Syllabus :GS 2/Governance
In News
- The Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) 2024 revealed that enrolment in both government and private schools has returned to pre-pandemic levels.
Annual Status of Education Report(ASER)
- The word aser means ‘impact’ in Hindustani.
- It is a nationwide citizen-led household survey that provides a snapshot of children’s schooling and learning in rural India.
- It captures data from all children, including those who are not in school or are absent.
- It tracks children aged 3 to 16 for schooling status, and children aged 5 to 16 are tested for basic reading and arithmetic abilities.
- The survey is coordinated by ASER Centre and facilitated by the Pratham network.
- The first ASER survey was conducted in 2005 and repeated annually for 10 years (2005-2014).
- 2016 Onwards: Shifted to an alternate-year model:
- Basic ASER Survey: Conducted every alternate year to assess foundational learning in children.
- Gap Years: Instead of a full survey, ASER explores specific age groups or new dimensions of children’s learning using a different research lens.
| Earlier Surveys – ASER 2017 focused on the activities, abilities, and aspirations of youth aged 14-18. – ASER 2019 targeted young children aged 4-8, assessing their cognitive, early language, and early numeracy skills. – ASER 2023 returned to the 14-18 age group, adding a focus on digital literacy. – ASER 2024 returned to the nationwide ‘basic’ format, covering almost all rural districts in India. |
Focus
- Enrollment status was collected for all children aged 3-16.
- Children aged 5-16 were tested for basic reading and arithmetic skills.
- Older children (14-16) were asked about digital access and usage, and also completed smartphone-based tasks to assess digital abilities.
Key Findings: Recent Survey
- Improvement in Learning: The proportion of Class 3 students in government schools able to read a Class 2 text rose to 23.4% in 2024, up from 16.3% in 2022.
- Basic arithmetic skills also improved across both government and private schools.
- For Class 3, two-thirds could not solve subtraction problems, and only 30.7% of Class 5 students could solve division problems. Class 8 students saw slight improvement, with 45.8% mastering basic arithmetic.
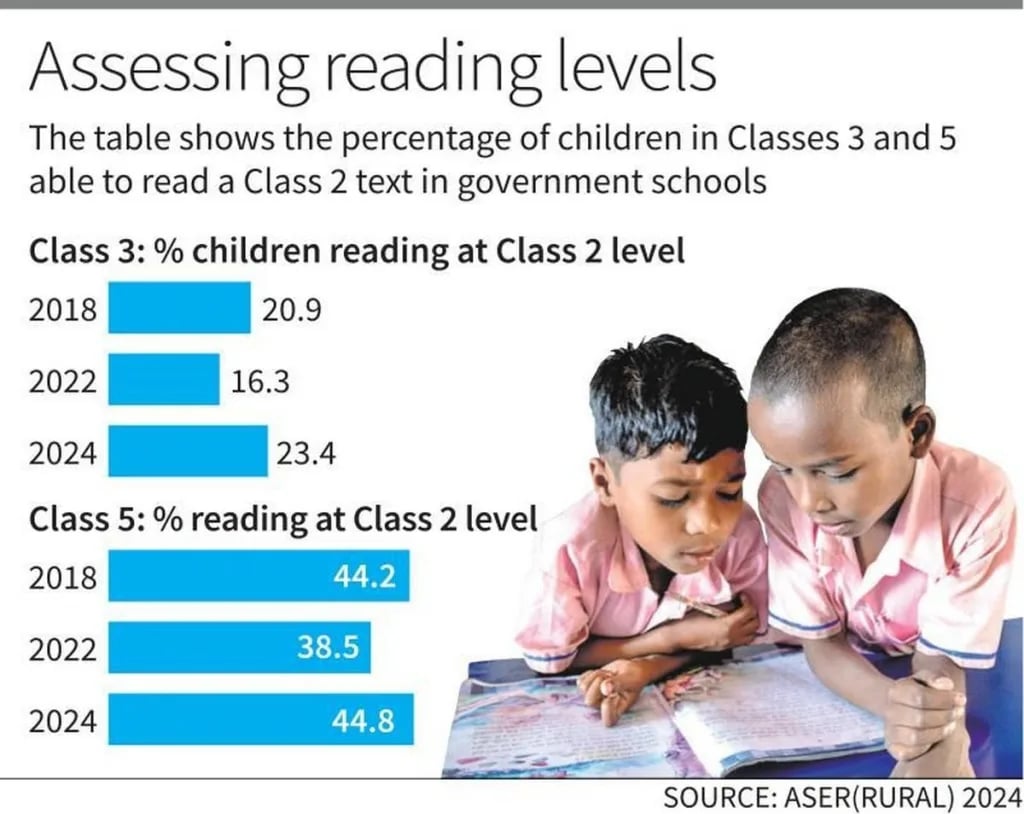
- Regional Variations: States like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Haryana, and Odisha saw notable gains in reading levels. Uttar Pradesh had the largest increase, with a 15-percentage-point rise in reading skills.
- Government vs Private Schools: Learning recovery has been stronger in government schools, while private schools still lag behind their pre-pandemic levels. Despite improvements, 30% of children still struggle with reading a Class 2 text.
- Enrolment Trends: School enrolment for children aged 6-14 is at 98.1%, close to pre-pandemic levels. However, government school enrolment, which rose during the pandemic, has dropped to 66.8% in 2024 from 72.9% in 2022. The proportion of underage children in Class 1 also declined to 16.7%, the lowest ever recorded.
- Digital Literacy: Smartphone access has increased significantly in rural areas, with 84% of households owning smartphones in 2024. Among teenagers, 57% use smartphones for educational purposes, but 76% use them for social media. There is a gender gap in smartphone use, with more boys reporting smartphone use and ownership than girls.
- Factors Driving Learning Trends: The report credits the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the Nipun Bharat Mission for improvements in foundational literacy. Digital tools, especially smartphones, have played a key role in continuing education during and after the pandemic.
Suggestions
- The recovery in learning outcomes is evident, substantial gaps in literacy and numeracy persist, particularly in government schools.
- Efforts like the NEP 2020 and the use of digital tools continue to drive improvements, but challenges such as uneven access to educational resources and digital skills remain.
- School readiness programs and the increasing role of digital literacy are helping, but more work is needed to bridge these gaps.
Source :TH
Previous article
News In Short 28-1-2025
Next article
Union Budget