Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
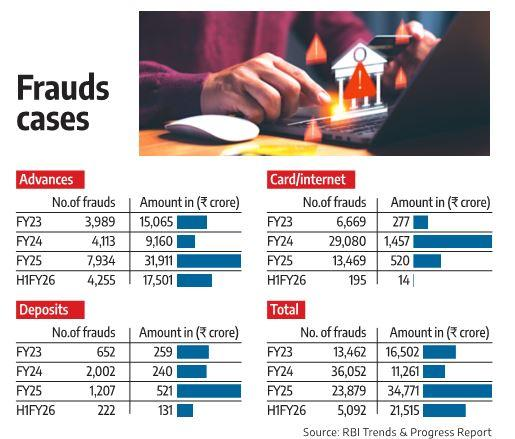
- The RBI’s Trend and Progress of Banking in India 2024–25 shows that even as the incidence of banking frauds has declined, the value of losses has increased significantly, pointing to deep-seated structural and supervisory weaknesses in the banking system.
Key Findings from the RBI Report
- Nature of Frauds: During 2024-25, Card and internet frauds accounted for 66.8% of total cases, highlighting persistent vulnerabilities in digital banking. In terms of amount, the share of advances-related frauds was 33.1 percent.
- Bank-wise Distribution: In 2024-25, private banks accounted for 59.3 percent of the total number of frauds reported, while PSBs accounted for 70.7 percent of the amount involved.
Reasons for Rise in Fraud Amounts
- Weak credit appraisal and monitoring mechanisms, particularly in consortium and multiple banking arrangements, enable fund diversion and misreporting.
- Delayed recognition and reporting of frauds allow losses to accumulate over several years before being disclosed.
- Governance gaps and limited accountability in sanctioning and restructuring large loans contribute to repeated instances of high-value fraud.
- Advances-related frauds involve high-value corporate loans, which inflate the total amount even when the number of cases declines.
- The sharp increase in fraud amounts is largely due to the re-examination and fresh reporting of large legacy cases, following compliance with the Supreme Court judgment of March 27, 2023.
Impacts of Rising Banking Frauds
- Large frauds weaken bank balance sheets by increasing non-performing assets and provisioning requirements.
- Repeated fraud disclosures erode public confidence in the banking system, especially in public sector banks.
- The need for government recapitalisation of banks imposes a fiscal burden and diverts public resources.
- Banks become risk-averse, leading to credit contraction, particularly affecting MSMEs and productive sectors.
Initiatives taken by government
- The Central Fraud Registry (CFR) has been established to enable information sharing among banks and prevent repeat frauds.
- Early Warning Systems (EWS) and Red-Flagged Accounts (RFA) frameworks have been mandated to detect stress and potential frauds at an early stage.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 has strengthened credit discipline and improved recovery mechanisms.
- Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI): RBI directed all banks to adopt the FRI technology developed by the Department of Telecommunications. It supports real-time monitoring and alerts to protect customers from cyber and UPI-related frauds.
Way Ahead
- Early detection and real-time intelligence sharing is needed to catch fraud before damage spreads.
- Stronger internal governance and clearer escalation norms within banks and financial entities are required.
- Better consumer protection, including dispute resolution and liability protections must be ensured.
- Technology leverage (AI, shared platforms, risk indicators) is needed to stay ahead of sophisticated digital frauds.
Source: IE
Previous article
India Poised to Become $26 Trillion Economy By 2047–48