Syllabus: GS3/Agriculture
Context
- The year 2025 marked a transformative milestone for India’s agricultural sector, showcasing the cumulative impact of policy continuity, institutional reforms, and strategic investments made over the past decade.
Key Highlights For India’s Agricultural Sector (2025)
- Agriculture and allied activities remained the backbone of the rural economy, contributing nearly 16% to India’s GDP and supporting livelihoods for over 46% of the population.
- Union Budget 2025–26 allocated ₹1.52 lakh crore to agriculture and allied sectors, with a focus on research, infrastructure, and farmer welfare.
Record Production and Food Security
- India achieved its highest-ever foodgrain production of 357.73 million tonnes in 2024–25, an 8% rise over the previous year and 106 million tonnes higher than in 2015–16.
- Rice: 150.184 million tonnes;
- Wheat: 117.945 million tonnes;
- Pulses and Oilseeds: Significant gains supported by targeted missions and procurement assurances;
- Millets (Shree Anna): Steady rise reaffirming India’s leadership in climate-resilient cereals;
Strengthening Farmer Incomes
- MSP Policy: It continued as a pillar of income assurance, guaranteeing at least 50% return over cost of production.
- Since 2014, procurement operations have transferred over ₹20 lakh crore in MSP payments, ₹14.16 lakh crore for paddy and ₹6.04 lakh crore for wheat, directly benefiting millions of farmers.
- Direct Income Transfers and Credit Expansion: Under PM-Kisan Samman Nidhi, over ₹3.90 lakh crore was directly credited to 11 crore farmers through 20 installments by August 2025.
- The Kisan Credit Card scheme further expanded access to institutional finance, with ₹10 lakh crore disbursed to 7.71 crore farmers, including those in livestock and fisheries.
Risk Management and Irrigation Expansion
- Crop Insurance and Risk Coverage: The Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) continued to mitigate risks, disbursing claims worth ₹1.83 lakh crore since 2016.
- Increasing participation from non-loanee farmers reflected greater trust and transparency.
- Water Efficiency and Irrigation: The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY) accelerated completion of irrigation projects and promoted micro-irrigation, enabling shifts to high-value crops and improved water-use efficiency.
Infrastructure and Market Ecosystem
- Investment in Agricultural Infrastructure: More than 1 lakh projects were sanctioned through the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund, including Custom Hiring Centres, warehouses, and cold storage units, reducing post-harvest losses and creating rural jobs.
- The PM Kisan Samriddhi Kendras strengthened village-level access to quality inputs and advisory services, bridging last-mile delivery gaps.
- Market Reforms and Farmer Institutions: The e-NAM platform expanded nationwide, promoting price discovery and transparency.
- The establishment of 10,000 FPOs enabled collective marketing, input procurement, and value addition, empowering women farmers and smallholders.
Growth in Allied Sectors
- Dairy: 239.30 million tonnes in 2023–24, aided by the Rashtriya Gokul Mission and dairy development programmes;
- Fisheries: 195 lakh tonnes in 2024–25, led by rapid inland fisheries growth;
- Horticulture: Record expansion in fruits and vegetables;
- Food Processing: Exports crossed USD 49.4 billion by July 2025, reflecting rising value addition.
Sustainability and Climate Resilience
- Natural and organic farming gained momentum under national missions.
- The Soil Health Card (SHC) Scheme advanced balanced nutrient use through extensive testing and farmer training.
- The Ethanol Blending Programme reached 19.05% by July 2025, reducing crude oil imports and providing additional income for sugarcane farmers.
- Under PM-KUSUM, solar pump installations expanded, fostering renewable energy adoption and decentralized solar power generation.
Human Capital and Skill Development
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) trained millions through hands-on demonstrations and vocational programs.
- Schemes like ATMA, STRY, and PMKVY built a robust rural skilling ecosystem, empowering farmers, women, and youth to embrace modern farming and agri-entrepreneurship.
- Skill integration across horticulture, livestock, mechanization, and processing enhanced employability and innovation across the agri-value chain.
Inclusive Growth and Local Impact
- Convergence of income support, irrigation, infrastructure, and training translated into higher rural incomes, reduced migration, and improved living standards.
- Women farmers, FPOs, and rural entrepreneurs became pivotal agents of change in local agri-economies.
