Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- Ahead of the Union Budget 2026–27, representatives of MSME have flagged rising industrial stress and sought targeted reforms in credit access, risk protection, and compliance norms.
What are MSMEs?
- MSMEs or Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises are businesses that are defined by their investment and turnover levels.
- They are considered an important sector of the economy as they create jobs, generate income, and promote entrepreneurship.

Contribution of MSMEs
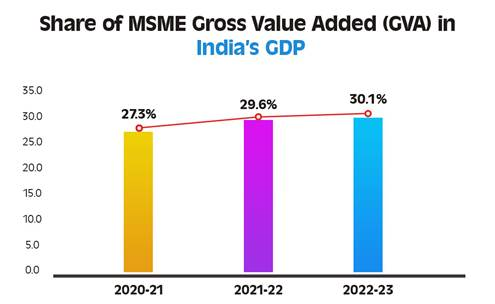
- Contribution in Economy: MSMEs are often called the backbone of the Indian economy; they account for more than 11 crore jobs and contribute around 27% of India’s GDP.
- Employment Generation: The sector consists of around 6.4 crore MSMEs , with 1.5 crore of them registered on the Udyam portal and employs around 23% of the Indian labor force, making it the second-largest employer in India after agriculture.
- Output and Exports: They account for 38.4% of the total manufacturing output and contribute 45.03% of the country’s total exports.
Challenges faced by MSMEs in India
- Access to Finance: MSMEs struggle to secure capital due to a lack of collateral, limited credit history, or inadequate access to formal financial institutions.
- Increased Competition: MSMEs face stiff competition from larger, more established companies that have greater resources and market influence.
- Lack of Technological knowledge: Many MSMEs lack the technical expertise needed to modernize their operations, adopt new technologies, and stay competitive in the market.
- Marketing and Networking Opportunities: Limited resources and networks prevent MSMEs from effectively marketing their products and services.
Key Demands of MSMEs
- Affordable Credit Access: Statutory collateral-free lending up to ₹1 crore for micro enterprises and interest rate cap of 6–7 percent on such loans to ensure affordability.
- Protection Against Trade Shocks: Establishment of an Export Risk Equalisation Fund to compensate micro exporters affected by sudden tariff hikes.
- Safeguards from Exchange Rate Volatility: Introduction of a forex fluctuation protection scheme for micro enterprises with limited hedging capacity.
- Simplified and subsidised foreign exchange hedging instruments to be considered by the Reserve Bank of India for micro units.
- Simplification of Compliance: Higher exemption thresholds under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime for micro enterprises.
- Introduction of a single, simplified GST return for micro units.
- Creation of an Emergency Working Capital Window during wars or global disruptions affecting raw materials, fuel, and shipping routes.
Government initiatives to promote the MSME sector
- MSME Champions scheme: The objective of the scheme is to modernize MSMEs’ manufacturing processes, reduce wastages, encourage innovativeness, sharpen business competitiveness and facilitate their National and Global reach and excellence.
- Udyam Registration: It is an online registration process to simplify the registration of MSMEs. The objective is to provide MSMEs with a streamlined process to avail themselves of various benefits and incentives offered by the government.
- Section 15 of the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006, and newly enacted Section 43B(h) of the Income-tax Act says that businesses must pay these MSME Registered Enterprises within 15 days, or up to 45 days if they have an agreement.
- Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE): This scheme provides collateral-free credit to micro and small enterprises through a credit guarantee mechanism.
- Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI) was launched in 2005-06 to organise traditional artisans into clusters for improved competitiveness, product development and sustainable income generation.
Way Ahead
- MSMEs are revolutionising India’s growth story by driving innovation, generating employment, and empowering local communities.
- Addressing MSME concerns through targeted credit support, s and simplified compliance can strengthen enterprise resilience, protect employment, and reinforce India’s manufacturing and export ecosystem.
Source: IE
Previous article
News In Short 26-12-2025
Next article
Birth Anniversary of Guru Gobind Singh