Chandra Shekhar Azad Birth Anniversary
Syllabus: GS1/History
In News
- The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi has paid tributes to Chandra Shekhar Azad on his birth anniversary.
Chandra Shekhar Azad
- He was born in 1906 in present-day Madhya Pradesh, grew up in poverty and became involved in the freedom struggle as a teenager during the Non-Cooperation Movement.
- He was Arrested for protest activities, he famously declared his name as “Azad” and vowed never to be captured alive.
- He was Disillusioned by Gandhi’s withdrawal of the movement in 1922
Role in Freedom struggle
- He joined the Hindustan Republican Army (HRA), later transforming it with Bhagat Singh into the more radical Hindustan Socialist Republican Association (HSRA).
- He was involved in the 1925 Kakori Train robbery, an attempt to blow up the India Viceroy’s train, and the shooting of British police officer JP Saunders in 1928 to avenge the killing of the great freedom fighter, Lala Lajpat Rai.
- After the Central Assembly bombing in 1929 and the subsequent British crackdown, Azad remained underground, trying to free Bhagat Singh.
Death and Legacy
- On February 27, 1931, surrounded by police in Allahabad’s Alfred Park, he helped a comrade escape, killed three policemen, and, with only one bullet left, shot himself to avoid capture.
- He died at just 24, staying true to his name and vow — Azad (free) until the end.
- His role in India’s quest for freedom is deeply valued and motivates our youth to stand up for what is just, with courage and conviction”.
Source :PIB
Birth Anniversary of Lokmanya Bal Gangadhar Tilak
Syllabus: GS1/History
Context
- PM Modi has paid tributes to Lokmanya Tilak on his birth anniversary.
Early Life
- Born on July 23, 1856, in Maharashtra’s Ratnagiri, he was a freedom fighter, social thinker, philosopher, teacher, one of the first and strongest advocates of Swaraj (“self-rule”) who had played an important role in India’s freedom movement.
- He organized two important festivals, Ganeshotsav in 1893 and Shiv Jayanti in 1895.
Political career
- In 1890, Tilak joined the Indian National Congress.
- Tilak opposed the moderate views of Gopal Krishna Gokhale, and was supported by fellow Indian nationalists Bipin Chandra Pal in Bengal and Lala Lajpat Rai in Punjab. They were referred to as the “Lal-Bal-Pal”.
- The trio also mobilized Indians against the Bengal partition and proposed the Swadeshi movement and boycott of foreign goods.
- Tilak was arrested by the British on the charges of sedition in 1908 and sentenced to six years of imprisonment in Mandalay (Burma).
- He founded the Home Rule League in April 1916 at Belagavi, aiming to increase political awareness and mobilize support for self-rule.
- In 1916, he concluded the Lucknow Pact with Mohammed Ali Jinnah, which provided for Hindu-Muslim unity in the nationalist struggle.
- He was conferred with the title of “Lokmanya”, which means “accepted by the people (as their leader)” and Mahatma Gandhi called him “The Maker of Modern India”.
Literary Work
- He launched two weeklies, Kesari (in Marathi) and Mahratta (in English), which criticized British policies of the time.
- He published The Orion or Researches into the Antiquity of the Vedas (1893) and The Arctic Home in the Vedas (1903).
- In the Mandalay jail, he wrote the Srimad Bhagavadgita Rahasya (Secret of the Bhagavadgita), an original exposition of the most sacred book of the Hindus.
Source: PIB
Rajendra Chola I
Syllabus :GS1/History
In News
- The Ministry of Culture to celebrate the birth anniversary of Chola emperor Rajendra Chola I with the Aadi Thiruvathirai Festival at Gangaikonda Cholapuram, Tamil Nadu.
Rajendra Chola I (1014–1044 CE)
- He was one of the most powerful and visionary rulers in Indian history.
- Under his leadership, the Chola Empire expanded its influence across South and Southeast Asia.
- He established Gangaikonda Cholapuram as the imperial capital after his victorious campaigns, and the temple he built there served as a beacon of Shaiva devotion, monumental architecture, and administrative prowess for over 250 years.
- Today, the temple stands as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, renowned for its intricate sculptures, Chola bronzes, and ancient inscriptions.