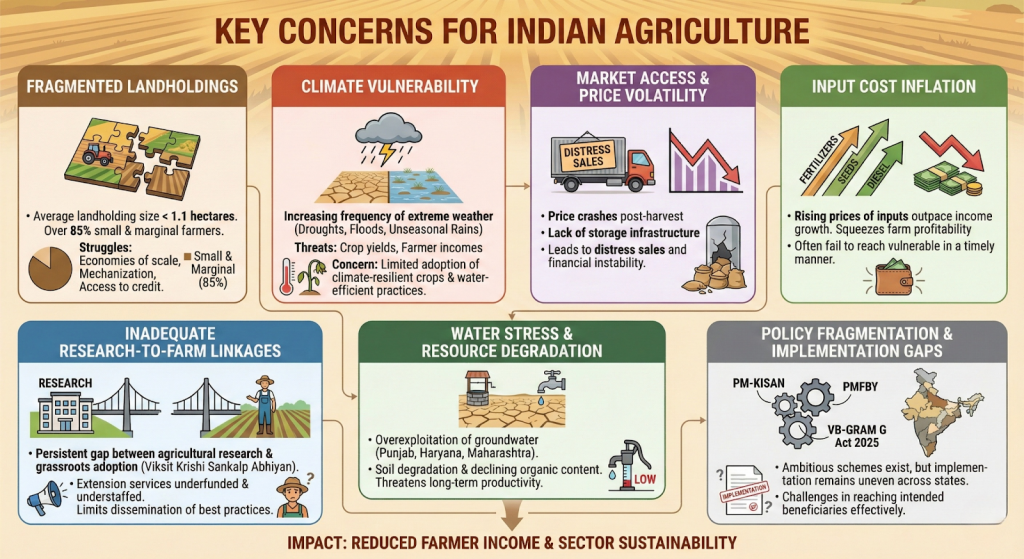
Related Efforts & Initiatives
- Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS): Available to farmers availing short term crop loans up to Rs.3.00 lakh at an interest rate of 7% per annum for one year.
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF): To mobilize a medium – long term debt financing facility for investment in viable projects for post-harvest management.
- All loans under this financing facility have interest subvention of 3% per annum up to a limit of ₹ 2 crore.
- National Bee Keeping and Honey Mission (NBHM): Launched as a part of the Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan; Goal of ‘Sweet Revolution’.
- Namo Drone Didi: To provide drones to 15000 selected Women SHGs; application of fertilizers and pesticides.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF): To develop 15,000 clusters covering 7.5 lakh Ha area and establish 10,000 need based Bio-Input Resource Centres (BRCs).
- Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA): To provide price support for pulses, oilseeds, and copra;
- Agri Fund for Start-ups & Rural Enterprises (AgriSURE): To boost innovation and entrepreneurship in the agricultural and rural ecosystem.
- Per Drop More Crop (PDMC): To increase water use efficiency at the farm level through Micro Irrigation technologies namely Drip and Sprinkler Irrigation systems.
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY): For promotion of organic farming in the country.
- Soil Health & Fertility (SH&F): To promote balanced and integrated nutrient management through the Soil Health Card (SHC) initiative.
- Special initiatives include establishment of school mini soil labs (1,020 functional, expanding to 5,000 PM SHRI schools) and capacity building through demonstrations, campaigns, and farmer training.
- Rainfed Area Development (RAD): A component under National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA), focuses on Integrated Farming System (IFS).
- Sub-Mission on Agroforestry: Under National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) with the motto of ‘Har Medh Par Ped’.
- Crop Diversification Programme (CDP): To shift farmers from water-intensive crops like paddy to more sustainable and profitable alternatives such as pulses, oilseeds, and coarse cereals.
- Sub-Mission on Agriculture Extension (SMAE): Making the extension system farmer driven and farmer accountable by disseminating technology to farmers through new institutional arrangements viz. Agricultural Technology Management Agency (ATMA) at district level.
- National Mission on Edible Oils (NMEO)-Oil Palm: To promote oil palm cultivation with special focus on North-Eastern States and A&N Islands.
- Digital Agriculture Mission: To improve the existing National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture (NeGPA) by developing a digital public infrastructure for agriculture.
- National Bamboo Mission: Implemented through the State Bamboo Missions (SBM)/ State Bamboo Development Agency (SBDA).
Next article
News In Short 27-12-2025