Syllabus: GS1/Geography; GS2/Global Groupings & Agreements
Context
- India has strategically expanded its claim in the Central Arabian Sea, adding nearly 10,000 square kilometers to its Extended Continental Shelf (ECS).
About the Continental Shelf
- It is a critical concept in maritime law, defined under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- It refers to the submerged extension of a country’s landmass, stretching from the coastline to the deep ocean floor.
- Coastal nations have sovereign rights over their continental shelf for exploring and exploiting natural resources, such as minerals, oil, and gas.
| India’s Expanding Claims – Recent Addition in the Arabian Sea: According to the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Goa, India’s seabed and sub-seabed area could nearly equal its land area of 3.274 million square kilometers. – Modified Strategy: In response to Pakistan’s objections over disputed areas in the Western Arabian Sea, the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS) rejected India’s entire claim in the region in March 2023. 1. Recently, India restructured its claims into partial submissions, securing uncontested areas while leaving disputed regions for bilateral discussion. |
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and Beyond
- Nations are entitled to an EEZ extending 200 nautical miles from their coastline, granting exclusive rights to fishing, mining of minerals, polymetallic nodules, and resource extraction like oil reserves.
- India currently possesses 12 nautical miles of territorial sea and 200 nautical miles of EEZ.
- Beyond the EEZ, countries can claim an ECS if they provide scientific evidence to the CLCS that the shelf is a natural extension of their landmass.
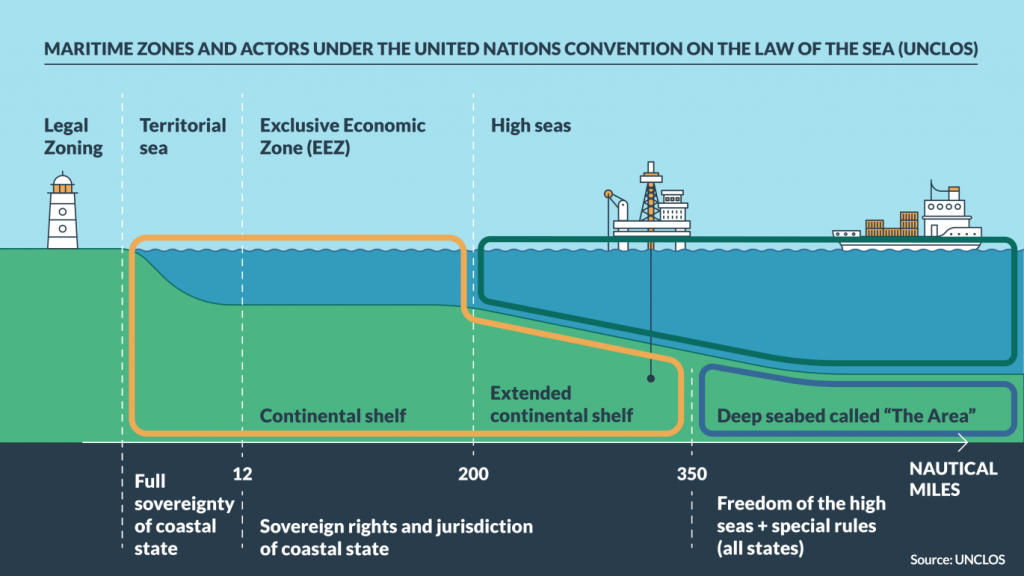
| UNCLOS and the CLCS – UNCLOS, adopted in 1982, provides the legal framework for defining and claiming the continental shelf. – The CLCS, established under UNCLOS, reviews scientific data submitted by countries and makes recommendations on the outer limits of their continental shelf. Process of Claiming a Continental Shelf Under UNCLOS – Scientific Evidence: Nations must provide detailed scientific data proving that the continental shelf is a natural extension of their landmass to the seabed. 1. It includes geological and geophysical surveys, bathymetric mapping, and sediment analysis. – Submission to the CLCS: It includes technical data and maps outlining the proposed boundaries. – Review and Recommendations: The CLCS reviews the submission and may request additional data or modifications. 1. It provides recommendations on the outer limits of the continental shelf, which are binding once accepted. – Resolving Overlaps: If the claimed area overlaps with another country’s continental shelf, bilateral negotiations or agreements are required to resolve disputes. – Final Approval: Once the CLCS recommendations are accepted, the claiming nation gains rights to explore and exploit resources in the ECS, including minerals, oil, and gas. |
Navigating Geopolitical Challenges
- Sir Creek Dispute: Located in the marshes of the Rann of Kutch, continues to challenge India’s maritime claims.
- Pakistan raised objections to portions of India’s ECS submission, citing overlaps near the maritime border.
- Oman Overlap: India’s ECS in the Arabian Sea overlaps with Oman’s claims; however, an Agreement in 2010 ensures that this shared region is not under dispute.
- Contests in the East: On India’s eastern and southern coastlines, ECS claims in the Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean span 300,000 square kilometers but have faced challenges from Myanmar and Sri Lanka.
Previous article
News In Short-26-04-2025