Centre Allocating Funds for Harappan site of Rakhigarhi
Syllabus: GS1/Ancient History
Context
- The Central Government has allocated Rs 500 crore in the Union Budget for the development of Rakhigarhi, a site of the ancient Harappan civilisation.
About
- Aim: The initiative is expected to place Rakhigarhi strengthening India’s archaeological presence worldwide.
- Rakhigarhi: It is the largest Harappan site in the Indian Subcontinent.
- It is situated in the Hisar district of Haryana and is located in the Ghaggar-Hakra river plain.
- The site was first excavated by Amarendra Nath of Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
Harappan Civilization
- The Harappan civilization is believed to be one of the oldest world civilizations together with Egypt and Mesopotamia.
- It was developed along the river Indus and for that reason it is also known as the Indus Valley Civilization.
- The Harappan civilization is identified as a Bronze-age civilization because many objects have been found that are made up of copper based alloys.
Major Harappan Sites
| Site | Present Day |
|---|---|
| Harappa | Punjab, Pakistan |
| Mohenjo-Daro | Sindh, Pakistan |
| Dholavira | Kutch district of Gujarat, |
| Kalibangan | Rajasthan |
| Lothal | Gujarat |
| Rakhigarhi | Haryana |
| Chanhudaro | Sindh, Pakistan |
| Ganweriwala | Punjab, Pakistan |
| Sutkagendor | Baluchistan Province, Pakistan |
| Alamgirpur | Uttar Pradesh |
Source: IE
Veer Bal Diwas
Syllabus:GS1/History
In News
- The Prime Minister addressed the national programme marking ‘Veer Baal Diwas’ at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
Veer Bal Diwas
- Historical linkages: Sahibzada Zorawar Singh Ji and Sahibzada Fateh Singh Ji, the two youngest sons of Guru Gobind Singh Ji, the tenth Sikh Guru, were bricked alive and martyred at Sirhind (present-day Fatehgarh Sahib, Punjab) on December 26, 1704 for refusing to abandon their faith under coercion.
- Veer Bal Diwas is observed on December 26 every year in remembrance of the martyrdom of Guru Gobind Singh ji’s sons Sahibzada Zorawar Singh ji and Sahibzada Fateh Singh ji.
- The day honour the bravery of the two young heroes of the country, and help inculcate the spirit of exemplary courage and sacrifice in the youth of today.
- The martyrdom of the Sahibzadas symbolizes faith, courage, and moral strength, reflecting the heritage and bravery of the Sikh Gurus.
Source :PIB
Alawite Minority in Syria
Syllabus: GS1/ Geography
Context
- Eight people were killed in an explosion at a mosque of the Alawite minority sect in the Syrian city of Homs.
About
- The Alawites are a religious minority group primarily concentrated in Syria, with smaller populations in Turkey and Lebanon.
- Alawites follow Alawism, a heterodox sect that emerged from Shia Islam (linked historically to Twelver Shia).
- Their beliefs incorporate elements of Shia Islam, mysticism, and local traditions, making them doctrinally distinct from mainstream Sunnis and Shias.
- The Assad family that ruled Syria from 1971 to 2024 are Alawites and made the community politically dominant there.
- The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) is planning to expand full-fledged Aadhaar enrolment and update centres for adults from 88 to 473 by September 2026, aiming to ensure at least one centre for every two districts.
- It is a statutory authority established under the provisions of the Aadhaar (Targeted Delivery of Financial and Other Subsidies, Benefits and Services) Act, 2016 (“Aadhaar Act 2016”) under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- UIDAI issues aadhaar numbers to Indian residents, ensuring they are robust, verifiable, and cost-effective to prevent duplicates and fraud.
- It is responsible for the enrolment, authentication, and management of the entire Aadhaar lifecycle, including policy development, system operation, and security of identity and authentication data.
- UIDAI is collaborating with Google to map centre locations. Recent Aadhaar issuance requires field verification to prevent illegal enrolments, especially for non-resident Indians and overseas citizens.
- To maintain data integrity, date-of-birth changes will be strictly regulated, allowing only one correction per affidavit, and parents falsifying children’s birth details may face criminal action, as highlighted by an Allahabad High Court case.
- The Kimberley Process (KP) Plenary has selected India to assume the chairmanship of the Kimberley Process from 1 January 2026.
- The Kimberley Process is a tripartite initiative involving governments, the international diamond industry and civil society to prevent the trade in conflict diamonds.
- Conflict diamonds are rough diamonds used by rebel groups or their allies to finance conflicts that undermine legitimate governments, as defined in United Nations Security Council resolutions.
- History: The Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS), established pursuant to a UN resolution, came into effect on 1 January 2003.
- Members: The Kimberley Process (KP) is open to any country that can meet its standards.
- Currently, it comprises 60 participants representing 86 countries, with the EU and its 27 Member States counted as one participant under the European Commission.
- India is a founding member of the KP.
- The members account for over 99 percent of the global rough diamond trade.
- The chair oversees the implementation of the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) and operations of the working groups, committees and administration that activate the KP.
- Secretariat: The Kimberley Process Secretariat is headquartered in Gaborone, Botswana.
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) issued a clarification to address misleading labelling of beverages marketed as tea.
- As per Food Safety and Standards (Food Product Standards and Food Additives) Regulations, 2011, tea must originate from Camellia sinensis.
- Labelling and Display Regulations, 2020 require the food name to reflect its true nature.
- Use of the word ‘tea’ for other products amounts to misbranding under the FSS Act, 2006.