Major Roles
- Rajendra Chola I is famed for his exploits, but his military expedition to the Gangetic plains about a thousand years ago remains one of the most celebrated in the history of the Chola dynasty.
- During the expedition to the Gangetic plains, Rajendra Chola I defeated several kings and chieftains, including the Kalinga ruler and the Pala ruler Mahipala of Bengal.
- Rajendra Chola I also brought several beautiful Chalukya and Kalinga sculptures as war trophies.
- The Tiruvalangadu, Esalam, and Karanthai Copper Plates, several inscriptions, and literary works celebrate his victory and the construction of the Brihadisvara Temple, listed as one of the three great living Chola temples by UNESCO.
Source :PIB
Chola Gangam Lake
Syllabus: GS1/ Places In News
In News
- The Tamil Nadu government has recently announced a major initiative to develop the historic Chola Gangam Lake (also known as Ponneri Lake).
About
- Chola Gangam Lake was constructed by Rajendra Chola I (1014–1044 CE) and is an exemplary work of Chola-era hydraulic engineering, originally built to commemorate his victorious northern campaign and bring sacred Ganga water to his new capital.
- The lake and its associated canals were integral to the functioning and prosperity of Gangaikonda Cholapuram, illustrating advanced water management and urban planning under the Cholas.
Source: TH
Palna Scheme
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
Context
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development has approved 14,599 Anganwadi-cum-Crèches (AWCCs) under the Palna Scheme, aimed at providing quality daycare and protection to children.
About the Palna Scheme
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development has introduced the Palna Scheme under the Samarthya Vertical of Umbrella Mission Shakti for all States and Union Territories in 2022.
- Target Beneficiaries: All children aged 6 months to 6 years and their mothers (irrespective of employment status).
- Key Features:
- Provision of full-day childcare support through Anganwadi Centres.
- Focus on nutrition, health, cognitive development, and growth monitoring.
- Integration with existing Anganwadi infrastructure to ensure last-mile delivery.
Source: PIB
Vitamin D Deficiency
Syllabus: GS2/Health
Context
- A major new study suggests that the vitamin D levels might contribute to psychological and neurodevelopmental conditions.
Vitamin-D
- It is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for bone and immune health.
- Two main forms:
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) – from plant sources and fortified foods.
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) – produced in the skin upon sunlight (UVB) exposure; also found in animal sources.
- Recommended Intake: 600 IU/day for adults.
- Higher needs in the elderly, pregnant and lactating women.
- 1 IU is the biological equivalent of 0.025 mcg cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol.
- Functions:
- Calcium and phosphorus absorption from the intestine.
- Maintains bone and dental health.
- Supports immune system regulation.
- Plays a role in muscle function and cell growth.
- Sources: Natural Sources – Sunlight, Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), Egg yolks
- Supplements – Common in case of deficiency, especially in northern latitudes or sedentary indoor lifestyles.
- Diseases: Rickets in children (bone deformities), Osteomalacia in adults (soft bones), Osteoporosis (brittle bones), Increased susceptibility to infections.
Source: TH
National Broadcasting Day
Syllabus :GS2/Governance/GS3/Economy
In News
- National Broadcasting Day is observed on July 23 to commemorate the first-ever radio broadcast in India.
History and Significance of Broadcasting in India
- India’s broadcasting journey began in June 1923 with the Radio Club of Bombay’s first transmission.
- The Indian Broadcasting Company (IBC) was established on July 23, 1927, marking the birth of organized radio broadcasting in the country.
- All India Radio (AIR) emerged in 1936, evolving from the Indian State Broadcasting Service.
- Post-independence, AIR expanded rapidly, adopting the name “Akashvani” in 1956.
- Today, AIR operates 591 stations, reaching 98% of India’s population and broadcasting in 23 languages and 146 dialects.
Importance
- Broadcasting has played a crucial role in India’s development. During the independence struggle, radio was a powerful tool for disseminating information and fostering unity.
- Post-independence, it has been instrumental in promoting literacy, health awareness, and agricultural knowledge, especially in rural areas.
- The introduction of FM channels and the transition to digital transmission using Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) technology demonstrate AIR’s commitment to modernization.

