costs aim is to boost the present businesses and startups and incentivise the youth to enter into businesses and initiate startups.
- Wider Tax Base and Revenue Stability: Simpler rates and improved compliance have expanded the GST taxpayer base to over 1.5 crore, while gross collections reached ₹22.08 lakh crore in FY 2024–25, reinforcing fiscal sustainability.
Labour Reforms
- The Government of India consolidated 29 existing labour laws into four Labour Codes;
- The Code on Wages, 2019,
- the Industrial Relations Code, 2020,
- the Code on Social Security, 2020 and
- the Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020.
Export Promotion mission
- Announced in the Union Budget 2025–26, EPM marks a strategic shift from fragmented export support schemes to a single, outcome-based and digitally driven framework, aimed at empowering MSMEs, first-time exporters, and labour-intensive sectors.

Challenges Ahead
- Digital Divide: Digital-first governance in taxation, trade, and welfare delivery risks exclusion of smaller firms and workers lacking digital literacy or infrastructure.
- Global Economic Uncertainty: Sluggish global demand, geopolitical tensions, and supply-chain disruptions could limit export growth despite domestic reform momentum.
- MSME Compliance Burden: Despite simplification, smaller enterprises still struggle with digital compliance, quality standards, and access to affordable credit, particularly in semi-urban and rural areas.
- Centre–State Coordination: Reforms such as GST 2.0, labour codes, and rural employment require strong fiscal and administrative coordination, which continues to face operational frictions.
Way Ahead
- The reforms reflect a shift towards outcome-based governance, reducing friction for citizens and businesses, enhancing transparency, and laying the foundation for sustained, inclusive growth.
- The measures collectively foster trust, resilience, and global competitiveness in India’s economy.
Source: PIB
Previous article
News In Short 30-12-2025