Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- The World Bank has released the Global Economic Prospects (GEP) report 2025.
- It is a flagship biannual publication of the World Bank Group that examines trends and projections in the global economy. It emphasizes emerging markets and developing economies.
Major Highlights
- Global Economy: It is projected to expand by 2.7% in both 2025 and 2026, the same pace as in 2024.
- Emerging Market and Developing Economies (EMDEs) have undergone significant transformation since 2000, now contributing about 45% of global GDP, compared to 25% at the start of the century.
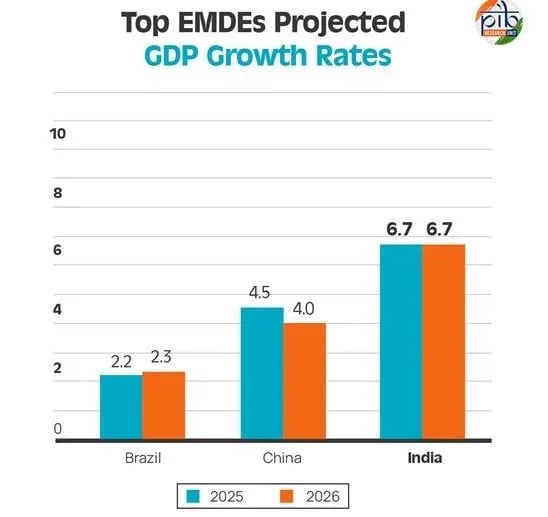
- India, China, and Brazil, the three largest EMDEs, have collectively driven approximately 60% of annual global growth since the start of the century.
- Trade Restrictions: New global trade restrictions in 2024 were five times the 2010-19 average.
- As a result, overall economic growth dropped—from 5.9% in the 2000s to 3.5% in the 2020s.
- Challenges and Recommendations:
- Rising trade tensions could reduce global growth. Persistent inflation could delay expected cuts in interest rates.
- With the right policies, these economies can even transform some challenges into significant opportunities.
- All countries, meanwhile, should work together to strengthen global trade governance, with the support of multilateral institutions.
India Specific Highlights
- Growth: India is projected to remain the fastest-growing large economy for FY26 and FY27 (growth rate – 6.7%), reaffirming its dominance in the global economic landscape.
- Growth in India’s services sector is expected to remain robust, while manufacturing activity will strengthen.
- Investments: India’s Investment growth is expected to remain steady, supported by rising private investments, improved corporate balance sheets, and favourable financing conditions.
Reasons for the Growth
- Infrastructure development under the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan.
- Fostering innovation through initiatives like Startup India and the Production Linked Incentive Scheme, these reforms are transforming sectors such as manufacturing, digital economy, and financial inclusion.
Conclusion
- The continued strength of India’s economic performance, as projected by both the World Bank and IMF, underscores the country’s resilience and highlights the sustained strength of its economic fundamentals, making India a crucial player in the global economic landscape.
| About World Bank – It is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of developing countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. – It was established along with the International Monetary Fund at the 1944 Bretton Woods Conference. – It comprises two institutions: the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), and the International Development Association (IDA). – Mandate: The World Bank Group has a mandate to reduce poverty and support sustainable development. 1. The institution focuses on a wide range of areas, including education, health, agriculture, infrastructure, and environmental sustainability. – Reports: World Development Report (WDR), Global Economic Prospects (GEP), Business Ready (B-READY), Global Financial Inclusion (Findex) Database, Poverty and Shared Prosperity Report. |
Source: PIB
Previous article
RBI Issued Norms for Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs)
Next article
Population That cannot Afford a Healthy Diet on Rise