Source: AIR
ADB Lowers India’s FY26 Growth Forecast to 6.5%
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB), in its Asian Development Outlook July 2025, revised India’s GDP growth forecast for FY2025–26 downward to 6.5% from 6.7%, primarily due to the effects of US tariff policies.
About Asian Development Bank
- ADB is a regional development bank established in 1966 for Social and Economic Development. It has 68 members.
- It is a multilateral development bank, which seeks to help its developing member countries to reduce poverty and improve their people’s quality of life through inclusive economic growth, environmentally sustainable growth and regional integration.
- Headquarters: Manila, Philippines.
Source: BS
Star – HOPS‑315
Syllabus: GS3/ S&T
In News
- Astronomers have, for the first time, witnessed the early stages of rocky planet formation by directly detecting minerals condensing from vapor around a young star, HOPS‑315.
What is HOPS-315?
- HOPS‑315 is a newborn protostar located about 1,300 light-years away in the Orion molecular cloud. It is surrounded by a dense, flat, rotating protoplanetary disc made of gas and dust, which is uniquely inclined so that Earth-based telescopes can peer deep into its interior—a rare vantage point for studying early planet formation.
Significance of the Discovery
- Planet Formation Genesis: This breakthrough offers direct insight into the fundamental process of how rocky planets, like Earth, initially form from vaporized rock in protoplanetary discs.
- Solar System Parallel: The observed processes and the types of minerals found around HOPS-315 remarkably mimic the early stages of our own Solar System’s formation.
- Interstellar Mineral Match: The mineral types detected, such as forsterite and enstatite, mirror those found as inclusions in chondritic meteorites on Earth.
Source: TH
Vanuatu
Syllabus: GS1/Places in News
Context
- Led by Vanuatu, the International Court of Justice will issue an advisory opinion on what legal obligations nations have to address climate change and what consequences they may face if they don’t.
Vanuatu
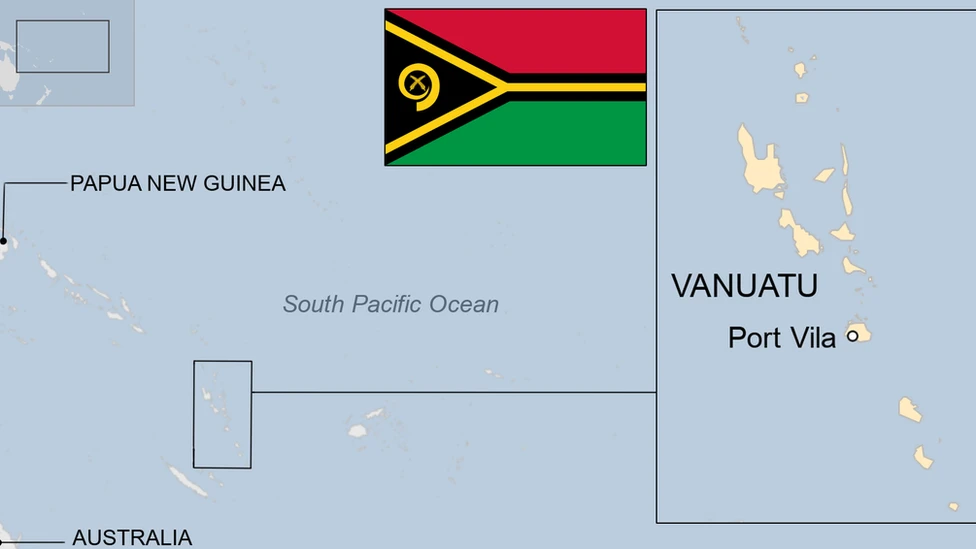
- Vanuatu is a double chain of 13 principal and many smaller islands in the south-western Pacific Ocean.
- Gained full independence in 1980 and joined the Commonwealth of Nations and the United Nations.
- The islands are volcanic and coral in origin.
- They lie about 800 kilometres west of Fiji and nearly 1800 kilometres east of Australia.
- Located in the “Ring of Fire” – prone to earthquakes, cyclones, and volcanic eruptions.
Source: TH
Previous article
Study on GST Burden on Indian Households
Next article
National Cooperative Policy, 2025