Syllabus: GS2/International Relations
Context
- The Middle East is currently grappling with a profound crisis of leadership which struggles have far-reaching implications for peace, stability, and development.
About the Middle East
- The Middle East, often regarded as the ‘cradle of civilization’, holds immense significance for India and the global community, positioned at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- For India: The Middle East is an indispensable partner in trade, energy security, diaspora engagement, and strategic cooperation.
- For the World: The Middle East plays a crucial role in global energy supply, security dynamics, and international trade routes.
- The Middle East remains a geopolitical flashpoint due to conflicts such as the Israel-Palestine issue, the Yemen war, and Iran’s nuclear ambitions.
Causes of the Leadership Vacuum in Middle East
- Historical Context of Leadership Challenges: After the collapse of the Ottoman Empire, Western powers carved up the region, often installing rulers who prioritized external interests over domestic stability.
- The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed a series of conflicts — including the Iran-Iraq War, Gulf Wars, and the Arab Spring (2010–2012) — that further exposed leadership failures.
- Short-term Political Gains Over Long-term Stability: Many nations in the Middle East are led by regimes that prioritize short-term political gains over long-term stability and development.
- For instance, the reconstruction plans for Gaza, proposed by the United States and Arab states, have been met with skepticism due to the absence of a cohesive and inclusive political framework.
- Authoritarian Rule and Lack of Democratic Institutions: The lack of democratic institutions and free elections has prevented political transitions, often resulting in uprisings and revolts.
- Sectarian and Ethnic Divisions: Countries like Iraq, Lebanon, and Yemen have experienced prolonged conflicts due to power struggles among different sectarian groups particularly between Sunni and Shia Muslims.
- External Interventions and Proxy Wars: Foreign interventions from global powers such as the United States, Russia, and regional powers like Iran, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey have exacerbated instability.
- Conflicts in Syria, Libya, and Yemen have turned into proxy wars, where different factions receive backing from external actors.
- Corruption and Economic Mismanagement: Many regimes prioritize personal enrichment over national development, leading to widespread inequality and economic grievances.
- Countries like Lebanon, which is experiencing an economic collapse, have seen massive protests due to financial mismanagement.
- Weak Civil Society and Suppression of Dissent: Without an active and empowered civil society, meaningful reforms become difficult.
- Governments often use security laws to crack down on dissent, as seen in countries like Saudi Arabia and Iran.
Consequences of the Leadership Crisis
- Prolonged Conflicts and Humanitarian Disasters: Countries like Syria, Yemen, and Libya have been engulfed in conflicts for years.
- Millions of people have been displaced, and humanitarian conditions remain dire.
- Economic Decline and Unemployment: The lack of stable governance has deterred foreign investment and economic growth.
- Unemployment rates, especially among the youth, remain high in countries like Egypt, Tunisia, and Iraq.
- Economic hardship has led to increased migration and brain drain.
- Rise of Extremism and Terrorism: The lack of strong governance and security apparatus has allowed groups such as ISIS and Al-Qaeda to exploit political instability and spread their influence.
Importance of the Middle East For India & World
- Trade and Economic Ties: India’s trade relations with the Middle East accounting for nearly 20% of India’s total trade. Key aspects include:
- Exports and Imports: India exports pharmaceuticals, machinery, textiles, and food products, while importing crude oil, petrochemicals, and fertilizers.
- UAE-India Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), 2022: It aims to boost bilateral trade to $100 billion in the coming years.
- Infrastructure Investments: Gulf nations, particularly the UAE and Saudi Arabia, are investing in Indian infrastructure, real estate, and startups.
