Syllabus: GS2/Government Policy and Intervention
Context
- Recently, the Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister, approved the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS) by replacing the National Pension System (NPS).
About
- It is based on the recommendations of T. V. Somanathan Committee (2023), will be effective from April 1, 2025.
- The UPS proposes to amalgamate advantages of both Old Pension Scheme (OPS) and New Pension Scheme (NPS).
- It represents a forward-looking approach to retirement planning in India, aiming to provide a secure and sustainable pension system for all eligible employees.
- It aims to provide long-term financial security to government employees while maintaining flexibility and choice.
Key Features of the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS)
- Guaranteed Pension: Under the UPS, eligible employees are assured a pension equal to 50% of their average basic pay drawn over the last 12 months prior to superannuation.
- For service periods between 10 and 25 years, the pension will be proportional.
- Minimum Qualifying Service: Employees with a minimum qualifying service of 25 years will receive the full assured pension.
- In case of an employee’s demise, their family will receive an assured pension equal to 60% of the employee’s pension before their demise.
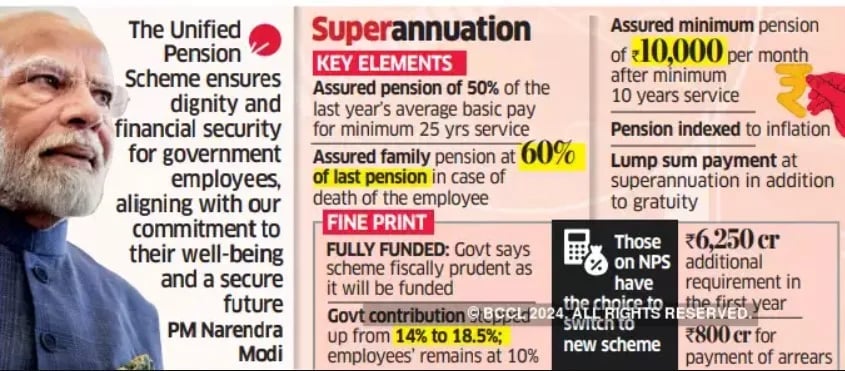
- Assured Minimum Pension: Upon superannuation after a minimum of 10 years of service, employees will receive an assured minimum pension of Rs 10,000 per month. It ensures a safety net for retirees.
- The UPS promises central government employees who have completed at least 25 years of service a guaranteed pension.
- It is calculated as half of their average basic salary over the 12 months preceding superannuation.
- Inflation Indexation: The UPS applies inflation indexation to the assured pension, assured family pension, and assured minimum pension.
- In the form of Dearness Relief based on All India Consumer Price Index for Industrial Workers (AICPI-IW), similar to service employees.
Read our detailed article on Inflation: Meaning, Types, Measures, Effects & More
- Lump Sum Payment: In addition to gratuity, 1/10th of monthly salary+ Dearness Allowance for every completed six months of service.

- Financial Contributions: Employees choosing the UPS will continue to contribute 10% of their salary.
- The government’s contribution will increase from 14% to 18.5%.
- It ensures that employees do not face any additional financial burden.
Choice Between UPS and NPS
- Central government employees have the option to choose between the UPS and the National Pension Scheme (NPS).
- Unlike the UPS, the NPS is market-linked.
| Similarities to the Old Pension Scheme (OPS) – The UPS shares similarities with the old pension scheme in terms of benefits. However, it differs significantly in its funding mechanism. – Unlike the OPS, which was a pay-as-you-go program, the UPS is fully funded each year from the budget and absorbed into it. This approach prevents future generations from bearing the burden of pension payments. Choice for NPS Subscribers – Employees currently under the National Pension System (NPS) have the option to shift to the UPS. – NPS, introduced in 2004, is a defined contribution scheme where employees accumulate a retirement corpus based on their contributions. – UPS provides an alternative for those seeking a more assured pension. |
Previous article
News In Short – 24-08-2024