Syllabus: GS2/Health
Context
- World AIDS Day is observed on December 1 every year.
About
- It is observed every year to raise awareness about the HIV/AIDS epidemic.
- It was first marked in 1988 by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Theme 2025: Overcoming disruption, transforming the AIDS response.
- This theme highlights the urgency of addressing disruptions caused by pandemics, conflicts, and inequalities that limit access to care.
HIV AIDS
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system.
- HIV targets the body’s white blood cells, weakening the immune system. This makes it easier to get sick with diseases like tuberculosis, infections and some cancers.
- Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) occurs at the most advanced stage of infection.
- Spread: HIV is spread from the body fluids of an infected person, including blood, breast milk, semen and vaginal fluids. It can also spread from a mother to her baby.
- Treatment: There is no cure for HIV infection. It is treated with antiretroviral drugs, which stop the virus from replicating in the body. Untreated HIV can progress to AIDS, often after many years.
HIV AIDS in India
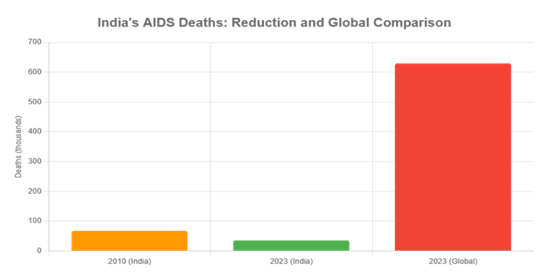
- There has been a decline in infection from 0.33% in 2010 to 0.20 in 2024.
- India’s prevalence is significantly lower than the global average of 0.7%.
- India’s new infections represent only about 5% of the global total (1.3 million in 2024).
The National AIDS Control Programme (NACP)
It has evolved through five phases, shifting from basic awareness to comprehensive prevention, testing, treatment, and sustainability.
- NACP I (1992–1999): It was India’s first comprehensive HIV/AIDS prevention and control programme.
- Aim: Slow the spread of HIV and reduce morbidity, mortality, and overall impact of AIDS.
- NACP II (1999–2006): Strengthen long-term national capacity to respond to HIV/AIDS.
- NACP III (2007–2012): Halt and reverse the HIV epidemic by 2012.
- Strategy: Scale up prevention among High-Risk Groups (HRGs) and the general population.
- NACP IV (2012–2017): 50% reduction in new infections (compared to 2007 baseline).
- Extended (2017–2021) to advance the goal of Ending AIDS by 2030.
- Major initiatives during extension: HIV/AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act, 2017)- It prohibits discrimination against people living with HIV (PLHIV).
- Mission Sampark: Its purpose was to “bring back” people living with HIV (PLHIV) who had stopped antiretroviral therapy (ART).
- Routine Universal Viral Load monitoring.
- NACP V (2021–2026): Launched as a Central Sector Scheme, aims to build on past achievements and address persistent challenges.
- The goal of this Phase is to support the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal 3.3 by helping end the HIV/AIDS epidemic as a public health threat by 2030.
Conclusion
- India’s AIDS decline is more prominent than the global average, supported significantly by broadened testing, enhanced access to antiretroviral therapy, focused outreach to high-risk groups, and initiatives to combat stigma, all implemented through collaborative state and community actions.
Source: TH
Previous article
News In Short 29-11-2025
Next article
Durand Line: The Fragile Frontier