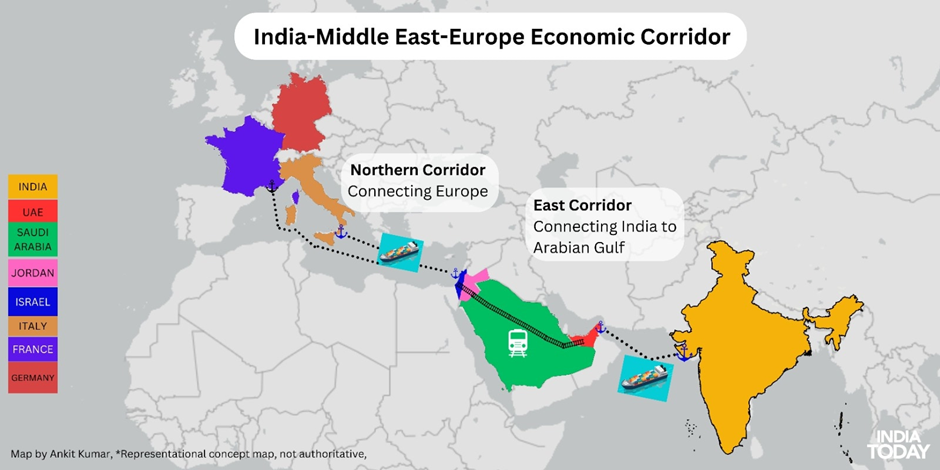
- The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) aims to strengthen connectivity and trade.
- Energy: Over 50% of the world’s proven oil reserves and nearly 40% of natural gas reserves.
- India, which imports over 85% of its crude oil needs, relies heavily on countries such as Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Iraq, and Iran for energy security.
- India has signed long-term agreements with key Gulf nations to secure its energy needs and is investing in strategic petroleum reserves (Strategic Energy Partnerships).
- Strategic and Geopolitical Importance: Middle East is a volatile but strategically significant region for India and the world. Key geopolitical factors include:
- Security and Counterterrorism: India collaborates with Gulf nations on counterterrorism, intelligence sharing, and defense cooperation to combat extremist threats. The Indian Navy’s presence in the Persian Gulf ensures maritime security in critical sea lanes.
- Chabahar Port and Strategic Access: India’s investment in Iran’s Chabahar Port provides direct access to Afghanistan and Central Asia, bypassing Pakistan.
- It also strengthens India’s connectivity strategy under the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
- Israel-India Relations: India and Israel share strong defense, technology, and agricultural partnerships, with Israel being a key supplier of advanced military equipment to India.
- Diaspora and Cultural Ties: Middle East hosts over 9 million Indian expatriates, making them the largest foreign workforce in the region. Their contributions include:
- Remittances: Indian workers in the Gulf send home over $50 billion annually, boosting India’s forex reserves.
- Soft Power and Cultural Influence: India shares deep historical and cultural ties with the Middle East, with Bollywood, Indian cuisine, and yoga being widely popular.
- Labour Reforms and Welfare: India works closely with Gulf nations to ensure better working conditions and legal protections for its workers.
Role in Global Economy and Stability
- Strategic Trade Routes: The Suez Canal and the Strait of Hormuz handle a major share of global oil and cargo shipments.
- Any disruptions—like the 2021 Ever Given crisis in the Suez Canal—can severely impact global supply chains.
- Gulf Sovereign Wealth Funds (SWFs): Countries like Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Qatar invest billions in global markets, influencing financial trends worldwide.
- China’s Expanding Influence: China has deepened its ties with the Middle East through its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and strategic investments, presenting challenges to India and the West.
Path Forward
- Inclusive Governance: Leaders must prioritize the inclusion of diverse voices in decision-making processes to rebuild trust and foster unity.
- Strengthening Institutions: Robust and transparent institutions are essential for ensuring accountability and delivering public services effectively.
- Regional Cooperation and Conflict Resolution: Diplomatic efforts, such as the Abraham Accords and Saudi-Iran talks, show that dialogue can be a path forward.
- More countries should engage in diplomatic negotiations to resolve conflicts.
- Empowering Youth: The region’s young population holds immense potential for driving change. Investing in education, employment, and leadership development can pave the way for a new generation of leaders.
Conclusion
- The leadership vacuum in the Middle East presents a complex mix of risks and opportunities for India.
- While instability in the region can threaten energy security, trade, and the well-being of the Indian diaspora, it also allows India to strengthen its strategic and economic engagements.
- By adopting a pragmatic foreign policy, deepening bilateral ties, and enhancing security cooperation, India can navigate the challenges posed by the Middle East’s power vacuum while capitalizing on new geopolitical openings.
| Daily Mains Practice Question [Q] Critically examine the factors contributing to the crisis of leadership in the Middle East. How do internal governance challenges and external geopolitical influences shape this crisis, and what measures can foster stable and visionary leadership in the region? |
Previous article
Beyond ‘Beijing Declaration’: Unlocking a Feminist Future in India