- Tea is defined as a product exclusively derived from the plant Camellia sinensis.
- This includes traditional variants such as, Black tea, Green tea, Kangra tea and Instant tea (in solid form).
- Tea is traditionally prepared from two leaves and a bud plucked from Camellia sinensis.
- The Quality Council of India(QCI) announced a set of next-generation quality reforms on the eve of Sushasan Divas 2025.
- It was established as a National body for Accreditation on recommendations of the Expert Mission of the EU after consultations in the Inter-ministerial Task Force, Committee of Secretaries and Group of Ministers through a Cabinet decision in 1996.
- It is a non-profit organization registered under the Societies Registration Act XXI of 1860.
- The Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion, Ministry of Commerce and Industry was designated as the nodal point for all matters connected with quality and QCI to structure and help implement the Cabinet decision.
- QCI has been established to create a mechanism for independent third party assessment of products, services and processes.
- It plays a pivotal role at the national level in propagating, adoption and adherence to quality standards in all important spheres of activities including education, healthcare, environment protection, governance, social sectors, infrastructure sector and such other areas of organized activities.
- Q Mark – Desh ka Haq: It is a QR-coded Mark of Quality to enable citizens to know their laboratory, hospital and MSME, ensuring full disclosure and eliminating fake certificates.
- Trust-based governance: Reduced paperwork, fewer inspections, shorter timelines, and digital processes.
- Assessor pool expansion: The assessor pool will be expanded across boards and divisions by lowering entry barriers to bring in young experts and strengthen last-mile reach.
- Quality Setu platform: It is a secure ticket-based system for time-bound grievance redressal and feedback resolution.
- One-stop accreditation portal: Paperless, modular system replacing multiple portals.
- MSME and manufacturing support: Training for 1 lakh MSMEs and SHGs, reduced ZED and Lean certification fees, and focus on Tier-2 and Tier-3 suppliers.
- Laboratory reforms: India positioned as a global testing hub, standardized medical lab scopes, technical training for 5,000 personnel, and simplified approval processes.
- Healthcare reforms (NABH): Healthcare reforms under the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals and Healthcare Providers (NABH) will focus on improving patient safety and expanding access to accreditation,graded penalties, AI-assisted surveillance, and mentorship via NABH MITRA, including smaller hospitals.
- Certification reforms (NABCB): Reforms under the National Accreditation Board for Certification Bodies (NABCB) aim to help Indian products access global markets.
- Fast-track accreditation for emerging technologies, Quality Passport for Indian products, and support for global market access.
- The reforms aim to simplify accreditation, reduce procedural friction, enhance transparency, and strengthen citizen trust, positioning quality as a driver of sustainable growth and globally competitive enterprises.
- These measures are designed to strengthen India’s quality ecosystem and support the vision of Viksit Bharat 2047.
| About Syria – Syria is a West Asian country in the Levant region. – Bordering Countries: Bordered by Turkey (north), Iraq (east), Jordan (south), Israel (south-west) and Lebanon (west). – It has a small Mediterranean coastline. – Important river: Euphrates (lifeline for agriculture). |
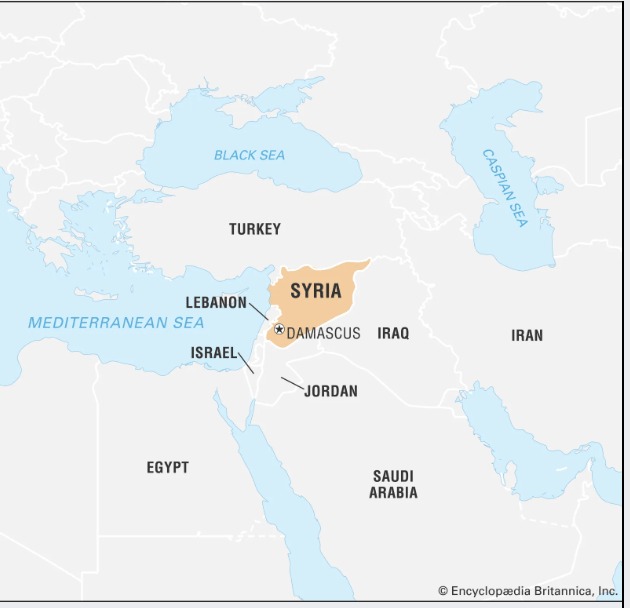
Source: DD
Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI)
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
In News
About Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI)
Source :TH
Kimberley Process
Syllabus: GS2/ International Institutions
Context
About
Source: PIB
Camellia sinensis
Syllabus: GS3/ Agriculture and Economy
Context
Regulatory Framework
What Is Tea as per FSSAI?
| Geographical Condition for Tea production – The tea plant grows well in tropical and subtropical climates. Tea bushes require a warm and moist frost-free climate all through the year. – Soil: It requires deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter. – Temperature: The average annual temperature for tea plants to grow well is in the range of 15-23°C. – Precipitation: The rainfall needed is between 150-200 cm. Frequent showers evenly distributed over the year ensure continuous growth of tender leaves. – Major tea producing states are Assam, hills of Darjeeling and Jalpaiguri districts in West Bengal, Tamil Nadu and Kerala. a. Apart from these, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Meghalaya, Andhra Pradesh and Tripura are also tea-producing states in the country. |
Source: TH
Quality Council of India Announces Quality Reforms
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
In News
Quality Council of India (QCI)
Functions
Latest Reforms
Significance
Source :Air
Previous article
India’s Agricultural Sector in 2025
Next article
Financial Asymmetry in Political Funding in India