Syllabus: GS2/International Relation
Context
- PM Narendra Modi’s visit to Mauritius as the guest of honor at its Independence Day celebrations highlights the strategic depth of India-Mauritius relations amid global geopolitical uncertainties.
- The visit reaffirms India’s commitment to Mauritius’ security, economic growth, and regional stability.
About India-Mauritius Partnership
- Historical and Cultural Connections: Mauritius is a former British and French colony that gained independence from British rule in 1968.
- Both countries share a historical connection dating back to the 19th century when Indian indentured laborers were brought to the island under British rule.
- Mahatma Gandhi’s visit to Mauritius (Oct 29 – Nov 15, 1901): Advocated education, political empowerment, and ties with India.
- Today, nearly 70% of Mauritius’s population traces its roots to India, and this cultural affinity has remained a cornerstone of bilateral relations.
- Institutions like the Mahatma Gandhi Institute and the World Hindi Secretariat further nurture these cultural connections.
- India’s cultural influence is evident in Mauritius’s language, cuisine, festivals, and traditions.
| Republic of Mauritius – It is an island nation located in the Indian Ocean, approximately 2,000 kilometers off the southeastern coast of Africa. – Capital: Port Louis |
- Political and Diplomatic Engagement: Diplomatic relation was established in 1948.
- Mauritius has consistently supported India’s position in international forums, including at the United Nations (UN) and the Commonwealth.
- India, in return, has backed Mauritius’s territorial claim over the Chagos Archipelago, a matter of dispute with the United Kingdom.
- Economic and Trade Relations:
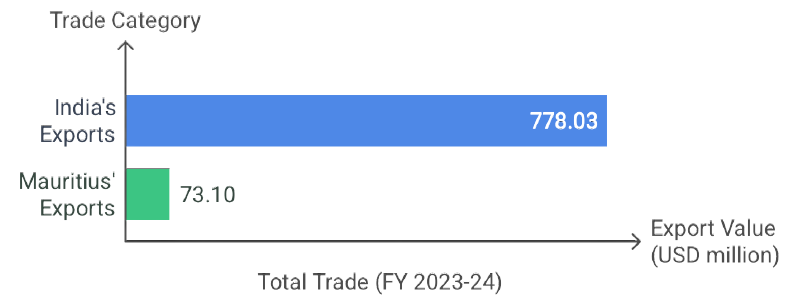
- Trade: It has grown in the last 18 years, from USD 206.76 million in 2005-06 to USD 851.13 million in 2023-24.
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA): The first such agreement between India and an African nation, granting preferential market access.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Mauritius was the second largest source of FDI into India for FY 2023-24, after Singapore.
- Since the signing of the Double Taxation Avoidance Convention (DTAC), FDI inflows from Mauritius have dropped from USD 15.72 bn in 2016-17 to USD 6.13 bn in 2022-23.
- Financial Assistance: India has provided multiple lines of credit, including a $100 million defense credit line.
- Special Economic Zones (SEZs): India is helping Mauritius develop infrastructure for economic growth.
- Development Assistance:
- Metro Express Project: Improving public transport in Mauritius.
- Social Housing Project: Affordable housing for citizens.
- Health Sector Support: Assistance in building hospitals and providing COVID-19 vaccine aid during the pandemic.
- Strategic and Defense Cooperation: Mauritius holds strategic importance for India as a sentinel of the western Indian Ocean.
- Maritime Surveillance: India assists Mauritius in patrolling its waters to counter piracy and illegal fishing.
- Infrastructure Development: India has contributed to the construction of a new naval dockyard in Mauritius.
- India has assisted in setting up radar networks to enhance maritime monitoring.
- India is developing infrastructure on the Agalega Islands, improving air and naval connectivity
- Defense Equipment Supply: India continues to supply defense equipment under favorable credit terms.
- Anti-Piracy Operations: Joint efforts to combat piracy and illicit activities in the region.
- Vision SAGAR and Regional Growth: India’s Vision SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) emphasizes regional cooperation and maritime security.
- Mauritius, as a close maritime neighbor, plays a pivotal role in this vision.
Emerging Areas of Cooperation
- Digital Economy and FinTech: India is assisting Mauritius in developing digital payment systems modeled after India’s UPI (Unified Payments Interface).
- Cybersecurity cooperation is being strengthened to counter digital threats in the financial sector.
- Renewable Energy and Climate Change: India is helping Mauritius transition to clean energy solutions, including solar and wind power projects.
- Mauritius is a member of the International Solar Alliance (ISA), an initiative led by India to promote solar energy adoption.
- Space Cooperation: India has offered satellite technology and remote sensing capabilities to Mauritius for disaster management, weather forecasting, and maritime security.
Key Challenges
- Tax Treaty Amendments: India’s revision of the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) with Mauritius has reduced its attractiveness as an FDI gateway.
- Growing Chinese Influence: China is increasing its economic footprint in Mauritius, particularly through investments in infrastructure and trade, potentially challenging India’s strategic leverage.
- Security Threats: Rising maritime piracy and illegal fishing in the Indian Ocean demand stronger maritime cooperation.
Road Ahead: Future Prospects
- Expanding Trade Agreements: Strengthening CECPA by including more sectors like IT and healthcare services.
- Boosting Defense Ties: Increasing India’s role in Mauritius’ defense modernization and joint military drills.
- Strengthening Regional Cooperation: Mauritius can act as a bridge for India’s deeper engagement with Africa and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
Conclusion
- The India-Mauritius partnership is a model bilateral relationship, built on shared history, economic cooperation, and strategic alignment.
- As India expands its Indo-Pacific strategy and Africa outreach, Mauritius remains a crucial partner in achieving regional stability and economic growth.
- With increasing collaboration in trade, defense, digital economy, and climate change, this partnership is set to grow stronger in the years to come.
| Daily Mains Practice Question [Q] Examine the historical, cultural, and strategic factors that have shaped the enduring relationship between India and Mauritius. How can it further deepen long-standing ties and promote mutual growth and cooperation in the region? |
Previous article
Leadership Crisis In Middle East
Next article
Digital Technologies: Women & Farm Work in India