Syllabus: GS3/Environment
Context
- India is the world’s largest rice exporter despite being a highly water-stressed country which represents a policy paradox.
About
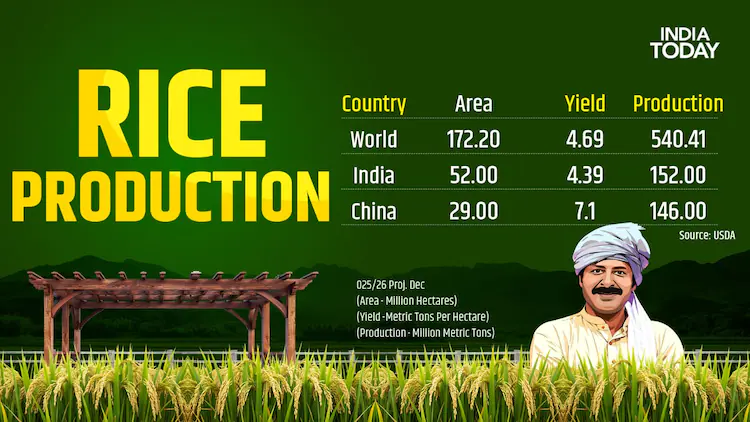
- India overtook China as the world’s largest rice producer and now accounts for ~40% of global rice exports.
- Rice exports crossed 20 million metric tonnes in the latest fiscal year.
- India exports rice to 179 other countries.
- A major chunk of basmati exports go to West Asia, with the likes of Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Iran and the United Arab Emirates being bigger markets than the US.
Concerns with India’s Rice Export
- Groundwater Depletion: Rice cultivation is highly water-intensive, unsuited to Punjab–Haryana’s agro-ecology.
- Aquifers are classified as over-exploited and weak monsoon years worsen recharge stress.
- Groundwater levels have fallen from ~30 feet to 80–200 feet in a decade.
- These States extract 35–57% more groundwater than annual recharge.
- Incentive Structure: Minimum Support Price (MSP) for rice has risen ~70% in a decade. Free or subsidised electricity encourages over-extraction of groundwater.
- Government subsidies discourage farmers from switching to less water-intensive crops
- Rising Cost of Cultivation: Farmers are forced to drill deeper borewells and invest in stronger pumps to support the growing demand.
- Climate Vulnerability: Groundwater-dependent farming increases exposure to climate variability.
- It leads to reduced resilience during weak monsoons or heat stress periods.
- Ethical Concern: Producing 1 kg of rice consumes 3,000–4,000 litres of water, far above the global average.
- It raises ethical and strategic questions on exporting water-intensive crops from a water-stressed country.
- Global Implications: Being the largest rice exporter, any reduction in India’s rice output affects global food prices and food security.
- Environmental Concerns: Rice is a semi-aquatic plant cultivated in flooded fields, where it thrives under a layer of stagnant water.
- This creates the ideal anaerobic conditions for bacteria to thrive on decomposing organic matter and release methane.
- This phenomenon contributes significantly to global methane emissions.
Way Forward
- Shift to Sustainable Cropping Patterns: Gradually discourage water-intensive rice cultivation in water-stressed regions and promote millets, pulses and maize through MSP reform and procurement diversification.
- Water-Smart Agriculture: Scale up Direct Seeded Rice (DSR), micro-irrigation, and precision farming; rationalise free power to curb groundwater over-extraction.
- International Coordination: Engage with importing countries and global institutions to reduce price volatility and ensure responsible food trade during crises.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Use real-time data on groundwater, production and stocks to guide export decisions instead of ad-hoc administrative controls.
Conclusion
- A sustainable rice export strategy must balance farmer welfare, ecological limits, food security and global responsibility, shifting India from being merely the largest exporter to a responsible agricultural power.
Source: TH
Previous article
100 Years of Quantum Mechanics
Next article
Issues with Gig Workers in India